Visual Abstract
Abstract
Therapy with 90Y-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitors (90Y-FAPIs) was recently introduced as a novel treatment concept for patients with solid tumors. Lesion and organ-at-risk dosimetry is part of assessing treatment efficacy and safety and requires reliable quantification of tissue uptake. As 90Y quantification is limited by the low internal positron–electron pair conversion rate, the increased effective sensitivity of digital silicon photomultiplier-based PET/CT systems might increase quantification accuracy and, consequently, allow for dosimetry in 90Y-FAPI therapy. The aim of this study was to explore the conditions for reliable lesion image quantification in 90Y-FAPI radionuclide therapy using a digital PET/CT system. Methods: Two tumor phantoms were filled with 90Y solution using different sphere activity concentrations and a constant signal-to-background ratio of 40. The minimum detectable activity concentration was determined, and its dependence on acquisition time (15 vs. 30 min per bed position) and smoothing levels (all-pass vs. 5-mm gaussian filter) was investigated. Quantification accuracy was evaluated at various activity concentrations to estimate the minimum quantifiable activity concentration using contour-based and oversized volume-of-interest–based quantification approaches. A ±20% deviation range between image-derived and true activity concentrations was regarded as acceptable. Tumor dosimetry for 3 patients treated with 90Y-FAPI is presented to project the phantom results to clinical scenarios. Results: For a lesion size of 40 mm and a clinical acquisition time of 15 min, both minimum detectable and minimum quantifiable activity concentrations were 0.12 MBq/mL. For lesion sizes of greater than or equal to 30 mm, accurate quantification was feasible for detectable lesions. Only for the smallest 10-mm sphere, the minimum detectable and minimum quantifiable activity concentrations differ substantially (0.43 vs. 1.97 MBq/mL). No notable differences between the 2 quantification approaches were observed. For the investigated tumors, absorbed dose estimates with reliable accuracy were achievable. Conclusion: For lesion sizes and activity concentrations that are expected to be observed in patients treated with 90Y-FAPI, quantification with reasonable accuracy is possible. Further dosimetry studies are needed to thoroughly investigate the efficacy and safety of 90Y-FAPI therapy.
The high-energy β-particle emitter 90Y is a radionuclide that is used in oncologic radionuclide therapy regimens. Typical applications include local radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma by selective internal radiation therapy (1) or systemic therapies using, for example, somatostatin receptor agonists like 90Y-DOTATATE/DOTATOC to target neuroendocrine tumors after intravenous injection (2). Recently, systemic treatments of sarcoma or pancreatic cancer patients using 90Y-labeled fibroblast activation protein (FAP) inhibitors (90Y-FAPIs) were introduced (3,4). The target molecule, fibroblast activation protein α, is a cell surface dipeptidyl peptidase expressed by cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment of various solid tumors as well as cancer cells such as sarcoma and mesothelioma (5).
Intratherapeutic 90Y bremsstrahlung whole-body scintigraphy or SPECT imaging is established and well tolerated by patients for rapidly verifying tracer accumulation in the tumor tissue and for investigating tracer biodistribution (6). However, these imaging modalities do not allow reliable quantification of 90Y activity concentrations, which is mandatory for intratherapeutic lesion dosimetry in systemic radionuclide therapy (7). Limiting factors are, for example, an inaccurate compensation of scattered and septal penetrating photons of the continuous bremsstrahlung energy spectrum and the difficulty of choosing an appropriate energy window, as no discrete γ-photons are emitted (7,8). In 90Y-FAPI therapy, lesion dosimetry is required for dose-response investigations and can be part of the decision-making process regarding the application of further therapeutic cycles.
As an alternative to bremsstrahlung imaging, 90Y PET can be performed (9) to provide higher visual image quality and higher detectability for small lesions (6,8). Moreover, the possibility of reliable 90Y PET quantification for selective internal radiation therapy was demonstrated (10). However, tumor activity concentrations in selective internal radiation therapy are typically high (>1 MBq/mL) (11), whereas in systemic radionuclide therapies, considerably lower activity concentrations are accumulated by the tumor tissue (3). As 90Y PET imaging is limited by poor counting statistics due to internal positron–electron pair conversion occurring in only 0.00326% of pairs per decay (11), quantification of low activity concentrations is extremely challenging (12).
The recently introduced digital silicon photomultiplier-based PET/CT systems offer higher effective sensitivity and higher spatial and coincidence timing resolutions than previous-generation systems. Therefore, image quality and lesion detectability are improved, particularly for small lesions with low tracer uptake (13–17). The improvements were described for different radionuclides, including 18F (positron branching ratio, 97%) and 68Ga (positron branching ratio, 89%), and for the nonstandard tracer 124I (23%). Recently, first applications of digital 90Y PET in the context of selective internal radiation therapy were described (12,18) but—to our knowledge—no performance evaluation for systemic radionuclide therapy has been performed yet.
The aim of this study was to explore the conditions for reliable lesion image quantification in 90Y-FAPI radionuclide therapy using a digital PET/CT system.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Design
The study consisted of 2 parts: a phantom study and a clinical case study. A National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) tumor phantom and an anthropomorphic abdominal tumor phantom were scanned under different conditions to estimate the size-dependent minimum detectable activity concentration (MDAC), minimum quantifiable activity concentration (MQAC), and quantification accuracy. Two approaches for partial-volume effect correction were compared. Additionally, tumor dosimetry for 3 patients treated with 90Y-FAPI was performed and evaluated, considering the results of the phantom data. A condensed version of the methods used is given in this article; full experimental details are presented as supplemental materials (supplemental materials are available at http://jnm.snmjournals.org).
Simple Approaches to Correct for Partial-Volume Effects
In clinical tumor dosimetry, the mean imaged activity concentration within the tumor boundary is commonly used to derive the (mean) tumor absorbed (radiation) dose. When the mean activity concentration is used, a partial-volume effect correction is necessary unless the objects are extremely large, that is, an equivalent sphere diameter of greater than or equal to 47 times the PET spatial resolution (19). Two simple approaches were applied in this study to correct for this effect. In the first, the contour-based approach, measured sphere recovery coefficient (RC) values were used to correct the mean imaged activity concentration within the lesion boundary. RC values were derived from the NEMA tumor phantom. The second approach, the oversized volume-of-interest (VOI)–based approach, included the total activity within the lesion volume using an oversized VOI, whose borders had an approximate distance of 1 time the PET spatial resolution of the actual geometric (CT-derived) boundary of the lesion. It was assumed that this oversized VOI contained the main activity to compensate for partial-volume effects; however, to compensate for a contribution from background activity, a background subtraction was performed as previously described (20).
Phantoms
Setup and Preparation
The NEMA tumor phantom is a torso-shaped phantom containing 6 spheres (with diameters of 9.7, 12.6, 17.4, 22.2, 27.7, and 37.0 mm). The anthropomorphic abdominal tumor phantom (Abdo-Man) (21) contains a refillable liver insert, in which 4 spheres (diameters of 10.0, 20.0, 30.0, and 40.0 mm) are attached. It was selected from the phantoms available at our institution (University Hospital Essen) to resemble the human body scattering geometry more realistically than the NEMA tumor phantom. Moreover, an investigation of quantification accuracy with the NEMA phantom would have been biased for the contour-based method, as the RC values were determined using images of the same phantom.
On the basis of clinical data, spheric inserts and the cavity were filled with 90Y solution at a representative initial sphere activity concentration of about 3.3 MBq/mL and a signal-to-background ratio of about 40. The initial activity concentration was determined as the mean of measurements using 3 different calibrated vial geometries in 2 different dose calibrators; the maximum error of the initial activity concentration was estimated to be ±7% at the 95% confidence level (Supplemental Table 1). Activity concentrations at the PET start time were 3.36, 1.96, 1.22, 0.73, 0.34, 0.20, 0.12, and 0.05 MBq/mL for the NEMA tumor phantom and 3.33, 1.97, 1.23, 0.73, 0.34, 0.20, 0.12, and 0.06 MBq/mL for the anthropomorphic tumor phantom.
PET Acquisition and Image Reconstruction
Phantom PET data were acquired using a single bed position on a digital Biograph Vision 600 PET/CT scanner (Siemens Healthineers; detailed specifications are given in Supplemental Table 2), which exhibits a time-of-flight resolution of 210 ps (22). Initially, the NEMA tumor phantom was scanned for 6 h to determine RC values at high counting statistics. Thereafter, PET data for both phantoms were acquired for 30 min and used to reconstruct 30- and 15-min acquisition time PET images.
Images were reconstructed with the time-of-flight option and with point spread function modeling as previously recommended for quantitative 90Y PET imaging on the Biograph Vision scanner (12). Two postreconstruction smoothing filter levels (all-pass and 5-mm gaussian filters) were applied. The images had a voxel size of 3.30 × 3.30 × 3.00 mm, and the measured system spatial resolution (average full width at half maximum) (23) was 6.0 mm for a 5-mm gaussian smoothing filter.
Patients
Patient Characteristics
Retrospective analysis of clinical data was approved by the local ethics committee (permit no. 20-9558-BO). Datasets for 3 patients who had progressive, advanced-stage solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) and received 90Y-FAPI-46 therapy (first cycle) under compassionate access after clinical indication were included. The decision about radionuclide treatment was made by a multidisciplinary tumor board. All patients had either previously shown progressive disease during established treatment options or were not eligible for other established treatment concepts. The administered therapeutic activities were 8.90 GBq (patient 1), 3.82 GBq (patient 2), and 3.67 GBq (patient 3).
PET Acquisition and Image Reconstruction
PET/CT examinations were scheduled as described in a previous study (3). Because of symptomatic patients and logistical reasons, serial PET/CT acquisitions were performed at slightly different time points: 17, 22, and 41 h after injection for patient 1; 2, 20, and 43 h after injection for patient 2; and 1, 4, and 20 h after injection for patient 3. PET data acquisition and image reconstruction were performed as described for phantoms (15-min acquisition time per bed position and 5-mm gaussian smoothing filter).
Phantom Analysis
MDAC
The images of the NEMA tumor phantom at various activity concentrations were used to determine the MDAC as previously described (13,24). In brief, the visual detectability of each sphere was determined in a human observer study. Next, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of each sphere was determined to estimate the SNR threshold indicating detectability. Finally, the MDAC was calculated for each sphere. The MDAC was defined as the activity concentration at the threshold SNR.
Quantification Accuracy Evaluation
To evaluate the lesion quantification accuracy, the activity concentration ratio of PET-imaged measurements to (decay-corrected) dose calibrator–derived measurements was investigated. A ±20% deviation range of the activity concentration ratio was regarded as acceptable considering the uncertainty for the 90Y activity concentration dose calibrator measurement, the 18F PET cross-calibration measurement (25), and the frequency of the positron–electron pair conversion (26–29).
MQAC
The results of the quantification accuracy evaluations were used to estimate the MQAC, that is, the minimum activity concentration for which the quantification appears to be reliable. In its derivation, the values for the quantification accuracy should lie within the ±20% deviation range.
Patient Analysis
In the patient analysis, key quantities related to the estimation of the tumor absorbed dose were derived. The procedure used was previously described (3). In brief, the tumor volumes were estimated by manual segmentation (VOI technique) using the respective CT images, and the VOIs were used to determine the tumor uptake values at 3 imaging time points. Mean tumor activity concentrations were determined using both the contour-based approach and the oversized VOI–based approach. The resulting uptake curves were parameterized by fitting a monoexponential function to the measured uptake values to determine the effective half-lives. The time-integrated activity coefficients (residence times) were determined and used to estimate the tumor absorbed doses with the sphere model of OLINDA/EXM (30). A logarithmic approach was applied for interpolation between tumor absorbed doses in the OLINDA tables.
Software/Statistics
PET image analysis and VOI segmentation were performed using PMOD 4.202 (PMOD Technologies); MATLAB R2021a (The MathWorks) was used for data handling and computations. The tumor absorbed dose was calculated using OLINDA/EXM 2.2 software (Hermes Medical Solutions AB). Graphics were created using BioRender.com (BioRender; www.BioRender.com).
RESULTS
Recovery Coefficients
Fitting parameters for calculating measured and fitted RC values are listed in Supplemental Table 3. The agreement between fitted and measured RC values was high (maximum percentage deviation of –6%), indicating a small contribution of the fitting process to the total error of the quantification approaches.
MDAC
Figure 1 shows exemplary PET images for the NEMA tumor phantom. The human observer study revealed an SNR threshold of greater than or equal to 6 for distinguishing between spheres that were not detected and spheres that were detected (Supplemental Fig. 1). The MDAC for each sphere size is shown in Table 1. The SNR is presented as a function of the activity concentration for all acquisition conditions in Supplemental Figure 2. The 5-mm smoothed images provided improved detectability for smaller spheres, and the MDAC was smaller by a mean factor of 0.54 in comparison with the results for images without gaussian smoothing. For a 30-min acquisition time, the MDAC was reduced by a factor of 0.53 compared with that for a 15-min acquisition time.
PET images of NEMA tumor phantom showing different investigated emission times and gaussian filter levels at highest sphere activity concentration of 3.36 MBq/mL (A) and different investigated sphere activity concentrations for 15-min acquisition time and 5-mm gaussian smoothing level (B).
Estimated MDAC for Investigated Sphere Diameters, Acquisition Time Durations, and Smoothing Levels
As the detectability was higher for the 5-mm gaussian filter, the following evaluation of the anthropomorphic phantom and patient examples was restricted to this filter level. Moreover, an acquisition time of 30 min per bed position is excessively long and not feasible for patients who are in pain and undergoing 90Y-FAPI-46 therapy (typically, a PET scan comprises at least 2 bed positions); therefore, only an acquisition time of 15 min (per bed position) was further evaluated.
Figure 2 shows exemplary PET maximum-intensity projections (MIPs) of the anthropomorphic abdominal tumor phantom. Only detectable spheres were included in the quantification accuracy analysis (detectable was defined as an activity concentration greater than or equal to the size-dependent MDAC; the MDAC for the 9.7-, 17.4-, 27.7-, and 37.0-mm spheres in the NEMA tumor phantom were used for the 10.0-, 20.0-, 30.0-, and 40.0-mm spheres in the anthropomorphic abdominal tumor phantom).
PET MIP images of anthropomorphic abdominal tumor phantom at 4 different activity concentration levels. Images were reconstructed using 15-min acquisition data and smoothed with 5-mm gaussian filter. In the MIP images, the largest sphere is marginally discernible at 0.12 MBq/mL.
Quantification accuracy results from the contour-based and oversized VOI–based quantification approaches are shown in Figure 3. For the 40- and 30-mm spheres, accurate quantification was feasible for detectable lesions using both approaches. The oversized VOI–based approach revealed slightly more accurate results for the 30-mm sphere. For the 20-mm sphere and activity concentrations of less than or equal to 1.23 MBq/mL, quantification accuracy for the contour-based method was slightly below the –20% deviation threshold, whereas accurate quantification was feasible down to activity concentrations of greater than or equal to 0.34 MBq/mL using the oversized VOI–based approach. For the smallest (10-mm-diameter) sphere, quantification accuracy was limited for activity concentrations of less than or equal to 1.23 MBq/mL, and the contour-based approach revealed slightly more accurate results. In general, a trend toward an underestimation of the activity concentration was observed for low activity concentrations.
Contour-based and oversized VOI–based quantification accuracy using anthropomorphic tumor phantom. Dashed horizontal lines indicate ±20% error margins. Missing bars correspond to spheres regarded as “not detected” and as such not considered for quantification accuracy evaluation. Only PET images with 5-mm gaussian filter and acquisition time of 15 min (per bed position) were analyzed. AC = activity concentration.
MQAC
The MQAC ranged from 0.12 MBq/mL for the 40-mm sphere to 1.97 MBq/mL for the 10-mm sphere. Detailed results are presented in Table 2.
Estimated MQAC of Reliability at Lesion Sizes Derived From Images Reconstructed with 15-min Acquisition Time Data and Smoothed with 5-mm Gaussian Filter
Patient Tumor Dosimetry
Lesion dosimetry was performed for 3 tumor sites in 3 patients with thoracic/pleural SFT. In patient 1, a left paracardial supradiaphragmatic SFT was evaluated; in patient 2, a right lateral SFT of the third thoracic vertebra was evaluated; and in patient 3, a left lateral SFT of the aortic arch was evaluated (Figs. 4–6). Almost all activity concentration measurements were considered reliable (Fig. 7). The activity concentration at the last measurement in patient 1 was below the MQAC for the largest sphere investigated in the phantom study (sphere diameter of 40 mm), which is why we did not use the data point for the lesion dosimetry estimation.
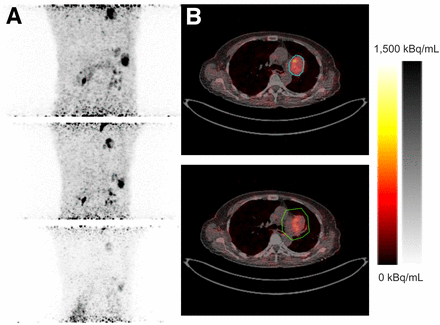
PET/CT imaging and lesion delineation for patient 1. 90Y-FAPI-46 PET MIP images (A) and axial PET/CT images (B) show contour-based VOI (blue) and oversized VOI (green). Only first 2 PET data points were considered for tumor absorbed dose estimation.
PET/CT imaging and lesion delineation for patient 2. 90Y-FAPI-46 PET MIP images (A) and axial PET/CT images (B) show contour-based VOI (blue) and oversized VOI (green).
PET/CT imaging and lesion delineation for patient 3. 90Y-FAPI-46 PET MIP images (A) and axial PET/CT images (B) show contour-based VOI (blue) and oversized VOI (green).
Tumor activity concentration (AC) derived from either contour-based or oversized VOI–based approach as function of time after administration (3 time points). Values within parentheses are respective equivalent sphere diameters. ACs above horizontal dashed lines indicate reliable quantification based on Figure 3. Asterisk indicates value that appears to be “unreliable” in terms of quantification (see text for details).
The relevant key dosimetry data derived from both the oversized VOI–based and the contour-based quantification approaches are listed in Table 3. The tumor absorbed dose estimation ranged from 0.6 to 12.0 Gy/GBq. Overall good agreement (absolute percentage deviation of <20%) of the relevant quantities was observed between the 2 approaches, except for the effective half-life of the tumor in patient 1 (8.4 vs. 12.2 h).
Key Dosimetry Quantities for Estimating Tumor AD per Administered Activity Using Contour-Based and Oversized VOI–Based Approaches
DISCUSSION
FAP-targeted radionuclide therapy is emerging for patients with solid tumors and, recently, several case reports and case series using different ligands and radionuclides were published (31–33). For example, 90Y-FAPI therapy was described for the treatment of sarcoma and pancreatic cancer patients (3,4) as well as a patient with both breast and colorectal cancers (34). Safety and efficacy studies, including dosimetry, have been reported for 177Lu-labeled FAP–targeted radionuclide therapy (32,35). Given that 90Y-based dosimetry for systemic radioligand therapy is not as well established and documented as 177Lu-based dosimetry, it is even more important to establish the basis for accurate radionuclide quantification. Doing so will have relevance in pharmacovigilance processes of authorization (such as the evaluation of safety) in the form of dosimetry for organs at risk and efficacy in the form of tumor dosimetry for investigating the dose effects of novel 90Y radioligand therapy agents.
In the present study, we applied a heuristic approach for reliable lesion quantification in 90Y-FAPI therapy. To the best of our knowledge, no reports on reliable PET-derived 90Y tumor quantification for activity concentration ranges as they appear in systemic radionuclide therapies have yet been published. The phantom evaluation (Figs. 1 and 2) showed that for detectable lesions greater than or equal to 30 mm in diameter, reliable quantification is feasible (Fig. 3). For the 20-mm-diameter sphere, the difference between the MQAC and the MDAC was small (0.34 vs. 0.16 MBq/mL). Only for the smallest sphere (10-mm diameter) was the MQAC notably higher than the MDAC (1.97 vs. 0.43 MBq/mL). Possible explanations are the low absolute amount of 90Y activity resulting in poor counting statistics and the proximity to the 40-mm sphere (also, see a comparison of MDACs between NEMA and anthropomorphic phantoms in the supplemental materials and Supplemental Table 4).
In current clinical scenarios, patients undergoing 90Y-FAPI-46 therapy will most likely exhibit larger tumor masses, as this therapy is offered in end-stage diseases when established therapy options have already been exhausted (3,4). In the evaluated patients (Figs. 4–7), the accumulated tumor activity concentration was, except for 1 data point, larger than the size-dependent MQAC of 0.12 MBq/mL (40-mm-diameter lesion). We therefore assume that reliable quantification in the context of intratherapeutic tumor dosimetry is feasible in 90Y-FAPI-46 therapy using a digital PET/CT system. The tumor absorbed dose estimation ranged from 0.6 to 12.0 Gy/GBq (Table 3).
As cancer-associated fibroblasts were described to be nonuniformly distributed in the tumor microenvironment (36), 90Y-FAPI accumulation will most likely follow that pattern and lead to nonuniform tumor uptake in PET imaging. Because the high β-particle energy of 90Y leads to a high particle range, tumor cells surrounding FAP-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts will be targets of crossfire and bystander radiation (37). Therefore, 90Y—which deposits its energy at a distance of up to 1 cm—may be more suitable for FAPI radionuclide therapy than 177Lu—with an energy deposition in close proximity to the source (38). However, the consequences of nonuniform FAPI uptake for the quantification of accumulated activity, dosimetry, and the dose response remain unclear. In the present study, quantification approaches were projected without adjustments from the homogeneous conditions of the phantom study to the patient images. Therefore, accumulated activity was measured as the mean activity concentration. This approach might be appropriate given a high level of influence of crossfire and bystander effects, which might lead to a homogenization of the radiation dose. Voxel-based dosimetry might be an alternative to take into account a nonuniform activity distribution (39); however, its clinical relevance might be limited by the low accumulated activity concentrations in systemic 90Y radionuclide therapy.
Future evaluations of clinical data will be necessary to investigate possible effects on determined tumor doses and, especially, dose-response effects to select the optimal quantification approach. With increasing application of 90Y FAPI therapy, sufficient data will probably be available for a systematic evaluation. At the moment, the number of investigated patients with sufficient follow-up data is limited. In the present study, we investigated the quantification accuracy of a current-generation PET scanner as a basis for future clinical evaluations.
The comparison of 15- and 30-min acquisition times per bed position revealed a lower MDAC for the 30-min acquisition time, by a factor of approximately 2 (Table 1). Thus, an approximate linear correlation between MDAC and acquisition time was observed. This finding is in line with the results of a previous study using a different radionuclide (13). Typically, PET scans in patients receiving 90Y-based therapy are performed using at least 2 bed positions (3). Therefore, in most patients, an extension of the acquisition time will most likely not be tolerable. Moreover, detectability was improved when a 5-mm gaussian filter was applied (Table 1). In a systematic comparison of previous-generation Siemens PET/CT systems for quantitative 90Y imaging, the use of a gaussian filter was left to the user’s decision (40). We therefore propose an acquisition time of 15 min for clinical imaging protocols and the application of a 5-mm gaussian filter.
Both evaluated quantification methods exhibit limitations and advantages. On the one hand, the contour-based approach is more reproducible, but it has no background activity concentration correction. On the other hand, although the oversized VOI–based approach will represent the lesion activity surrounded by a uniform and low activity concentration background, accounting for a nonuniform background might be challenging, making the quantification prone to error. Regarding quantification accuracy in phantom data and estimated activity concentrations in patient data, both methods yielded comparable results (Figs. 3 and 7), probably because of a low and visually uniform background. Larger differences might be possible for tumor lesions close to a region with high physiologic tracer accumulation, such as the kidney.
Only a few previous studies investigating 90Y PET imaging in the context of systemic radionuclide therapy were published, and none of these used a digital PET system. Fabbri et al. (41) identified an MDAC of 0.20 MBq/mL for the 3 largest spheres of the NEMA tumor phantom using a previous-generation time-of-flight–capable PET scanner. In that study, 30-min acquisitions with no background activity were reconstructed with 3-dimensional ordered-subset expectation maximization using 2 iterations and 4 subsets and a 5-mm gaussian filter. In the present study, for a 30-min acquisition time, the MDAC was smaller (0.06–0.09 MBq/mL) (Table 1). The improvement is explained by the improved time-of-flight resolution of the digital PET system and is comparable to the improvement that we observed in a direct comparison of 2 PET/CT systems for 124I (13). Of note, Fabbri et al. (41) did not investigate quantification accuracy. Walrand et al. (42) also investigated previous-generation PET systems (42); they predicted a reliable estimation of the mean absorbed kidney dose after 90Y-DOTATOC therapy using a kidney phantom filled with an activity concentration of about 0.33 MBq/mL—substantially larger than the MQAC for the largest sphere in the present study (0.12 MBq/mL). Moreover, the investigated kidney cortex had a volume of 107 mL—considerably larger than the largest sphere in the present study (sphere volume of 33.5 mL).
Future improvements might be possible through the application of total-body PET/CT scanners (43), which cover an extended field of view and allow complete acquisition of all necessary PET data in a patient scan using a single bed position. Moreover, increased sensitivity may allow for shorter acquisition times (44) or, alternatively, improved accuracy of detection and quantification of lesions at lower activity concentrations.
CONCLUSION
For 90Y-treated-lesions with a diameter of greater than or equal to 40 mm—typical in patients receiving FAPI radionuclide therapy—reliable quantification was possible for activity concentrations of at least 0.12 MBq/mL using a digital PET system. For lesions with a diameter of greater than or equal to 30 mm, the minimum detectable activity and minimum quantifiable activity were in good agreement, suggesting that dosimetry can be performed for detectable lesions. Further dosimetry studies are needed to thoroughly investigate the efficacy and safety of novel 90Y-FAPI radionuclide therapies.
DISCLOSURE
This work was supported by the Universitätsmedizin Essen Clinician Scientist Academy (UMEA)/German Research Foundation (DFG [Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft]) under grant FU356/12-1 to David Kersting and Rainer Hamacher and by a Universitätsmedizin Essen Clinician Scientist Academy (UMEA) grant to Robert Seifert. David Kersting reports a research grant from Pfizer outside the submitted work. Walter Jentzen received research funding from Siemens Healthineers. Maurizio Conti is a full-time employee of Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc. Ken Herrmann reports personal fees from Bayer, personal fees and other fees from Sofie Biosciences, personal fees from SIRTEX, nonfinancial support from ABX, personal fees from Adacap, personal fees from Curium, personal fees from Endocyte, grants and personal fees from BTG, personal fees from IPSEN, personal fees from Siemens Healthineers, personal fees from GE Healthcare, personal fees from Amgen, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from ymabs, personal fees from Aktis Oncology, personal fees from Theragnostics, and personal fees from Pharma15 outside the submitted work. Christoph Rischpler reports a research grant from Pfizer, consultancy for Adacap and Pfizer, and speaker honoraria from Adacap, Alnylam, BTG, GE Healthcare, Pfizer, and Siemens Healthineers outside the submitted work. Rainer Hamacher received travel grants from Lilly, Novartis, and PharmaMar as well as fees from Lilly outside the submitted work. Wolfgang P. Fendler reports fees from Sofie Bioscience (research funding), Janssen (consultant, speakers bureau), Calyx (consultant), Bayer (speakers bureau), and Parexel (image review) outside the submitted work. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
KEY POINTS
QUESTION: Does digital PET allow reliable quantification for lesion dosimetry in 90Y-FAPI radionuclide therapy?
PERTINENT FINDINGS: For lesion sizes and activity concentrations that are expected to be observed in patients treated with 90Y-FAPI, quantification with reasonable accuracy is possible.
IMPLICATIONS FOR PATIENT CARE: Reliable lesion dosimetry in 90Y-FAPI radionuclide therapy is mandatory for dose-response evaluations and for decisions about treatment continuation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Ulrich Graf (Sirtex Medical Europe GMBH) for providing the anthropomorphic abdominal tumor phantom (Abdo-Man).
Footnotes
Published online Aug. 18, 2022.
- © 2023 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
REFERENCES
- Received for publication April 30, 2022.
- Revision received August 13, 2022.