Imaging RNA interference: Hong and colleagues offer perspective on current investigations into in vivo molecular imaging of RNA interference, a technique for regulating or silencing specific genes, with potential applications in numerous diseases.
Page 169
SUV—silly or smart metric?: Visser and colleagues provide an overview of perspective on challenges to meaningful quantitation in PET imaging and preview an article in this issue of JNM that identifies superior approaches.
Page 173
PET cost-effectiveness in HNSCC: Uyl-de Groot and colleagues compare the cost-effectiveness of whole-body 18F-FDG PET and chest CT in pretreatment screening for distant metastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Page 176
Pharmacokinetics of 18F-FDHT: Beattie and colleagues describe a clinically applicable, noninvasive method using PET and this fluorinated androgen analog to quantify changes in androgen receptor levels in patients undergoing therapy for prostate cancer.
Page 183
Imaging coronary artery macrophage activity: Rominger and colleagues correlate uptake of 68Ga-DOTATATE in the coronary arteries with the presence of calcified plaques and cardiovascular risk factors to explore a potential role for this tracer in plaque imaging.
Page 193

Vascular territories in hybrid PET/CT: Javadi and colleagues review standard techniques for assignment of vascular territories in myocardial perfusion imaging and suggest an alternative approach to correct for inaccuracies in PET/CT resulting from morphologic variability in the coronary tree.
Page 198


MPS change quantification: Prasad and colleagues analyze variables in a large group of rest–stress myocardial perfusion SPECT studies to improve optimal automatic detection of ischemia and coronary artery disease.
Page 204
Movement correction for human brain PET: Wardak and colleagues describe a retrospective image-based movement correction method and evaluate its implementation on dynamic 18F-FDDNP PET images of patients with Alzheimer disease and cognitively intact controls.
Page 210

11C-methionine uptake in normal brain: Uda and colleagues determine uptake of this increasingly useful PET tracer in normal brain and detail inter- and intraindividual variations in standardized uptake values.
Page 219

Imaging presynaptic monoaminergic system integrity: Okamura and colleagues report on the utility of 18F-AV-133, a novel radiolabeled tetrabenazine derivative, in PET assessment of the vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 in Parkinson disease patients and healthy individuals.
Page 223

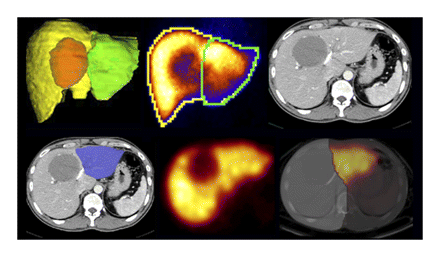
SPECT with scintigraphy for liver function: de Graaf and colleagues determine the value of the addition of SPECT to dynamic 99mTc-mebrofenin hepatobiliary scintigraphy in SPECT/CT evaluation of liver function in patients before liver resection.
Page 229
Time-of-flight PET/CT: Lois and colleagues investigate the qualitative and quantitative effects of incorporating time-of-flight data into reconstruction of clinical studies in patients with cancer.
Page 237

Assessing brown adipose tissue activation: Baba and colleague measure brown adipose tissue densities as CT Hounsfield units in a rodent model and in patients to determine whether changes in these metrics correlate with brown adipose tissue activity.
Page 246

AgRP scaffold–based PET probe: Jiang and colleagues describe experiments to determine the potential of engineered αvβ3 integrin–binding agouti-related protein peptides for use as cancer imaging agents in living subjects.
Page 251

Annexin-A5 uptake in myocardial ischemia: Kenis and colleagues explore the use of 99mTc-labeled annexin-A5 for γ-imaging of phosphatidylserine externalization as a byproduct of cardiomyocite apoptosis and report on the potential reversibility of the apoptotic process.
Page 259

Tumor volume and SUV estimation in PET: Tylski and colleagues assess the accuracy and robustness of 5 methods for tumor volume estimates in 18F-FDG PET and 10 methods for SUV estimates in a variety of configurations.
Page 268

Sincalide-stimulated cholescintigraphy: Ziessman and colleagues determine the infusion method with the least variability for calculation of gallbladder ejection fraction in sincalide-stimulated cholescintigraphy and establish reference values for the technique.
Page 277
Coin-shaped radiosynthesis microreactor: Elizarov and colleagues report on the design of an integrated microfluidic device, with a footprint equal to that of a postage stamp, and on its optimization for multistep radiosynthesis of PET tracers.
Page 282

18F-FLT fetal dosimetry: Bartlett and colleagues estimate radiation absorbed dose to the human fetus from nuclear medicine procedures with this tracer, using biodistribution data obtained with PET/CT studies in pregnant rhesus monkeys.
Page 288

Enhancing pediatric PET: Accorsi and colleagues determine quantitative injection rules for pediatric PET imaging that reduce scan time or dose while maintaining high image quality.
Page 293
90Y SIRT structural dosimetry: Gulec and colleagues describe a methodology for translating derived absorbed dose estimates to subunits of normal liver tissue into biologically relevant absorbed doses for more effective selective internal radiation treatment with 90Y microspheres.
Page 301
α-Particle emitter dosimetry: Sgouros and members of the MIRD committee review current targeted α-particle emitter therapies and provide guidance and recommendations for human α-particle emitter dosimetry in this abbreviated version of MIRD Pamphlet 23.
Page 311

ON THE COVER
Future remnant liver function is a crucial determinant of whether a patient can safely undergo major liver resection. The combination of SPECT data with measures of dynamic uptake function by planar hepatobiliary scintigraphy provides valuable information about segmental liver function and is an accurate measure of future remnant liver function.
See page 231.