Imaging of MMP activity in plaques: Schäfers and colleagues review the rationale, potential, and current status of matrix-metalloproteinases in the clinical context of stroke and myocardial infarction.
Page 663

Cardiac PET: Rudd provides perspective on the clinical appearance of acute aortic dissection and previews 2 articles in this issue of JNM on the utility of PET in predicting adverse outcomes.
Page 667
68Ga-DOTATOC PET/CT and NETs: Ambrosini and colleagues retrospectively assess the effect of 68Ga-DOTA-peptide PET/CT on staging and clinical management of patients with neuroendocrine tumors.
Page 669
Aortic dissection and PET/CT: Kato and colleagues investigate the use of 18F-FDG PET/CT to predict short- and midterm outcomes, including progression and increased risk of rupture, in patients with medically controlled acute aortic dissection.
Page 674

Bilateral pelvic 18F-FDG uptake: Yun and colleagues report on fallopian tube tracer uptake in premenopausal women at mid-menstrual cycle and discuss the relationship of these findings to the presence and influence of estrogen.
Page 682

Acute vs. chronic aortic dissection: Reeps and colleagues use 18F-FDG PET/CT to analyze aortic wall uptake differences in acute and chronic stable aortic dissection and point to the potential for clinical application of this technique.
Page 686
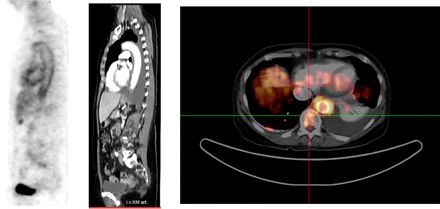
Fused PET–MRI and liver lesions: Donati and colleagues compare the accuracy of lesion detection and diagnostic confidence among 18F-FDG PET/CT, gadolinium-enhanced MRI, and retrospectively fused PET and MR images in suspected liver metastases.
Page 692

Intraoperative sentinel node imaging: Vermeeren and colleagues introduce and evaluate a portable γ-camera for intraoperative visualization of sentinel nodes in the head and neck region.
Page 700

Optimal NET imaging: Binderup and colleagues compare 111In-DTPA-octreotide somatostatin receptor scintigraphy, scintigraphy with 123I-MIBG, and 18F-FDG PET in patients with histologically verified neuroendocrine tumors.
Page 704

18F-FLT PET in oral cavity tumors: Troost and colleagues report on validation studies on the effectiveness of 18F-fluorothymidine as a PET tracer in noninvasive assessment of the proliferative state of squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity.
Page 713
18F-FLT kinetics in brain tumor treatment: Schiepers and colleagues detail the kinetics of 18F-fluorothymidine during treatment of malignant glioma with bevacizumab and irinotecan and describe the tracer's potential as a biomarker of cell proliferation.
Page 720
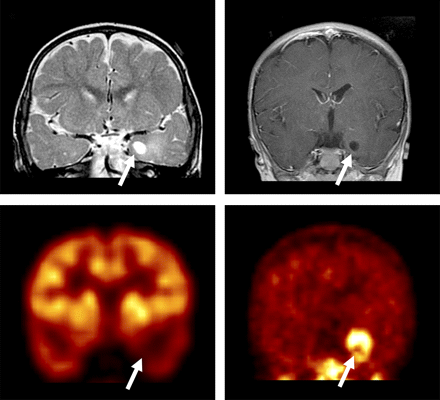
18F-FDG and 11C-methionine PET in epilepsy: Phi and colleagues compare these 2 tracers in PET evaluation of children with focal cortical dysplasia and mixed neuronal and glial tumors, where presurgical MRI may be indeterminate.
Page 728
Radioaerosol choice in V/Q SPECT: Jögi and colleagues compare 99mTc-DTPA and Technegas in ventilation–perfusion SPECT studies in patients with and without obstructive lung disease.
Page 735
Assessing liver function: de Graaf and colleagues provide an educational overview of nuclear imaging techniques, including biochemical and technical backgrounds, for assessment of hepatic function in liver surgery and transplantation.
Page 742
Biased PET images: Son and colleagues look at challenges in PET scanners with elongated fields of view and explore the effects of and remedies for inaccurate attenuation coefficients.
Page 753
Monitoring antiangiogenic response: Nagengast and colleagues study 89Zr-bevacizumab PET for early antiangiogenic tumor response evaluation after treatment with the new heat shock protein 90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922.
Page 761
Folate targeting in atherosclerosis: Ayala-López and colleagues examine the use of a folate-targeted 99mTc-labeled chelate for imaging macrophages that accumulate in atherosclerotic plaques, internalize cholesterol-rich lipoprotein particles, and evolve into foam cells to form vulnerable atherosclerotic lesions.
Page 768
Annexin V for apoptosis in breast cancer: Erba and colleagues use 99mTc-annexin V scintigraphy to define the time course of apoptosis induced by paclitaxel in a model of virus-induced murine breast cancer.
Page 775

Nanobodies for immune cell imaging: De Groeve and colleagues explore the use of nanobodies as a generic method for imaging in vivo biodistribution of specific immune cell types, with myeloid cells as an example.
Page 782
PET tracers in brain hematoma: Salber and colleagues compare patterns and time courses of 18F-FET and 3H-MET uptake in PET imaging of rats with cerebral hematomas and discuss challenges in differentiating between neoplastic and nonneoplastic hematoma origins.
Page 790
11C-choline in atherosclerosis imaging: Laitinen and colleagues investigate the feasibility of 11C-choline as a PET tracer in the assessment of degree of inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques in an atherosclerotic mouse model.
Page 798
18F-FDG fetal dosimetry: Zanotti-Fregonara and colleagues calculate the total fetal absorbed dose in a rare case of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in early pregnancy.
Page 803

Radiation dose variation with stature: Marine and colleagues assess variations in specific absorbed energy fractions in adults with different sizes but normal body stature.
Page 806

PET/MRI attenuation correction: Keereman and colleagues describe MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI using ultrashort echo time sequences.
Page 812

ON THE COVER
In a study exploring the feasibility of using 11C-choline to assess inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques, high 11C-choline uptake was found in the aortic plaques of atherosclerotic mice. Data suggest that macrophages may be responsible for the uptake.
See page 800.








