MRI in tumor microenvironments: Penet and colleagues review the potential for MRI of cancer cells within the complex environment formed by the extracellular matrix, blood and lymphatic vessels, infiltrating leukocytes, and other cells.
Page 687
131I therapy risks: Boreham and Dolling survey current challenges in assessing the effects of therapeutic exposure to radioiodine during pregnancy and preview an article on this topic in this issue of JNM.
Page 691
11C-MET PET of irradiated brain tumors: Terakawa and colleagues evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of 11C-MET PET for the differentiation of recurrence from radiation necrosis in patients previously treated for metastatic brain tumors or glioma.
Page 694

18F-fluoride PET accuracy: Frost and colleagues compare the precision of 18F-fluoride PET with that of biochemical markers of bone turnover in the assessment of regional bone disease over a 6-mo period.
Page 700
PET in uterine smooth muscle tumors: Yoshida and colleagues investigate whether combined MRI and 18F-FDG PET imaging is more accurate than MRI alone in differentiating nonbenign uterine smooth muscle tumors from leiomyomas.
Page 708

New HSV1-tk mutant: Likar and colleagues describe the development of a reporter gene with specificity and high phosphorylation activity for acycloguanosine derivatives and potential for PET imaging of suicidal gene therapy protocols.
Page 713
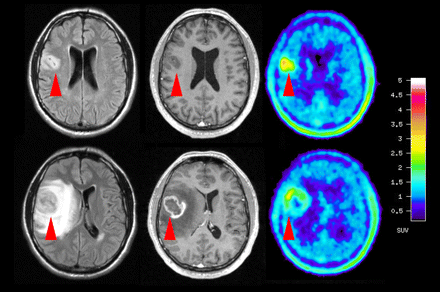
Metabolic imaging of human gliomas: Stadlbauer and colleagues report on research supporting multimodal evaluation of metabolic changes in cerebral gliomas, correlating 18F-FET uptake on PET and concentrations of choline, creatine, and N-acetyl-aspartate as determined with proton MR spectroscopic imaging.
Page 721
PET and MRI for NILs: Floeth and colleagues describe characteristic MRI growth patterns and 18F-FET uptake in nonspecific incidental brain lesions as predictors of eventual development of low- and high-grade gliomas.
Page 730
Radiation dose in cardiac PET/CT: Gould and colleagues test the quantitative accuracy of a single poststress cine CT attenuation scan for reconstructing cardiac rest perfusion images, thus eliminating resting CT attenuation scans and reducing cumulative radiation dose.
Page 738

Gated SPECT for diastolic function: Patel and colleagues explore the benefits of combining data on perfusion defects with data on diastolic impairment to predict left ventricular end-diastolic pressure at subsequent cardiac catheterization.
Page 746
SPECT/CT and brown adipose tissue: Goetze and colleagues assess the frequency with which uptake of 99mTc-MIBI is present in brown adipose tissue in an adult patient population.
Page 752

SPECT and the pathophysiology of anxiety: van der Wee and colleagues use SPECT to examine 123I-β-CIT binding potentials for serotonin and dopamine transporters in individuals with and without a generalized social anxiety disorder.
Page 757
rhTSH-stimulated ablation and recurrence: Tuttle and colleagues report on rates of disease recurrence with recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone administration after radioiodine therapy and compare these rates with those from conventional thyroid hormone withdrawal.
Page 764
Xenon gas index for emphysema: Mathews and colleagues investigate the potential of a new quantitative gas trapping index derived from a 133Xe ventilation scan to assess the severity of emphysema and provide valuable data for lung volume reduction procedures.
Page 771

Lower gastrointestinal tract evaluation: Mariani and colleagues provide an educational overview of the technical aspects and diagnostic performance parameters of nuclear medicine procedures used in patients with disorders of the lower gastrointestinal tract.
Page 776
In vivo evaluation of nanobodies: Gainkam and colleagues use SPECT/CT to compare in vivo tumor uptake and biodistribution of two 99mTc-labeled anti–epidermal growth factor receptor nanobodies with potential for radioimmunodetection of specific targets early after therapy.
Page 788

Galectin-3 targeting and breast tumors: Kumar and Deutscher evaluate the tumor cell–targeting and SPECT properties of a 111In-labeled galectin-3–avid peptide in human breast carcinoma cells and human breast tumor–bearing mice.
Page 796

HER2 PET with 18F-labeled affibody: Cheng and colleagues explore the potential of 2 radiofluorinated anti–human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 protein scaffold molecules as potential molecular probes for small-animal PET.
Page 804

18F-DPA-714 for imaging TSPO: James and colleagues detail the synthesis, radiofluorination, and pharmacologic evaluation of a new translocator protein–specific pyrazolopyrimidine.
Page 814

Imaging probe for melanoma: Miao and colleagues evaluate the potential utility of an imaging surrogate for an experimentally successful peptide-targeted α-therapy for melanoma and discuss the potential for patient-specific dosimetry and monitoring of tumor response.
Page 823
Novel ligand for angiogenesis imaging: Jeong and colleagues describe the conjugation and 68Ga labeling of an RGD derivative for angiogenesis imaging in ischemic tissue and detail the results of initial evaluations and PET studies.
Page 830
Dosimetry in myeloablative RIT: Rajendran and colleagues review the records of 100 patients who underwent tracer infusion of 131I-tositumomab before radioimmunotherapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma for data supporting an optimal approach to dosimetry.
Page 837
Radioiodine therapy and pregnancy: Garsi and colleagues update a 10-y-old study about pregnancy outcomes and the health of offspring of women exposed to 131I during thyroid carcinoma treatment.
Page 845
Internal dose uncertainties: Stabin presents a systematic analysis of inherent uncertainty in internal dose calculations for radiopharmaceuticals and discusses the level of risk and concern associated with this uncertainty in clinical practice.
Page 853

ON THE COVER
18F-FET PET and 1H MRSI provide insight into metabolic changes related to pathologic processes. Coregistration of data from these techniques with MRI data allows direct correlation of changes in amino acid uptake with changes in membrane, energy, and neuronal metabolism. The 2 metabolic imaging methods have been shown to provide complementary information on glioma metabolism that may be useful in planning and targeting surgery and radiochemotherapy.

See page 724.