Updated SSR imaging guideline: Balon offers background and perspective on the revised version of the SNM Practice Guideline for Somatostatin Receptor Scintigraphy that appears this month in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology.Page 1838
Toward clinical Raman spectroscopy: Zavaleta and colleagues provide an overview of the development and applications of this novel optical technology in molecular imaging, from in vitro studies to preclinical, clinical, and future capabilities.Page 1839
Reassessing pediatric imaging: Zanzonico offers perspective on elements involved in balancing the benefits of advanced imaging techniques against risks of radiation exposure in young patients and previews a related article in this issue of JNM.Page 1845
Plaque imaging with 11C-acetate: Derlin and colleagues examine the distribution and topographic relationship of 11C-acetate uptake and vascular calcification in major arteries in preparation for PET/CT imaging of fatty acid synthesis in atherosclerotic vessel walls.Page 1848

PET/CT in thyroid cancer: Kauhanen and colleagues compare the abilities of 18F-DOPA and 18F-FDG PET/CT with those of MRI in localization of metastatic disease in recurrent or persistent medullary thyroid cancer.Page 1855
68Ga-DOTATATE vs. 68Ga-DOTATOC: Poeppel and colleagues evaluate the comparative utility of PET lesion detection with these radiolabeled somatostatin analogs in the same group of patients with neuroendocrine tumors.Page 1864
18F-FDG and 18F-FLT PET in lung cancer: Kahraman and colleagues explore the prediction of clinical benefit from first-line erlotinib treatment using different quantitative parameters for both 18F-FDG and 18F-fluorothymidine PET in advanced non–small cell lung cancer.Page 1871
Antibody–antigen relationships for huA33: O'Donoghue and colleagues use PET to analyze the quantitative features of antibody–antigen interactions in tumors and normal tissue after administration of 124I-labeled antitumor antibodies to patients with colorectal cancer.Page 1878

sst2 antagonist vs. agonist binding: Cescato and colleagues assess in vitro binding of the 177Lu-DOTA-Bass somatostatin receptor antagonist and the 177Lu-DOTATATE agonist to a range of sst2-expressing human tumor samples.Page 1886
Arm motion and PET/CT: Lodge and colleagues investigate the mechanisms that underlie arm motion–induced cold artifacts on whole-body PET/CT images and propose a potential solution.Page 1891
18F-FLT PET in MCL: Herrmann and colleagues report on the ability of this in vivo proliferation marker to characterize mantle cell lymphoma and discuss its promise in clinical management.Page 1898
Imaging in sarcoma: Eary and Conrad offer an educational overview of 18F-FDG PET in sarcoma diagnosis and treatment response and highlight new areas of biologically specific PET techniques with potential for outcome stratification.Page 1903
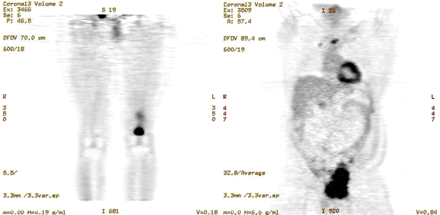
Biograph mMR performance: Delso and colleagues assess the performance of a new integrated whole-body PET/MR scanner during independent and simultaneous acquisition of PET and MR data.Page 1914
Risk and benefit in pediatric imaging: Sgouros and colleagues describe a rigorous and critical approach to balancing the benefits of adequate image quality against radiation risks in children, using an example based in 99mTc-DMSA scanning.Page 1923
Fast 3D dosimetry for 90Y-microspheres: Dieudonné and colleagues develop and evaluate a novel approach to standardized prescribed activity calculation in selective internal radiation therapy and highlight the potential value of 3D treatment planning strategies.Page 1930

Radionuclide therapy in ovarian cancer: Zacchetti and colleagues assess the preclinical specificity of a 131I-labeled human antibody fragment that binds to folate receptors in ovary cancer cells and investigate its therapeutic efficacy in tumor models.Page 1938
PET imaging of glutaminolysis: Lieberman and colleagues report on both in vitro and in vivo animal studies with 18F-(2S,4R)4-fluoroglutamine and detail its potential use as an alternative PET tracer for mapping glutaminolytic tumors.Page 1947

Imaging angiogenesis: Liu and colleagues detail the development of a novel 64Cu-labeled nanoprobe that detects upregulation of natriuretic peptide clearance receptors and offers sensitive detection with PET during development of angiogenesis in a mouse model.Page 1956

PET and gastric aromatase: Ozawa and colleagues use 11C-vorozole PET to investigate gastric aromatase expression, which has been implicated in pathophysiologic states in various diseases via estrogen expression.Page 1964
Bombesin antagonist for prostate imaging: Abiraj and colleagues detail the development of clinically translatable bombesin antagonist–based radioligands for SPECT and PET of gastrin-releasing peptide receptor–positive tumors.Page 1970
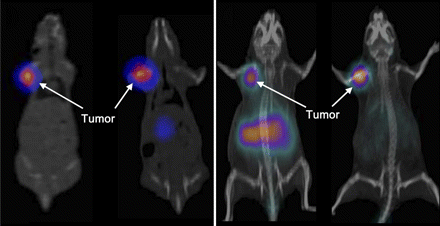
Cell-penetrating integrin α2β1 probe: Huang and colleagues report on studies designed to improve the targeting efficacy of the DGEA peptide for near-infrared fluorescence and microPET imaging of integrin α2β1 expression in prostate cancers.Page 1979

Semiquantitative stroke imaging in rats: Ceulemans and colleagues validate the use of 99mTc-HMPAO micro-SPECT/CT for semiquantification of infarct size after experimental stroke in rats.Page 1987
Development, sex, and cardiac risk: Guiducci and colleagues explore in minipigs the lifetime influence of innate factors, including mother's metabolism and sex of offspring, on cardiometabolic risk, including organ-specific insulin resistance, subclinical cardiac dysfunction, and DNA oxidative damage.Page 1993
89Zr-fresolimumab PET: Oude Munnink and colleagues use radiolabeled fresolimumab, which neutralizes all mammalian forms of transforming growth factor-β, to analyze the growth factor's expression, antibody tumor uptake, and organ distribution in hamster models of human breast cancer.Page 2001

Advances in Cerenkov techniques: Xu and colleagues review the physics, cross-validations, and wide range of potential applications of Cerenkov luminescence imaging and highlight recent technical advances.Page 2009

ON THE COVER

The recently released Biograph mMR is the first commercially available integrated whole-body PET/MR scanner. It has been shown to compare favorably with other state-of-the-art PET/CT and PET/MR scanners, indicating that the integration of the PET detectors in the MR scanner and their operation within the magnetic field do not have a perceptible impact on overall performance.See page 1921.
- © 2011 by Society of Nuclear Medicine