Abstract
241620
Introduction: Despite significant strides in cancer research, prostate cancer (PrC) remains a formidable and life-threatening condition. Trophoblast cell surface antigen 2 (TROP2), a transmembrane glycoprotein intricately involved in various signal transduction pathways within prostate cancer cells, has been identified as a potential therapeutic target in PrC. Elevated TROP2 expression is closely linked to a poor prognosis in PrC. This study aimed to produce, purify, and label two anti-TROP2 VHH-Fc constructs, along with a monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting TROP2. The objective was to assess the feasibility of visualizing TROP2 levels in PrC, paving the way for potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Methods: From screening the anti-TROP2 nanobody library, we successfully generated two humanized anti-TROP2 VHH-Fc and one anti-TROP2 mAb constructs, whose purity was verified using size exclusion chromatography (SEC)-HPLC and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Following labeling and purification, we assessed the radiolabeling efficiency and stability through radio instant thin-layer chromatography (radio-iTLC) with 0.01 M PBS as the eluting solvent. Subsequently, we conducted immunoSPECT imaging and biodistribution studies using PC3 subcutaneous xenograft models. All mice received intravenous injections of 99mTc-HYNIC-hRS7, 99mTc-HYNIC-B9, and 99mTc-HYNIC-C10 (18.5 - 22.2 MBq per mouse). Static images were captured at 2, 6, 12, 24, and 36 hours post-injection. After the final image acquisition, all mice were euthanized, and their organs and tissues of interest were harvested. Biodistribution results were expressed as the percentage of injected dose per gram of tissue (% ID/cc), with all radioactivity measurements undergoing attenuation correction
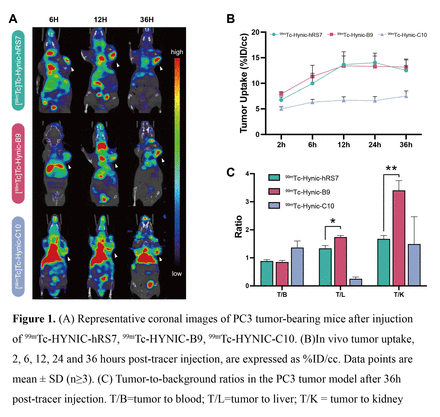
Results: The high purity of B9, C10 and hRS7 was confirmed through SEC-HPLC and SDS-PAGE analyses. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry experiments demonstrated elevated TROP2 levels in both PC3 cells and tumors. SPECT/CT imaging indicated that 99mTc-Hynic-hRS7 uptake in PC3 tumors was approximately 12.5 ± 1.8 %ID/cc, while the values for 99mTc-Hynic-B9 and 99mTc-Hynic-C10 were 13.2 ± 2.4 %ID/cc and 7.5 ± 1.7 %ID/cc, respectively, at 36 hours post-injection. Biodistribution studies corroborated the distribution patterns observed in the SPECT images. Sequential images captured at different time points revealed a progressive increase in the uptake of the three probes at the tumor site. Comparable tumor uptake values were observed for both 99mTc-Hynic-hRS7 and 99mTc-Hynic-B9 up to 36h after injection. Biodistribution studies of 99mTc-Hynic-hRS7 and 99mTc-Hynic-B9 have proved their long tumor retention effect, especially for 99mTc-Hynic-B9, high tumor uptake and low liver (p<0.05) and kidney (p<0.01) uptake make it the optimal compound.
Conclusions: We have successfully developed two TROP2-targeted probes utilizing humanized VHH-Fc, enabling noninvasive assessment of in vivo TROP2 levels in prostate cancer model. In contrast to mAb, VHH-Fc displays comparable affinity and cyclic half-life, coupled with reduced uptake in the liver and kidneys. This characteristic positions VHH-Fc as an optimal choice for radioimmunotherapy when labeled with isotopes like 177Lu or 90Y, offering promising prospects for enhanced therapeutic efficacy.