Abstract
241637
Introduction: Chemokines and chemokine receptors are indispensable to the development of malignant tumours. As one of the most widely expressed chemokine receptors, Chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 (CXCR4) has been a popular research focus. In most tumours, CXCR4 expression is significantly upregulated. Moreover, integrated nuclide diagnosis and therapy targeting CXCR4 shows great potential. [68Ga]Ga-pentixafor, a radioligand targeting CXCR4, exhibits a strong affinity for CXCR4 both in vivo and in vitro. However, [177Lu]Lu-pentixather, the therapeutic companion of [68Ga]Ga-pentixafor, requires significant refinement to mitigate its pronounced hepatic biodistribution. The objective of this study was to synthesize theranostic molecular tracers with superior CXCR4 targeting functions.
Methods: Tumour cell lines with high CXCR4 expression were screened by western blotting and flow cytometry. Based on the pharmacophore cyclo (-D-Tyr-n-me-d-Orn-L-Arg-L-2-NAL-Gly-) (CPCR4) of pentixafor, 6 tracers were synthesized: [124I]I-1 ([124I]I-CPCR4), [99mTc]Tc-2 ([99mTc]Tc-HYNIC-CPCR4), [124I]I-3 ([124I]I-pentixafor), [18F]AlF-4 ([18F]AlF-NETA-CPCR4), [99mTc]Tc-5 ([99mTc]Tc-MAG3-CPCR4) and [124I]I-6 ([124I]I-pentixafor-Ga). PET/SPECT imaging was performed in animal models to screen the most promising tracers for diagnosis and treatment. At the same time, the [124I]I-6 was also compared with the [68Ga]Ga-pentixafor. Finally, therapeutic nuclide labelling and animal model therapy were performed.
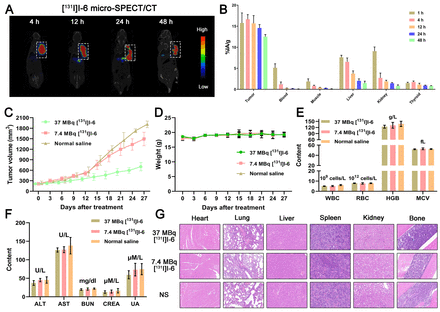
Results: CXCR4 was highly expressed in the Daudi cell line compared to the MM.1S cell line. A total of 6 CXCR4 radionuclide tracers, [124I]I-1, [99mTc]Tc-2, [124I]I-3, [18F]AlF-4, [99mTc]Tc-5 and [124I]I-6, were synthesized, and their radiochemical purities were all higher than 95%. After PET/SPECT imaging, [124I]I-6 had the best target-nontarget ratio, so Compound 6 was selected for therapeutic radionuclide labelling, and the animal model was treated with [131I]I-6. The volume of the tumour site was significantly reduced in the treatment group compared with the control group.
Conclusions: Modification of molecular probes using CPCR4 as pharmacophore requires great care, as changes in the chelating agent or even a single atom can significantly affect the affinity and metabolism of the probes. [124I]I-6 and [131I]I-6 showed excellent affinity for targeting CXCR4, and they showed great potential for the integrated diagnosis and treatment of tumours with high CXCR4 expression.