Abstract
1445
Objectives: Prospectively applying salivary gland dynamic imaging of quantitative evaluation of large dose of 131I treatment, vitamin C and selenium on patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) salivary glands, and then selecting the suitable methods of the salivary glands for the patients.
Methods: The postoperative patients who are part of DTC 50 cases (20 cases of male, 30 cases of female), age (44.10±10.26) are prospectively selected from the first hospital of Shanxi medical university fitting line of the first 131I treatment within period August 2019 to December 2019. Pathological types are papillary carcinoma, therapeutic doses are 100mCi, 47 cases of all are carrying cervical lymph node metastasis, 3 cases are lung metastasis. They are randomly divided into two groups: vitamin C group( 27 cases)—vitamin C and selenium group (23 cases). Patients in the vitamin C group were given orally 131I for 2 hours after treatment with vitamin C tablets (100mg/2h, 600-800mg/d, 3 days). The patients in the vitamin C and selenium group were taken orally (selenium yeast capsule) for 200ug/d one month, And the oral method of vitamin C tablets was the same as before. To evaluate salivary gland function in 50 patients, dynamic salivary gland imaging, static salivary total flow rate and PH measurement, oral dryness questionnaire, serum amylase and whole blood selenium level were performed before and one month after treatment, respectively.
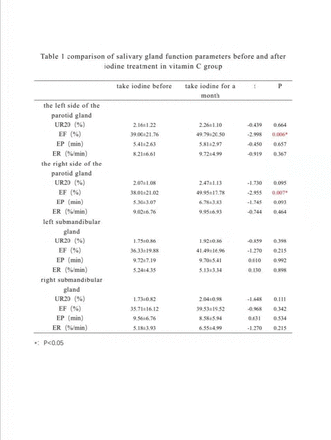
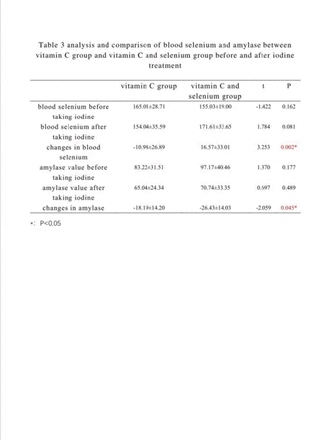
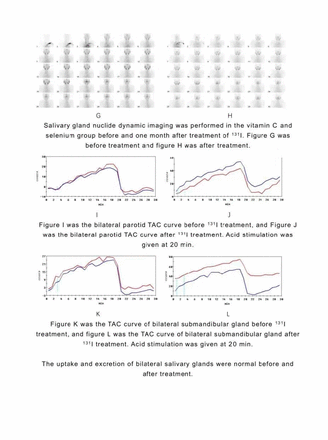
Results: Comparison in Parameters of DTC patients before and after 131I treatment: 1. The salivary glands of dynamic imaging vitamin C group of bilateral parotid excretion fraction (EF) was significantly increased (table 1).Vitamin C and selenium group of the left parotid glands within 20 minutes the maximum uptake ratio (UR20), excretion ratio (ER), EF was significantly increased; The EF and ER of the right parotid gland were much higher than before treatment.UR20, EF and ER in the left submandibular gland were significantly higher than before treatment. ER in the right submandibular gland was obviously higher than before treatment (table 2) (all P <0.05). 2. The blood selenium value in vitamin C group decreased after treatment, while that in vitamin C and selenium group increased after treatment,It suggests statistical difference between the two groups (P<0.05) (table 3). 3. The level of amylase decreased in both groups, and the level of amylase decreased in vitamin C and selenium group was dramatically higher than the one in vitamin C group (P<0.05) (table 3).
Conclusions: Vitamin C can improve the secretion function of parotid gland in DTC patients when treated with large dose of 131I. Vitamin C combined with selenium has a better protective effect on the uptake and secretion of parotid and submandibular glands. The increase of blood selenium level may have some effects on reducing the damage of radioactive salivary glands in DTC patients.