Abstract
α-radioimmunotherapy targeting CD45 may substitute for total-body irradiation in hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) preparative regimens for lymphoma. Our goal was to optimize the anti-CD45 monoclonal antibody (mAb; CA12.10C12) protein dose for 211At-radioimmunotherapy, extending the analysis to include intraorgan 211At activity distribution and α-imaging–based small-scale dosimetry, along with immunohistochemical staining. Methods: Eight normal dogs were injected with either a 0.75 (n = 5) or 1.00 (n = 3) mg/kg dose of 211At-B10-CA12.10C12 (11.5–27.6 MBq/kg). Two were euthanized and necropsied 19–22 h after injection, and 6 received autologous HCT 3 d after 211At-radioimmunotherapy, after lymph node and bone marrow biopsies at 2–4 and/or 19 h after injection. Blood was sampled to study toxicity and clearance; CD45 targeting was evaluated by flow cytometry. 211At localization and small-scale dosimetry were assessed using two α-imaging systems: an α-camera and an ionizing-radiation quantum imaging detector (iQID) camera. Results: 211At uptake was highest in the spleen (0.31–0.61% injected activity [%IA]/g), lymph nodes (0.02–0.16 %IA/g), liver (0.11–0.12 %IA/g), and marrow (0.06–0.08 %IA/g). Lymphocytes in blood and marrow were efficiently targeted using either mAb dose. Lymph nodes remained unsaturated but displayed targeted 211At localization in T lymphocyte–rich areas. Absorbed doses to blood, marrow, and lymph nodes were estimated at 3.1, 2.4, and 3.4 Gy/166 MBq, respectively. All transplanted dogs experienced transient hepatic toxicity. Liver enzyme levels were temporarily elevated in 5 of 6 dogs; one treated with 1.00 mg mAb/kg developed ascites and was euthanized 136 d after HCT. Conclusion: 211At-anti-CD45 radioimmunotherapy with 0.75 mg mAb/kg efficiently targeted blood and marrow without severe toxicity. Dosimetry calculations and observed radiation-induced effects indicated that sufficient 211At-B10-CA12.10C12 localization was achieved for efficient conditioning for HCT.
Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is a curative treatment option for many malignant and nonmalignant hematologic disorders. A key element is the HCT conditioning regimen, which prevents relapse after remission by reducing the underlying disease burden and facilitates allogeneic engraftment through host immunosuppression. In recent years, efforts have been made to increase the absorbed dose to target sites while reducing the radiation-induced adverse effects, through substitution of radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for standard pretreatment total-body γ-irradiation. The radioimmunotherapy regimens have generally used β-emitters such as 131I, which are suboptimal for killing hematopoietic cells because of their long particle range and low linear energy transfer. Conversely, short-ranged α-emitters deposit very high energies over a few cell diameters (40–100 μm), making α-radioimmunotherapy an appealing option for improving the specificity and efficacy of conditioning (1).
Our group has previously explored α-radioimmunotherapy preparative regimens for HCT in preclinical models, concluding that conditioning with either 213Bi- or 211At-anti-CD45-radioimmunoconjugates was efficacious, without significant nonhematopoietic toxicity (2–5). 211At was chosen over 213Bi for subsequent α-radioimmunotherapy studies because of its superior myelosuppression, lower cost, greater availability, and clinically less challenging half-life (7.2 h for 211At vs. 46 min for 213Bi).
CD45 is a cell surface tyrosine phosphatase that regulates T-cell and B-cell activation and maturation. It is broadly expressed (∼200,000 copies per cell) on all hematopoietic cells except platelets and erythrocytes, regardless of malignant transformation (6). Our overall goal is to achieve efficient targeting and pharmacokinetics with minimal normal-tissue toxicity using 211At-anti-CD45-radioimmunoconjugates to replace total-body irradiation or high-dose chemotherapy conditioning in HCT preparative regimens for hematopoietic diseases. In this study, we aimed to optimize the anti-CD45 mAb protein dose in a canine model, evaluating the results through blood counts, plasma chemistry, flow cytometry, immunohistochemical staining, α-imaging, and small-scale α-dosimetry.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Antibodies and Antibody Conjugates
Anticanine CD45 mAb CA12.10C12 (2,3,5,7) was conjugated with closo-decaborate(2−) to produce CA12.10C12-B10 for 211At-labeling, as previously described (8). Flow cytometry was performed as described by Sandmaier et al. (2). mAbs were produced and purified at the Biologics Production Facility at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (FHCRC).
Radioactivity
211At was produced using a MC-50 cyclotron (Scanditronix) at the University of Washington and isolated through a wet-chemistry method (8). Subsequent 211At-labeling of CA12.10C12-B10 was performed using the procedure of Chen et al. (5). All radioactive materials were handled according to approved protocols at FHCRC and the University of Washington.
Dogs
The dogs were raised at FHCRC and given standard immunizations. The experimental protocol was approved by the FHCRC Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, and the study was executed according to principles outlined in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (9).
Flow Cytometry
Surface-bound anti-CD45 was detected through flow cytometry of cell suspensions prepared from samples of blood, lymph nodes, and bone marrow aspirates, as previously described (2,5). Antigen saturation was determined by comparing the mean fluorescence intensity of cells incubated with either fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated goat antimouse F(ab′)2 (FMF) or fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated anti-CD45 mAb (CD45F).
Biodistribution, Pharmacokinetics, and Toxicity
Two anti-CD45 mAb dose levels (0.75 mg/kg, n = 5; 1.00 mg/kg, n = 3) were evaluated with regard to in vivo distribution, pharmacokinetics, and normal-organ toxicity. The starting level was based on previous canine studies, which showed that 0.50 mg/kg insufficiently saturated available CD45 antigens (2,3,5). Unlabeled CA12.10C12 (0.05 mg/kg) was injected 30–60 min before 211At-mAb infusion to prevent nonspecific Fc receptor binding. Clearance of mAb and 211At was assessed using blood collected from 5 min before to 22 h after radioimmunoconjugate injection, using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay as previously described (2) and by radioactivity measurements, respectively. Eight dogs were infused with CA12.10C12-B10 labeled with 14.6–36.7 MBq 211At/mg mAb (Table 1); two were euthanized and necropsied without HCT 19–22 h after injection. Harvested tissues were weighed and measured for radioactivity, and the results were expressed as percentage injected activity (%IA) per gram after corrections for background and decay. Six dogs received autologous HCT 3 d after the 211At-mAb infusion. Marrow was aspirated from humeri and femora at least 2 wk before radioimmunotherapy and then processed and stored as previously described (10,11). Biopsies of lymph nodes and bone marrow were taken at an early (2–4 h) and/or a late (19–22 h) time point after 211At-mAb infusion. Samples were split for flow analysis, α-imaging, immunohistochemistry, and radioactivity measurement.
Dogs Treated with 211At-Anti-CD45 Radioimmunotherapy
Toxicities were evaluated by measuring complete blood counts, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, and liver enzymes at baseline, daily for the first 2 mo or until full hematopoietic recovery, and then weekly until the end of the study. Necropsies at euthanasia included gross examination and tissue harvesting for pathologic assessment of microscopic abnormalities.
α-Imaging
Two α-imaging systems were used for high-resolution ex vivo assessment of 211At localization and microdosimetry: an α-camera (12) and an ionizing-radiation quantum imaging detector (iQID) camera (13). Cryosections (10–12 μm) of popliteal lymph nodes and bone marrow cores were placed on a scintillation film (EJ-440; Eljen Technology) and imaged as previously described (14). Consecutive sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histological comparison with the imaged intraorgan 211At distribution.
Dosimetry
Absorbed doses to blood were estimated individually from the blood samples by creating time–activity curves (%IA/g as a function of time) assuming 100 %IA in blood at injection (t = 0). Blood volumes were derived from individual dog weights and a standardized total blood volume of 102.6 mL/kg (15). The cumulated 211At activity ( ) was calculated after exponential curve fitting for each time–activity curve. Using an absorbed fraction of α-particles (
) was calculated after exponential curve fitting for each time–activity curve. Using an absorbed fraction of α-particles (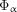 ) of 1 and including contributions exclusively from α-particles, the absorbed dose (D) in Gy was calculated using the equation
) of 1 and including contributions exclusively from α-particles, the absorbed dose (D) in Gy was calculated using the equation where m denotes tissue mass in kilograms and Δα is the mean energy released per 211At decay (1.09 × 10−12 J). Mean absorbed dose rates at biopsy were calculated and normalized to the individual injected activities (μGy/MBq-s) for bone marrow (core and aspirate) and lymph nodes using radioactivity measurements of the samples. Total absorbed doses (Gy/MBq) to marrow were estimated by interpolation between early and late time points using polynomial curve fits of the time–activity curves, assuming zero tissue radioactivity at t = 0.
where m denotes tissue mass in kilograms and Δα is the mean energy released per 211At decay (1.09 × 10−12 J). Mean absorbed dose rates at biopsy were calculated and normalized to the individual injected activities (μGy/MBq-s) for bone marrow (core and aspirate) and lymph nodes using radioactivity measurements of the samples. Total absorbed doses (Gy/MBq) to marrow were estimated by interpolation between early and late time points using polynomial curve fits of the time–activity curves, assuming zero tissue radioactivity at t = 0.
Small-scale dosimetry was performed for marrow and lymph nodes through quantification of the radioactivity concentration (Bq/g) at biopsy in the α-imaged samples. Individual section masses were estimated using the area and thickness of each imaged section and a tissue density of 1 g/cm3. Small-scale mean absorbed dose rates were calculated as described above and compared with those calculated for “macroscopic” (i.e., nonsectioned) biopsies using traditional whole-tissue dosimetry methods (16). Dose rate differences between various subcompartments in α-imaged samples were also examined.
Image-based small-scale 3-dimensional dosimetry was performed for lymph nodes from 2 dogs, using voxel dose-point kernels and α-camera imaging of serial sections (17). Briefly, series of 13 consecutive 12-μm sections were imaged, registered, and stacked to a 3-dimensional matrix of 12 × 12 × 12 μm3 voxels. Voxel dose-point kernels for 211At were generated using Monte Carlo simulation and convolved with the radioactivity images using MATLAB (The MathWorks, Inc.) to estimate the absorbed dose rate in each voxel. Dose rate distribution maps were thereby achieved for the centermost section (7/13) of each series.
Histology and Immunohistochemistry
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded lymph node samples were stained on a BOND RX system (Leica) with antibodies against CD3 (3 μg/mL, MCA1477; Serotec), MAC 387 (0.2 μg/mL, M0747; Dako), and cleaved caspase-3 (0.3 μg/mL, CP229B; Biocare Medical) after ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid–based antigen retrieval. The CD3 antibody was followed by a rabbit antirat secondary, and all antibodies were then detected and visualized using Power Vision HRP polymers and Refine DAB (Leica Biosystems). The slides were scanned using an Aperio AT scanscope system (Leica) with ×40 image capture magnification and analyzed using the ImageScope viewing software.
RESULTS
211At-B10-CA12.10C12
Astatination of CA12.10C12-B10 was achieved with 74%–91% labeling yields. The radiochemical purity of the 211At-B10-CA12.10C12 was always greater than 98%, as determined by radio–high-performance liquid chromatography or instant thin-layer chromatography.
Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics
The in vivo distributions in selected tissues from nontransplanted dogs (H573 and H585) are shown in Figure 1A. The 211At accumulation was highest in lymphocyte-rich target tissues such as spleen (0.31–0.61 %IA/g), lymph nodes (0.02–0.16 %IA/g), and bone marrow core (0.06–0.08 %IA/g), and in the liver (0.11–0.12 %IA/g). Uptake levels in other tissues were low. The activity concentration in bone marrow core for all dogs, at 1 or 2 biopsy time points, revealed no distinct trend in terms of accumulation or release over time (paired t test, P = 0.61). Clearance of circulating 211At from blood is shown in Figure 1B. The mean %IA/g did not vary significantly between the 2 mAb doses (unpaired t test, P = 0.62), whereas the mean anti-CD45 mAb concentration in plasma was higher for 1.00 mg/kg (P = 0.01; Supplemental Fig. 1; supplemental materials are available at http://jnm.snmjournals.org).
Biodistribution and clearance of 211At-anti-CD45 mAb. (A) Radioactive content expressed as %IA/g ± SD (n = 3) in selected tissues from 2 dogs euthanized 19–22 h after injection. (B) Retention of 211At in blood for all treated dogs, determined by radioactivity measurements of repeated blood samples (%IA/g ± SD, 0.75 mg/kg, n = 5; 1.00 mg/kg, n = 3). p.i. = after injection.
Anti-CD45 Saturation
Flow cytometry data for lymphocytes in marrow and lymph nodes are summarized in Tables 2 and 3, showing the mean fluorescence intensity and the relative percentage of FMF and CD45F staining, respectively. Bone marrow lymphocytes were rapidly and efficiently targeted by anti-CD45 mAb, as demonstrated by high intensity and percentage binding of FMF at the early time points. The corresponding CD45F numbers were low, indicating near saturation of CD45. In contrast, FMF staining of lymph node samples resulted in a low mean fluorescence intensity regardless of time point or mAb dose. This result, in combination with high CD45F intensity, confirmed the abundance of free antigen. Flow cytometry dot plots of fluorescein isothiocyanate versus forward scatter indicated cell depletion in marrow at the later time point, but no similar effect was seen for lymph nodes. The antigen binding differed significantly in terms of FMF and CD45F mean fluorescence intensity in blood lymphocytes after 211At-mAb infusion, confirming the efficient saturation of CD45 sites on circulating lymphocytes (Supplemental Fig. 2).
Mean Fluorescence Intensity after Staining of CD45+ Cells (Gated on Lymphocytes)
Percentage of Stained CD45+ Cells (Gated on Lymphocytes)
α-Imaging
Images acquired using the α-camera and the iQID camera showed heterogeneous 211At distribution in lymph nodes at all time points, with predominant localization to T lymphocyte–rich regions in the paracortex, as determined from consecutive H&E-stained cryosections (Fig. 2 and Supplemental Fig. 3). The lymph node medulla and follicles in the superficial cortex contained little radioactivity. Follicles in the superficial cortex presented as clearly defined dark, round areas in contrast to the high-intensity deep cortical units (Figs. 2A and 2C). Quantitative image analysis showed that the activity concentrations in high-activity lymph node regions could be a factor of 8 up to 65 times higher than those in lower-activity regions. Apart from the bone matrix, which exhibited no quantifiable activity uptake, the marrow samples displayed a more homogeneous uptake profile at both time points, with high levels of 211At activity in all regions containing hematopoietic cells (Figs. 2B and 2D).
Distribution of 211At in cryosectioned tissue samples imaged using iQID camera (A and B), and corresponding H&E-stained sections (C and D). A and C show lymph node sections from dog H638, biopsied 19 h after injection; B and D show sections of bone marrow core from dog H632, biopsied 2 h after injection. Green and yellow lines indicate lymph node follicles and paracortex (including visibly apoptotic areas), respectively, identified in H&E section. Overlaid with the α-image, outlined regions coincide well with low- and high-activity areas. Horizontal scale bars indicate 1 mm; color bars show 211At activity in microbecquerels.
Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
Visual examination of H&E slides and corresponding α-images revealed an apparent association between apoptotic cells and high-signal areas, particularly at the later time points. Radiation-induced damage and associated features (cellular debris and macrophage infiltration) were distinctly increased in lymph nodes biopsied at 19 h after injection. Immunohistochemical staining of paraffin-embedded lymph nodes allowed more detailed analysis than was possible with frozen samples, because of superior morphology preservation; however, few samples were large enough to enable both methods. The most comprehensive dataset was achieved for the H629 2-h biopsy seen in Figure 3. The paraffin-embedded sections were cut from the same lymph node as the α-imaged cryosection in Figures 2B and 2E, albeit not consecutively. Figure 3 shows representative regions, including cortex, paracortex, and medulla, demonstrating the general morphology, T-cell localization, apoptosis markers, and macrophage localization. As expected, T cells were abundant in the paracortex but typically scarce in the cortical follicles. B-cell staining was not achieved, because of unsatisfactory antibody performance in paraffin-embedded canine tissues. Similarly, efforts to assess the distribution of CA12.10C12-B10 in untreated lymph nodes were unsuccessful. At 2 h after injection, staining for cleaved caspase-3 indicated widespread apoptosis. Macrophages containing multifocal apoptotic cellular debris were present in medullary cords and interfollicular zones, as well as within occasional germinal centers.
Immunohistochemical staining of a formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded lymph node from dog H629, biopsied 2 h after 211At-B10-CA12.10C12 injection. (A) H&E-stained section, including representative areas of cortex, paracortex, and medulla. B–D show staining for T cells (CD3), apoptosis (cleaved caspase-3), and macrophages (MAC 387), respectively, in corresponding areas of serially cut sections from the same lymph node. Scale bar represents 200 μm.
Dosimetry
The absorbed dose to blood ranged from 0.013 to 0.030 Gy/MBq, corresponding to total absorbed doses of 1.6–5.7 Gy (mean, 3.1 Gy) for the mean injected 211At activity of 166 MBq (Table 4). Only minor intersubject variability was exhibited in absorbed dose rates to blood over time, analogous to the 211At blood clearance (Fig. 1B).
Mean Absorbed Dose to Blood After Injection of 211At-Anti-CD45 mAb
Concordance was seen between mean absorbed dose rates for marrow derived from either whole-tissue dosimetry of macroscopic samples (core and aspirate) or α-imaging (core), ranging from 0.05–0.60 to 0.01–0.11 μGy/MBq-s at early and late time points, respectively (Supplemental Fig. 4A). Polynomial curve fitting of the macro biopsy data resulted in mean absorbed doses to marrow of 2.4 Gy/166 MBq. For lymph nodes, the dose rates were 0.03–0.61 and 0.01–0.20 μGy/MBq-s early and late, respectively (Supplemental Fig. 4B). Interestingly, two 2-h data points for dog H632 were markedly elevated, indicating rapid and high lymph node uptake of 211At. A polynomial fit using these two high-dose data points and the mean of all data points at 19–22 h after injection resulted in a mean absorbed dose to a high-activity lymph node of 3.4 Gy/166 MBq of 211At.
Figure 4 compiles the lymph node data from the 3-dimensional small-scale dosimetry for dogs H638 and H689. Highly nonuniform dose rate distributions were observed in all 3 cases (Figs. 4A, 4C, and 4D), with small hot volumes (80–180 mGy/h) dispersed in main volumes of lower dose rate levels (0–20 mGy/h). Comparison with H&E-stained sections for dog H638 (Fig. 4B) indicated colocalization of areas with high dose rate and lymphocyte-rich subregions within the lymph node.
Dose rate images derived by 3-dimensional dosimetry using α-camera imaging. (A) Dose rate distribution at biopsy for dog H638 4 h after injection. (B) Corresponding H&E-stained section. (C and D) Dose rate distribution for dog H689 2 and 19 h after injection, respectively. Color bars express dose rate in mGy/h; scale bar (top right) indicates 1 mm.
Toxicity
Aspartate aminotransferase levels (Supplemental Fig. 5A) remained primarily within the reference range, except for dog H632, which experienced a brief initial spike with a 2-fold increase in numbers above the upper limits of normal 14–28 d after HCT before returning to normal on day 42. H629 displayed a more gradual effect, with a maximum on day 136 after HCT, at which point the dog was euthanized because of severe ascites that started developing on day 119. Alkaline phosphatase levels were initially elevated (1.1–2.6 times the upper limit of normal) overall but returned to normal between days 28 and 70 after HCT, except for dog H689, whose numbers remained just above the reference range (Supplemental Fig. 5B). Bilirubin and creatinine levels were unremarkable for all dogs (Supplemental Figs. 5C and 5D).
All 6 transplanted dogs experienced transient pancytopenia (Supplemental Figs. 5E–5G). The median nadir levels for granulocytes, lymphocytes, and platelets were 9 cells/μL (range, 0–24 cells/μL), 74 cells/μL (range, 57–124 cells/μL), and 4,500 platelets/μL (range, 3,000–6,000 platelets/μL), respectively, at a median time of 3 d (range, 3–5 d), 1 d (range, –1 to 2 d), and 7 d (range, 6–8 d) after HCT, respectively. The first of 3 consecutive days after nadir with absolute neutrophil counts of at least 500/μL occurred at a median of 9 d after HCT (range, 8–20 d), and the first of 7 consecutive days after nadir with platelet counts of at least 20,000/μL occurred at a median of 21 d after injection (range, 18–24 d). A median of 3 platelet transfusions were administered per dog (range, 1–6), with a transfusion threshold of 10,000/μL.
All dogs except H629 were euthanized in good condition after 32–48 wk of follow-up. Dogs H543, H689, H522, and H632 displayed no macroscopic or histologic evidence of toxicity in the liver, kidney, or other organs. Pathologic examination of dog H638 revealed signs of subacute bronchitis and increased iron stores in liver macrophages after 6 blood transfusions. The necropsy of dog H629 showed mild hepatic abnormalities, including features sometimes attributed to early sinusoidal obstructive syndrome. The dog’s seemingly mild liver toxicity did not correspond to the level of ascites found at the time of euthanasia—a discrepancy that remains unexplained. No signs of renal toxicity were seen in any of the transplanted dogs.
DISCUSSION
Radioimmunotherapy is a highly suitable treatment option for lymphoma because of the synergistic combination of high radiosensitivity of hematologic malignancies and accessibility of circulating radioimmunoconjugates to targets in lymph nodes, marrow, and spleen. Our group has previously demonstrated the safety and efficacy of CD45-targeted α-radioimmunotherapy in dogs as a potential substitute for external-beam total-body irradiation and high-dose systemic chemotherapy in HCT pretreatment regimens (2,3,5). The current study further assessed 211At-anti-CD45 radioimmunotherapy conditioning for use in upcoming therapy studies of spontaneously occurring canine lymphoma—a feasible and clinically relevant model, thanks to the many similarities to human lymphoma. Here, the administered mAb dose was optimized and the analysis was extended to include intraorgan 211At activity distribution and small-scale dosimetry at the micrometer range, using two α-imaging techniques along with immunohistochemical staining.
The starting dose of 0.75 mg/kg proved satisfactory for targeting lymphocytes in blood and marrow but left many lymph node binding sites vacant. Increasing the dose to 1.00 mg/kg did not improve the ratios; the only significant effects were an expected elevation in circulating anti-CD45 mAb levels and a minor shift in FMF fluorescence intensity corresponding to increased targeting of blood lymphocytes. Interestingly, the binding of fluorescein isothiocyanate–labeled anti-CD45 mAb also increased slightly; although significant, this effect was less pronounced. The results indicate that considerably higher amounts of anti-CD45 mAb likely would have been required to approach saturation in lymph nodes, causing increased nontarget irradiation by circulating radioimmunoconjugates. Therefore, further dose escalation was not explored.
The two mAb doses generated no distinguishable differences in hematologic toxicity or hepatic/renal function, and no trends were seen in the administered 211At activity level. No serious toxicity was seen after administration of the lower mAb dose (0.75 mg/kg). The main adverse event was severe ascites in 1 subject 20 wk after receiving the higher mAb dose (1.00 mg/kg; 14.6 MBq 211At/kg) and HCT. The clinical presentation and histologic features of that dog’s liver closely resembled those previously reported by our group for 2 nontransplanted dogs who were treated with 211At-anti-CD45 radioimmunotherapy using 0.50 mg mAb/kg (5). In that radiation dose escalation study, hepatic aberrations of clinical relevance were observed in dogs treated with more than 15.0 MBq/kg. Eight additional dogs received dog leukocyte antigen–identical marrow transplants after conditioning with a 7.5- to 23.1-MBq/kg dose of 211At-anti-CD45 radioimmunotherapy (0.50 mg mAb/kg), without any cases of evident liver failure. The mechanisms behind this tolerance discrepancy were not fully elucidated, but based on rat studies conducted by Harb et al. (18) it was hypothesized that radiation-induced hepatic damage may have been repaired by bone marrow–derived progenitor cells in transplanted dogs. In an earlier set of experiments, similar toxicity was seen in a dog after pretreatment with α-radioimmunotherapy (326 MBq/kg of 213Bi-anti-CD45 mAb; 0.50 mg/kg) before dog leukocyte antigen–identical transplantation (2).
As expected, the biodistribution showed higher accumulation of 211At in the liver than in other nontarget organs, as is typical for radioimmunotherapy because of internalization of circulating immunoglobulins by hepatic Kupffer cells and endothelial cells (19). In addition, a slightly increased %IA/g is expected for anti-CD45-radioimmunoconjugates because of the presence of CD45-expressing cells of hematopoietic origin in the liver (20). Even so, CD45 is attractive for radioimmunotherapy because of its abundance on target cells and its noninternalizing and nonshedding features. Most importantly, anti-CD45 mAbs do not compete with any anti-CD20 pretreatment (e.g., rituximab) for binding to target antigens, which may limit the efficacy of anti-CD20 radioimmunotherapy (21).
The estimated mean absorbed dose to blood of 3.1 Gy per 166 MBq of 211At was comparable to standard external total-body irradiation dose levels of 2–3 Gy (2). However, this level of absorbed dose increases markedly for 211At-radioimmunotherapy when one accounts for the relative biological effectiveness of α-emitters, generally assumed to be in the range of 3–5 (16). Corresponding absorbed doses to marrow and lymph nodes not adjusted for relative biological effectiveness and calculated using traditional whole-tissue dosimetry were comparable to the dose to blood, but the lymph node estimations were based on a limited number of time points. Nevertheless, the dose levels of 3 Gy and above are a strong indication of satisfactory targeting, which has not been demonstrated in this model before.
α-imaging revealed substantial dose rate variations within the lymph nodes, but congruence between hot areas and lymphocyte-rich regions sustained the perception of effective CD45 targeting. Furthermore, markedly higher dose rates (approximately a factor of 2) were seen in these high-activity areas at the early time points; the total absorbed dose to lymphocyte-rich target regions could thus be a factor of 2 higher than the 3.4 Gy/166 MBq that was calculated from the mean activities, should this be a characteristic time progression for each lymph node. Widespread indications of cell death observed in immunohistochemically stained sections supported the preliminary dose estimates, although more accurate dosimetry requires additional time points. Ongoing 211At-radioimmunotherapy studies in dogs will extend the dosimetric analysis further.
Concordance was also seen between flow cytometry data and in vivo activity profiles. The profuse 211At radioactivity registered in marrow matched the widespread targeting indicated by flow analysis; likewise, the heterogeneous activity distributions in lymph nodes corresponded well to the lower overall targeting discerned by the flow assays. CA12.10C12 supposedly targets all isoforms of CD45 expressed by T and B lymphocytes, yet our α-images consistently demonstrated absence of 211At in B-lymphocyte–containing follicles at all studied time points. A possible explanation could be that T-cell–associated isoforms (180–220 kDa) are more abundant or easier to access than B-cell isoforms (205–220 kDa).
CONCLUSION
Efficient targeting of 211At-anti-CD45 radioimmunotherapy to blood and marrow was achieved using a mAb dose of 0.75 mg/kg, without severe toxicity. Although antigen saturation was not reached, dosimetry calculations and observed radiation-induced effects in immunohistochemically stained lymph node samples indicated that sufficient 211At localization was achieved for use in HCT pretreatment regimens at levels of injected activity that should be tolerable for normal tissues. Our results highlight the importance of small-scale dosimetry for understanding therapeutic outcomes after α-radioimmunotherapy. Ongoing studies will reveal if efficient 211At-B10-CA12.10C12 conditioning can be achieved for autologous HCT curative therapy of relapsed lymphoma in dogs.
DISCLOSURE
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734. Research funding was provided by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants CA172582, CA044991, CA109663, and CA78902. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH or its subsidiary Institutes and Centers. Sofia H.L. Frost was supported by the David and Patricia Giuliani Family Foundation and a Doug and Maggie Walker Immunotherapy Fellowship. Brian W. Miller was supported by a PNNL Linus Pauling Distinguished Postdoctoral Fellowship, developing the iQID camera in collaboration with NIH grant P41EB002035 (CGRI). No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Acknowledgments
We thank the veterinarians and technicians at the canine facilities at FHCRC. Histology and immunohistochemistry was performed by Experimental Histopathology Shared Resources at FHCRC. Dr. George Sale is gratefully acknowledged for pathology support.
Footnotes
Published online Sep. 3, 2015.
- © 2015 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Inc.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication June 16, 2015.
- Accepted for publication August 20, 2015.











