Visual Abstract
Abstract
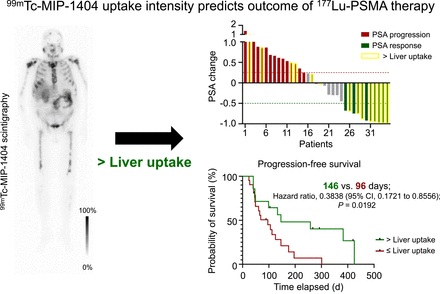
Our objective was to determine the feasibility, diagnostic performance, and predictive value of 99mTc-MIP-1404 SPECT in patients undergoing baseline staging and assessment of eligibility for prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)–targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy (RPT) for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Methods: Data of 46 patients undergoing 99mTc-MIP-1404 planar scintigraphy and SPECT/CT for staging and assessment of eligibility for 177Lu-PSMA RPT were retrospectively analyzed. Overall image quality was assessed, and images were visually analyzed for the presence and localization of pathologic uptake. Metastatic uptake was visually scored using a 3-point scale. 99mTc-MIP-1404 findings were compared with the results of posttherapeutic 177Lu-PSMA scans in patients subsequently commencing RPT (n = 35). The predictive and prognostic significance of uptake intensity in 99mTc-MIP-1404 scans was evaluated. Results: The image quality of 99mTc-MIP-1404 scans was rated as excellent in 98% of cases. Imaging results were concordant in 206 of 210 localizations, demonstrating almost perfect agreement with 177Lu-PSMA scans (κ = 0.957 [95% CI, 0.916–0.999]). Uptake intensity higher than liver uptake identified responders (P = 0.0115) and was associated with prolonged progression-free survival (median, 146 vs. 96 d; hazard ratio for progression, 0.3838 [95% CI, 0.1721–0.8556]; P = 0.0192). In multivariable analysis, 99mTc-MIP-1404 uptake higher than in liver emerged as an independent predictor of treatment response (odds ratio, 12.37 [95% CI, 1.613–203.3]; P = 0.0319). Nevertheless, 27% of responders demonstrated uptake no higher than that in the liver. Conclusion: 99mTc-MIP-1404 imaging is suitable for assessment of eligibility for RPT in patients with advanced metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. In particular, pretherapeutic uptake intensity is predictive of response to 177Lu-PSMA RPT.
Footnotes
Published online Feb. 6, 2025.
- © 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
SNMMI members
Login to the site using your SNMMI member credentials
Individuals
Login as an individual user