Imaging of apoptosis: Tait provides an overview of recent progress toward molecular imaging agents that can detect cell death in vivo and outlines the potential for future clinical applications in diagnosis and therapy.
Page 1573
Dual-time PET perspective: Hicks looks at the history and significance of temporal profiling of tracer localization and previews an article in this issue of JNM on PET characterization of focal abnormalities remote from primary cancer sites.
Page 1577
Total lesion glycolysis in sarcoma: Benz and colleagues investigate whether combined assessment of tumor volume and metabolic activity improves the accuracy of 18F-FDG PET for predicting histopathologic tumor response in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas.
Page 1579

PET/CT in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: Goudarzi and colleagues correlate CT and PET data in patients with bronchioloalveolar carcinoma or cancer of other histology to determine the contributions of the anatomic and functional components of PET/CT in differentiating lung disease.
Page 1585

PET in head and neck cancer: Scott and colleagues report on a multicenter study exploring the effect of PET on initial management plans, staging, and treatment outcomes in patients with untreated head and neck cancer.
Page 1593

Tracer uptake in synthetic grafts: Wassélius and colleagues assess 18F-FDG uptake in aortic grafts in patients with or without symptoms of graft infection and describe the risks of false-positive diagnoses in this setting.
Page 1601

Dual-time PET in lung cancer: Uesaka and colleagues evaluate the efficacy of dual–time-point 18F-FDG PET for staging lung cancer and for differentiating metastatic from nonmetastatic lung cancer lesions.
Page 1606
Nuclear imaging of pheochromocytoma: Ilias and colleagues compare functional imaging using 18F-fluorodopamine PET, 123I-MIBG scintigraphy, or somatostatin receptor scintigraphy in patients with biochemically proven nonmetastatic or metastatic pheochromocytoma.
Page 1613

Tumor blood flow reproducibility: Lodge and colleagues report on a method quantifying the reproducibility of the 15O-water technique for tumor blood flow applications and briefly outline the implications of their findings for drug development research.
Page 1620
nAChRs in smokers: Mukhin and colleagues describe the potential of quantitative PET imaging for elucidating the role of nicotine-induced upregulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in smoking and after smoking cessation.
Page 1628

Gated myocardial SPECT and reorientation: Knollmann and colleagues assess the possibility of algorithm-specific effects related to varying heart axes as a source of error in gated SPECT.
Page 1636

Gated 82Rb PET versus CT ventriculography: Chander and colleagues compare functional parameters from gated 82Rb PET with simultaneous high-resolution contrast-enhanced CT ventriculography, obtained as a byproduct of CT coronary angiography during hybrid cardiac PET/CT.
Page 1643

Small-animal SPECT and SPECT/CT: Franc and colleagues provide an educational overview of current technologies and advances in preclinical investigation with SPECT imaging.
Page 1651
Dosimetry of 18F-AH111585: McParland and colleagues detail the safety, biodistribution, and internal dosimetry of a radiolabeled peptide PET tracer with a high affinity for the αvβ3 integrin receptor involved in angiogenesis.
Page 1664
Full-ring micro insert device: Wu and colleagues describe a prototype full-ring insert device designed to enhance image resolution in existing small-animal PET scanners.
Page 1668

Imaging atheroma: Ishino and colleagues report on the design and preparation of 99mTc-LOX-1-mAb, a radiolabeled anti-lipoprotein receptor monoclonal IgG, and on initial animal studies of its utility as an atherosclerosis imaging agent.
Page 1677

Imaging microRNA targeting: Kim and colleagues review the development and analysis of a bioluminescent reporter system for monitoring functional targeting of microRNA-221, which plays a key role in gene regulation in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Page 1686

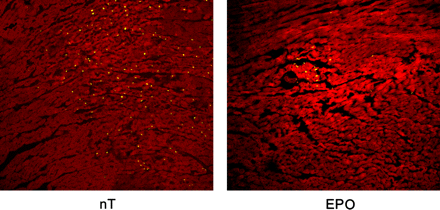
Assessment of erythropoietin cardioprotection: Doue and colleagues characterize the effect of erythropoietin on 99mTc-annexin V myocardial uptake in a rat model of ischemia and reperfusion.
Page 1694
Cardiac neuropathy in diabetic mice: Kusmic and colleagues investigate in a mouse model of long-lasting type II diabetes whether the mismatch between 123I-MIBG early uptake and washout is the consequence of a more generalized autonomic nervous system disorder.
Page 1701
Prolonged cholesterol loading and tracer uptake: Zhao and colleagues evaluate the aortic uptake of 18F-FDG and 99mTc-annexin A5 in apolipoprotein E–deficient and wild-type mice placed on high-fat diets.
Page 1707
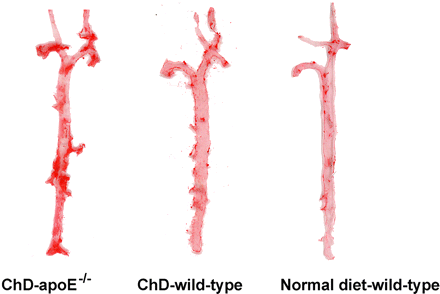
18F-labeled myocardial PET tracer: Higuchi and colleagues use small-animal PET to investigate the potential of a new 18F-labeled pyridazinone analog in a rat model of permanent and transient coronary occlusion.
Page 1715

Real-time PET monitoring of RF ablation: Bao and colleagues describe preclinical investigations of the use of 15O-water PET in providing real-time feedback and iterative image guidance to monitor intratumoral coverage of radiofrequency ablation therapy.
Page 1723

ON THE COVER
The need to study dynamic biologic processes in intact small-animal models has stimulated the development of high-resolution nuclear imaging methods. At right, small-animal SPECT/CT is applied to oncology research. In a prostate cancer xenograft model, radiolabeled antibodies for prostate-specific membrane antigen are used to monitor expression of the antigen. CT images and 3D rendering of fused images help define the tumor boundaries for more accurate image quantification.

See page 1658.







