Visual Abstract
Abstract
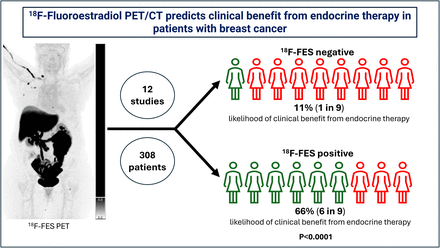
18F-fluoroestradiol (18F-FES) PET/CT has been investigated as a potential biomarker to predict response to endocrine therapies in patients with estrogen receptor (ER)–positive breast cancer. Although previous findings were promising, most had limited statistical significance because of small individual sample sizes. Therefore, we performed a systematic review and metaanalysis of the 18F-FES PET/CT literature to increase our power to evaluate the utility of 18F-FES PET/CT as a biomarker for prediction of clinical benefit from endocrine therapy in patients with ER-positive breast cancer. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted across multiple databases, including PubMed, MEDLINE via OVID, Embase, Web of Science, Emcare, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials through November 1, 2024, for studies that included patients with ER-positive breast cancer who received an 18F-FES PET/CT at baseline and received subsequent endocrine therapy. For each eligible study, data were extracted using a predesigned data extraction form. Random effects models were used to estimate the likelihood of clinical benefit from endocrine therapy after a positive 18F-FES PET scan, the likelihood of clinical benefit from endocrine therapy after a negative 18F-FES PET scan, and the risk ratio of clinical benefit from endocrine therapy comparing those who were 18F-FES–positive to those who were 18F-FES–negative. Results: From 1,105 database records retrieved, 12 studies were included in the metaanalysis (n = 308 participants with data on 18F-FES PET results and response to endocrine therapy). The likelihood of clinical benefit after a positive 18F-FES PET scan was 66% (95% CI, 51%–79%; I2 = 76.6%; n = 227 participants) and the likelihood after a negative 18F-FES PET scan was 11% (95% CI, 3.5%–22%; I2 = 0.0%; n = 81 participants). The risk ratio of response that compared those who were 18F-FES–positive with those who were 18F-FES–negative was 3.21 (95% CI, 1.96–5.25; I2 = 0.0%; P < 0.0001). Conclusion: 18F-FES PET is a successful biomarker for predicting the likelihood of success of endocrine therapy in patients with ER-positive breast cancer. There is strong evidence that patients with 18F-FES–negative disease are unlikely to derive clinical benefit from endocrine therapies, despite the presence of ER-positive disease on pathology. This supports a role for 18F-FES PET in identifying patients for whom endocrine therapy may or may not be an appropriate treatment option.
Footnotes
Published online Mar. 13, 2025.
- © 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
SNMMI members
Login to the site using your SNMMI member credentials
Individuals
Login as an individual user