Lewis looks at the development and current promise of radiolabeled cyclic peptide ligands for αvβ3 as powerful tools for molecular imaging and targeted radiotherapy of tumors undergoing angiogenesis.

Liao and colleagues examine the relative prognostic powers and clinical information provided by 3 assessment techniques in a high-risk population of patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease and discuss possible advantages in combining 2 or more of these approaches.
Schinkel and colleagues assess the value and feasibility of pharmacologically induced stress testing in the prediction of mortality and cardiac events in elderly individuals.
Brogsitter and colleagues report on the clinical performance of an electrocardiography-gated 3-dimensional 18F-FDG imaging protocol in patients with coronary artery disease and compare results with those from 2-dimensional acquisition.
Kluge and colleagues use 18F-FDG SPECT to measure metabolic rates of glucose uptake in myocardium in patients with pulmonary hypertension to identify prognostic parameters for cardiac dysfunction and poor survival.
Fukumitsu and colleagues measure and map the distribution of a major subtype A1 adenosine receptor in the human brain using a newly developed radioligand for PET imaging.
Kaiboriboon and colleagues apply the technique of composite subtraction ictal SPECT coregistered to MRI to demonstrate typical patterns of hyperperfusion in a group of patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.
Xiangsong and colleagues report on a novel approach to evaluating blood perfusion and ammonia metabolism in the pituitary gland and discuss the utility of this method in the diagnosis of hypopituitarism.
Salaun and colleagues document the reference range of 18F-FDG uptake in PET imaging of the gastroesophageal junction and gastric antrum in a retrospective study of patients with no history of gastroesophageal disease.
Metser and colleagues assessed the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of solid splenic masses in patients with known malignancy and incidentally found lesions in patients without known malignancy.
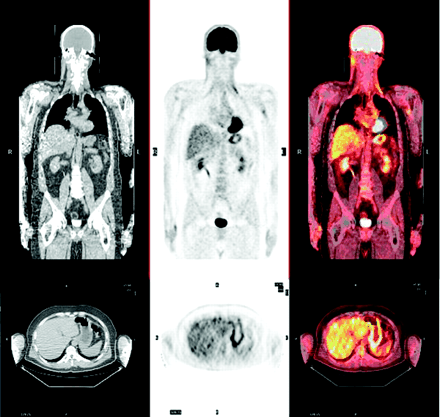
Lambert and colleagues detail the pharmacokinetics, organ dosimetry, and toxicity identified in a phase 1 study of intraarterial administration of 188Re-HDD/lipiodol, which shows promise in the palliative treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Bartel and colleagues investigate the use of a corn oil emulsion as an inexpensive cholecystagogue and alternative to sincalide in the scintigraphic diagnosis of chronic acalculous cholecystitis.
Kaufmann and Camici review the ways in which PET measurement of myocardial blood flow has contributed to advanced understanding of cardiac physiology and pathophysiology and look at the promise of new techniques and innovations.

Emfietzoglou and colleagues compare absorbed dose profiles within avascular prostate carcinoma spheroids for various β-, Auger-, and conversion-emitters delivered by liposomes and a monoclonal antibody and discuss the application of results to antibody-based radiotherapy.
Simões and colleagues investigate 124I-FIAU PET imaging of reporter gene expression in an isolated heart perfusion model.
Piert and colleagues compare 18F-FAZA with the standard hypoxia tracer 18F-FMISO in detection of tumor tissue hypoxia in murine tumor models.
Waldherr and colleagues evaluate in an animal model the utility of 18F-FLT PET to noninvasively measure changes in tumor cell proliferation in vivo after kinase inhibitor therapy.
Miao and colleagues examine in a mouse model the efficacy of a promising 188Re-labeled peptide for targeted radionuclide therapy of melanoma.
Chattopadhyay and colleagues report on the development and evaluation of a novel PET agent for imaging nicotine α4β2 receptors, which are implicated in the study of Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, substance abuse, lung cancer, and other disorders.
Kim and colleagues explore in an animal model the possibility of liver-targeted nuclear imaging with 99mTc-galactosyl–methylated chitosan bound to asialoglycoprotein receptors.
Joseph and colleagues assess the role of cytokines in regulating 99mTc-mebrofenin transport and discuss implications for using this process to identify and monitor organ inflammation, including hepatitis, fatty liver disease, allograft rejection, and responses to gene therapy vectors.
Govindan and colleagues develop a simple, remote, “1-pot” method for production of a residualizing 131I-labeled monoclonal antibody at levels needed for clinical therapy.

Igarashi and colleagues investigate in a rat model whether changes in myocardial uptake of fatty acid tracer after reperfusion subsequent to transient myocardial ischemia are closely related to alterations in intracellular fatty acid oxidation.
De Bondt and colleagues test the performance of 4 algorithms that calculate left and right ventricular ejection fractions from tomographic radionuclide ventriculography and discuss clinical implications of these dynamic cardiac models.
Higuchi and colleagues compare autoradiographic uptake of BMIPP and 201Tl in assessing serial changes in fatty acid metabolism associated with acute ischemia and reperfusion in rat hearts.
Manrique and colleagues determine the effect of perfusion defect and imaging sequence on the evaluation of myocardial stunning with gated perfusion SPECT, using a dynamic mathematic cardiac torso phantom.
Pichler and colleagues report a new application of radiolabeled RGD peptides targeting αvβ3 imaging of delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction in a mouse model of chronic inflammation.
ON THE COVER
The putative antagonist 18F-labeled 5-(3′-fluoropropyl)-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinylmethoxy)pyridine (nifrolidine) has been found to bind to α4β2 receptor–rich regions in rats and monkeys, indicating promise as a PET agent. In these images of rhesus monkey brain, correlation of 18F-nifrolidine PET images with MRI templates indicates significant binding in the thalamic regions and significant uptake by the temporal and frontal cortices. The summed images at bottom show that the anteroventral, anteromedial, and ventrolateral thalami are the regions of highest uptake, consistent with the reported distribution of the α4β2 receptor subtype in rhesus monkeys.








