Abstract
3007
Introduction: Deep learning techniques can be used to extract specific regions and structures in an image. The purpose of this study was to apply deep learning techniques to fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) images to detect abnormal and physiologic uptake on the images automatically and to evaluate the detection accuracy and coverage rate for abnormal findings.
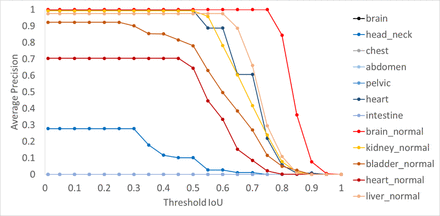
Methods: Data from patients who underwent an FDG-PET examination were used in this retrospective study. The abnormal and physiological uptake of 3,198 maximum intensity projection (MIP) images (491 cases) of a whole body FDG-PET examination were investigated for detecting the region as bounding boxes. The region of interest was defined as both physiological and abnormal uptake on MIP images used as supervised learning. The dataset was divided into 3,158 (451 cases) MIP images for learning and 40 (40 cases) MIP images for evaluation using the automatic detection method. YOLO v2, one of a deep learning model, was used for object detection. Evaluation of the detection model was performed with intersection over union (IoU) and average precision (AP), which are representative evaluation indices for object detection using deep learning. Additionally, a combination method with deep learning and software programming techniques for detecting abnormal uptakes was applied. This method used two fusion method techniques: 1) subtraction of physiological uptake from MIP images using information from the bounding box for object detection, and 2) a color map applied as a fusion image with software programming using subtracted and original FDG-PET images. A comparison of abnormal findings between the color map using the combination method and a review of the images by experienced radiologists found the combination method to be quite accurate. Results and Discussion: Each AP of the automatic detection method was shown in below figure. When the threshold of IoU was set to 0.5 for the automatic detection method, APs of physiological uptake of the brain, liver, kidney, bladder, and heart were 1.00, 0.975, 0.950, 0.780, and 0.645, respectively. The AP of abnormal heart uptake was relatively higher than other abnormal areas. There was some room for improvement in the accuracy of abnormal uptake in all areas except the heart. For the combination method, the coverage rate was 87.8% for detecting abnormal uptake with a color map. This method could have a complementary role in detecting abnormal uptake, as this method had almost perfect detection for physiological uptake.
Conclusions: The automatic detection method was able to detect abnormal uptake of the heart and physiological uptake with high accuracy. Furthermore, the combination the fusion technique with the automatic detection method correlates well with the detection of abnormal uptakes noted by radiologists. The combination method was useful for detecting abnormal uptake.