Metser reviews 2 approaches to 18F-FDG PET prediction of prognosis in patients undergoing treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer and comments on the clinical investigation by Dimitrakopolou-Strauss and colleagues in this issue.
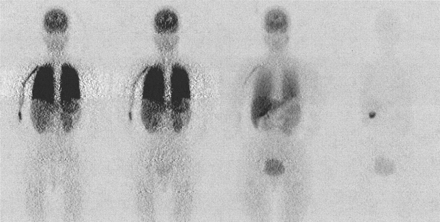
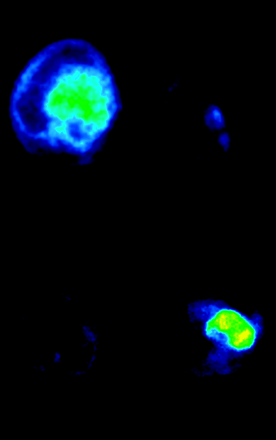
Thie provides perspective on standardized uptake value, the various methods of measuring it, and the influencing factors that limit its usefulness in comparisons—factors that Boellaard and colleagues specifically investigated and report in this issue.
Langen and Bröer trace the history of investigations into molecular transport mechanisms of radiolabeled amino acids for PET and SPECT, with special focus on the transport characteristics of 123I-2-iodotyrosine and the investigation reported by Lahoutte and colleagues in this issue.
Tio and colleagues report on PET research comparing the results of intramyocardial VEGF gene therapy and laser treatment in reducing ischemia in patients with end-stage coronary artery disease and angina.
Nishimura and colleagues outline a simple method for superimposing the image of the coronary artery tree on 3D surface map images generated from gated myocardial perfusion SPECT, effectively superimposing radiography on scintigraphy in the evaluation of coronary artery disease.
Imabayashi and colleagues assess the potential advantages of artificial intelligence as an adjunct to visual interpretation in identifying patients with very early Alzheimer’s disease.
Mamede and colleagues describe a novel method for quantification of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the human brain using 123I-5IA SPECT and assess the suitability of this approach.
Giovacchini and colleagues use PET to evaluate the effects of healthy aging on brain incorporation of 11C-arachidonic acid, before and after partial-volume correction, in both young adults and elderly individuals.
Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss and colleagues compare different quantification methods for use with 18F-FDG PET in the prediction of individual survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who are receiving chemotherapy with FOLFOX.
Poddar and colleagues report on an investigation on the effects of pretreatment with ursodeoxycholic acid, a choleretic agent, on the ability of 99mTc hepatobiliary scintigraphy to differentiate extrahepatic biliary atresia from neonatal hepatitis.
Brenner and colleagues evaluate the relationship between 18F-fluoride bone metabolic measures obtained by nonlinear regression, Patlak analysis, and PET standardized uptake value for a wide range of normal and pathologic bone conditions.
Reinartz and colleagues compare advances in ventilation/perfusion lung scintigraphy and multislice spiral CT in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism.

Torabi and colleagues describe the evolution of lymph node imaging techniques in nuclear medicine, from conventional anatomic modalities to molecular techniques in functional and physiologic assessment.
Boellaard and colleagues present the results of an experimental simulation study performed to determine the effects of noise, image resolution, and region-of-interest definition on the accuracy of standardized uptake values in 18F-FDG PET.
Strauss and colleagues evaluate 18F-FDG kinetics using compartment and noncompartment models of giant cell tumors and compare the results with gene expression data for a subgroup of patients.
Taki and colleagues study 99mTc-annexin V uptake in rats after coronary occlusion and reperfusion to determine the timing and location of apoptotic cell death after reperfusion.
Schmitt and colleagues explore the successful results of radiation therapy with 177Lu-DOTA-Tyr3-octreotate in a human small-cell lung cancer cell line in mice and point to possible applications in humans.
de Keizer and colleagues study the effects of recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone on bone marrow in a group of 14 patients and discuss the relevance of this data to the use of the hormone as an adjunct in radioiodine therapy.
Lu and colleagues provide dosimetry estimates for 11C-DASB, a selective radioligand for in vivo quantification of serotonin transporters, in human whole-body PET.
Green and colleagues investigate tracer kinetic models for 18F-FHBG dynamic microPET data and noninvasive methods for determining blood time–activity curves in an adenoviral gene delivery model in mice.
Kang and colleagues report on data supporting the use of sodium iodide symporter–based gene therapy using β-emit-ting radionuclides in the management of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Pain and colleagues propose the use of 2 positron-sensitive probes as an alternative to labor-intensive blood sampling for determination of input function after bolus injection of 18F-FDG in small animals.
Chen and colleagues follow up on previous studies by assessing the efficacy of using tissue-to-plasma activity ratio as a simple alternative to dynamic imaging in determining net 18F-FDG uptake during acute lung injury.
Lahoutte and colleagues characterize the interaction of 125I-2IT and h4F2hc-hLAT1, the major transporter subserving system in growing cells.
ON THE COVER
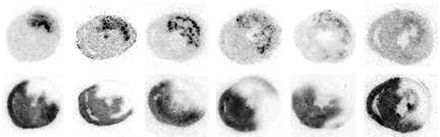
In these autoradiographs of heart slices from male Wistar rats, 99mTc-Annexin V shows the area of and intensity of apoptosis and 201Tl shows the area at risk. 99mTc-annexin V uptake was significant in the area at risk and decreased with time after reperfusion. Significant uptake of 99mTc-annexin V is seen predominantly in the mid myocardium at 0.5 and 1.5 h after reperfusion and expands to the subendomyocardial and subepicardial layers and lateral border zone of ischemia at 6 h after reperfusion. Annexin V uptake is still observed after 1 d of reperfusion and decreases during the 3 d after reperfusion.