Abstract
1880
Objectives Accurate assessment of diagnostic and therapeutic concentrations of radiopharmaceuticals is one of the most important goals of quantitative single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT). Although planar acquisition with a point-like source in a petri dish is the simplest way to measure the system sensitivity required for absolute activity quantification in SPECT, this method requires an iterative reconstruction with highly accurate corrections, especially for high-energy emitters. Recent technical advances in SPECT/CT systems allow more accurate physical corrections than before; thus, it is necessary to review the feasibility of planar sensitivity measurement using a point-like source for quantitative SPECT/CT calibration. In this study, we focused on the most widely used therapeutic high-energy emitter, 131I.
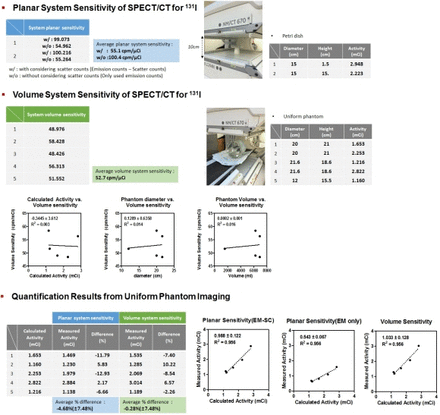
Methods The system sensitivity of a GE Discovery NM/CT 670 scanner equipped with an high-energy general-purpose collimator was measured using a petri dish filled with 131I solution and placed between two detector heads spaced 10 cm apart. Considering the large scatter fraction of 131I, we measured both the photopeak and scatter counts with energy windows of 364 keV ± 10% (photopeak) and 297 keV ± 10% (scatter). The planar system sensitivity (cpm/μCi) was determined by dividing the true counts of the planar scan (photopeak minus scatter counts) by the known activity and acquisition time. Uniform phantom experiments were also performed to calculate the volume-based system sensitivity and to validate the accuracy of absolute quantification. SPECT data were reconstructed with the preparation for Q.Metrix (GE Healthcare), which includes the ordered subset expectation maximization iterative reconstruction with attenuation correction, scatter correction, and resolution recovery. We assessed the quantitative accuracy of activity measurement by comparing the administrated (calculated) and reconstructed (measured) activities of three uniform phantoms of different sizes.
Results The proportion of scatter counts in the 131I planar scan was remarkably high. The measured system planar sensitivities with and without considering scatter counts were 55.1 and 100.4 cpm/μCi, respectively. The measured system sensitivity based on reconstructed volume image counts using a uniform phantom was 52.7 cpm/μCi. The percent differences between the calculated activity and measured activities based on planar and volume sensitivities and proper physical correction were −4.68% (±7.48%) and −0.28% (±7.48%), respectively. The measured activities based on planar and volume sensitivities both showed good linear correlation with the calculated activity (y = 0.99x ± 0.12 and y = 1.03x ± 0.13, respectively).
Conclusions The results of this study indicate that SPECT calibration using a petri dish and quantitative iterative reconstruction allows reliable absolute quantification of the 131I concentration.