Accelerating Development of Novel Molecular Imaging Probes: Manning and colleagues describe the role of alternative technologies, such as high-throughput, small-molecule screening, as vehicles to accelerate the discovery phase of imaging probe development.
Page 1401
New AML therapeutics: Weisburg reviews immunologic and targeting approaches in multidrug resistant acute myeloid leukemia and previews an article in this issue of JNM on a novel strategy using monoclonal antibody–mediated radioisotope delivery to cells.
Page 1405
PET/CT and pancreatic cancer staging: Strobel and colleagues evaluate the utility of contrast-enhanced 18F-FDG PET/CT in assessing the resectability of pancreatic cancer and compare these results with those from PET alone and unenhanced PET/CT.
Page 1408
Arachidonic acid imaging in neuroinflammation: Esposito and colleagues use PET to measure levels of arachidonic acid in the brains of individuals with Alzheimer's disease and discuss the potential of this technique for evaluation of neurodegenerative disease.
Page 1414

PET/CT and dental artifacts: Baek and colleagues investigate the clinical usefulness of PET/CT or CT-attenuated PET in the evaluation of patients with oral cavity cancer in whom dental artifacts distort conventional CT or MR images.
Page 1422

Bilateral hilar foci in PET: Karam and colleagues describe characteristic features of bilateral hilar 18F-FDG–avid foci in PET associated with benign and malignant causes.
Page 1429

18F-FLT PET and pancreatic lesions: Herrmann and colleagues report on a prospective study evaluating the utility of PET with this in vivo proliferation marker as a diagnostic adjunct to conventional imaging in differentiating cancer from benign lesions.
Page 1437

131I effective half-life and dosimetry: Remy and colleagues explore the parameters that influence the half-life of 131I and absorbed doses by extrathyroidal organs in the treatment of thyroid cancer.
Page 1445
PET in recurrent colorectal cancer: Scott and colleagues report on the results of a multicenter prospective study examining the effect of PET in changing management and subsequent disease-free survival in patients with proven or suspected colorectal cancer recurrence.
Page 1451
Sympathetic innervation in CAD: Fricke and colleagues use PET to investigate the long-term effect of reduced coronary flow reserve on myocardial sympathetic innervation in diabetic and nondiabetic patients after spinal cord stimulation.
Page 1458

Longitudinal CBF and amyloid deposition: Sojkova and colleagues explore patterns of long-term regional cerebral blood flow changes on PET in individuals without dementia in the years preceding measurement of amyloid deposition.
Page 1465

EGFR expression in cervical cancer: Eiblmaier and colleagues assess 64Cu-DOTA-cetuximab as a potential PET imaging agent for measuring anti–epidermal growth factor receptor concentrations in cervical cancer tumors.
Page 1472

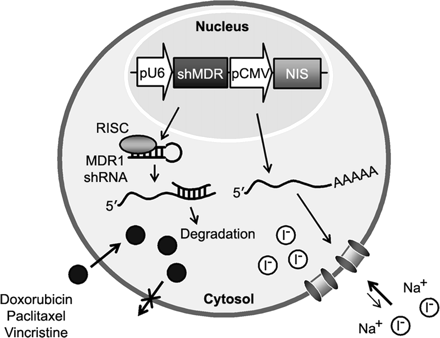
Novel combination therapy in colon cancer: Park and colleagues investigate the feasibility of a strategy allowing RNA interference–based gene therapy, sodium iodide symporter–based radioiodide therapy, and in vivo monitoring in colon cancer cells.
Page 1480
Visualization of HIF-1 activation: Yeom and colleagues describe bioluminescence and scintigraphic imaging to visualize hypoxia-inducible factor-1 transcriptional activation in tumors using the human sodium iodide symporter reporter gene, a technique that could predict responses to therapy.
Page 1489

Overcoming resistance to trastuzumab: Costantini and colleagues determine whether 111In-trastuzumab coupled to peptides harboring nuclear-localizing sequences can kill trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cell lines and whether the combination of radiosensitization with methotrexate could augment cytotoxicity.
Page 1498
Reducing renal uptake of radiopeptides: Vegt and colleagues analyze the effects of albumin and fragments of albumin on the renal reabsorption of 111In-octreotide, 111In-exendin, and 111In-minigastrin and outline potential advantages in peptide receptor radionuclide therapy.
Page 1506

Molecular imaging of SCI therapy: Lo and colleagues evaluate in rats a novel cell-based therapy for contusion spinal cord injury using embryonic-derived NIH3T3 cells, which endogenously express glial cell line–derived neurotrophic factor.
Page 1512

Molecular imaging of cell death: Reshef and colleagues report on synthesis, radiolabeling, biodistribution, and initial small-animal studies with 18F-ML-10, a small-molecule PET tracer for in vivo imaging of apoptosis.
Page 1520

PET radioligands for ETA receptors: Mathews and colleagues synthesize and evaluate radiolabeled analogs of a potent and selective endothelin subtype-A receptor that plays a central role in vasoconstriction, cell proliferation, and hormone production.
Page 1529

Single-step astatination of antibodies: Lindegren and colleagues describe a procedure for direct 211At-labeling of tumor-specific antibodies for the production of clinical activity levels.
Page 1537
Killing drug-resistant AML cells: Kersemans and colleagues report on basic investigations of targeted Auger electron radioimmunotherapy using 111In-labeled anti-CD33 monoclonal antibodies modified with nuclear-localizing sequences to overcome multidrug resistance in acute myelogenous leukemia.
Page 1546
Dosimetry in nuclear cardiology: Stabin reviews the technical basis for dose estimates for several radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear cardiology and addresses questions of uncertainty and risk assessment.
Page 1555
ON THE COVER
The use of enhanced PET/CT as a 1-stop-shop imaging protocol for assessing the resectability of pancreatic cancer is feasible and accurate. Enhanced PET/CT has been found to be significantly superior to PET alone. The volume-rendered 3-dimensional CT angiography/PET combination shown here clearly reveals the relationship between the important vessels and the pancreatic tumor.

See page 1413.







