Abstract
1489
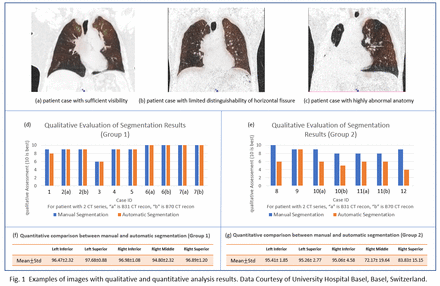
Objectives: SPECT/CT Lung Ventilation/Perfusion (LungVQ) images with lung lobe segmentation provide the ability to analyze lung function at lung lobe level, where the segmentation and image analysis used to be a very time-consuming manual process. We designed and developed a fully automatic research prototype LungVQ analysis workflow using fast automatic thoracic landmark detection [1] and deep learning-based segmentation [2] trained for lung fissure delineation on over 5000 chest CT image volumes. The objective of this study is to evaluate the performance of the proposed workflow on patient data with abnormal anatomy or images with limited lung fissure visibility from lower dose CT acquisitions. Methods: A total of 15 anonymized lung perfusion SPECT/CT patient scans, acquired using Symbia Intevo 16 SPECT/CT scanner (Siemens Healthineers, Hoffman Estates, IL, United States) were used for evaluation. The pitch factor of CT acquisition was 0.8 for 12 patients and 1.5 for 3 patients. Each patient dataset included at least one set of SPECT perfusion image and CT series reconstructed with B70 kernel at 1.5mm slice thickness. Five patient scans had an additional CT series reconstructed with B31 or equivalent soft kernel at 1.0mm slice thickness. These total 20 cases were used for lung lobe segmentation evaluation. For comparison, each dataset was manually segmented by an annotation specialist and reviewed by a board-certified nuclear medicine physician. Quantitative evaluation was performed by calculating the Dice score between manual and automatic segmentation results. Results: The automatic LungVQ analysis workflow completed successfully for all patient datasets. The total processing time for each patient was less than 30 seconds (HP ZBook 15 G3, Intel Core i7-6820HQ, 16GB RAM), which is significantly shorter than the manual lung fissure identification (>1 hour). Of the 15 patients, 7 patients had sufficient delineation of lung fissure, including 3 patients with two CT series, these 10 cases composed “group 1”; 5 patients could not be reliably performed a manual delineation of interlobar borders by the physician or had limited visibility of the horizontal fissure, including 2 patients with two CT series, these 7 cases composed “group 2” and 3 patients had highly abnormal anatomy or unclear anatomy at least unilaterally. Examples of patient images are shown in Fig. 1 (a), (b) and (c). Qualitatively, for the 10 cases in group 1, as shown in Fig.1 (d), both manual and automatic segmentation agree well; for the 7 cases in group 2, as shown in Fig. 1 (e), quantification differed due to the limited lung fissure visibility, which posed challenges for both manual and automated approaches. However, none of the segmentation discrepancies would cause misdiagnosis after review by a physician. Quantitatively, for group 1, the mean and standard deviation of Dice scores are 96.47±2.32 for left inferior lobe, 97.68±0.88 for left superior lobe, 96.98±1.08 for right inferior lobe, 94.80±2.32 for right middle lobe, 96.89±1.20 for right superior lobe. For group 2, the mean and standard deviation of Dice scores are 95.41± 1.85 for left inferior lobe, 95.26±2.77 for left superior lobe, 95.06±4.58 for right inferior lobe, 72.17±19.64 for right middle lobe, 83.83±15.15 for right superior lobe. The differences between manual and automatic segmentation increased because of limited lung fissure visibility. The 3 patients with highly abnormal anatomy were excluded from quantitative analysis. Conclusion: The visibility of lung fissures (CT image quality) played a critical role in the accuracy of quantitative analysis in SPECT/CT LungVQ analysis. In some cases of pathological lung anatomy or lack of lung fissure visibility, manual editing of the segmented volume in locations of pathology remains necessary. This evaluation demonstrates that the automatic LungVQ analysis workflow reduces the overall processing time significantly while maintaining similar accuracy as manual lung lobe segmentation.