Abstract
144
Objectives Segmentation of contrast CT and measurement of SPECT point spread function (PSF) are usually required for conventional partial volume correction (PVC). This study was to develop and validate a segmentation-free PVC method of the blind deconvolution (BD) incorporated with anatomical-based filtering. METHODS: The BD method was performed on SPECT reconstructed image using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization (MLEM) algorithm to estimate the BD restored image and the PSF simultaneously. A 3D Gaussian filter weighted by anatomical similarities from co-registered contrast CT image was used at each MLEM iteration. Parameters were optimized based on NCAT phantom simulation studies. GE Discovery 570c SPECT/CT system was used for 123I-mIBG imaging. NCAT phantoms with and without myocardium defect were simulated (2 noise levels: 5.28M and 1.76M counts, 30 realizations for each). The activity ratios in the normal myocardium, defect, liver, blood pool, background and lung were set to 10 : 5 : 10 : 2 : 2 : 1. The relative bias and standard deviation (SD) images were calculated on the reconstructed and BD restored images for comparison. Fifteen heart-to-mediastinum ratios (HMRs) ranging from 0.5 to 5.0 with increment of 0.5 and from 5.0 to 10.0 with increment of 1.0 were simulated for NCAT phantom. A physical anthropomorphic torso phantom with a cardiac insert configured with the same fifteen HMRs were imaged. Correlations between SPECT-quantified and true HMRs were calculated on both reconstructed and BD restored images for NCAT and physical phantoms. The proposed PVC method was also performed on 123I-mIBG studies of one normal dog (5 min acquisition starting at 15 min post-injection, dose=10.5 mCi)) and one normal human (15 min acquisition starting at 15 min post-injection, dose=5.87 mCi).
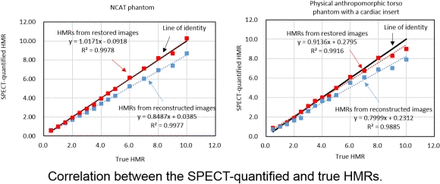
Results The relative bias and SD images of NCAT phantom showed that the proposed PVC method can reduce both the bias and the noise. The mean relative bias in the normal myocardium was improved from -16.9±0.5% (derived from reconstructed images) to -0.3±0.6% (derived from BD restored images) for low noise level, and was improved from -16.7±0.7% to -0.7±0.9% for high noise level. The mean relative bias in the myocardium defect was improved from -13.1±1.4% to 1.7±1.6% for low noise level, and was improved from -13.6±2.1% to 0.1±2.4% for high noise level. For both NCAT and physical phantom studies, HMRs from reconstructed images without PVC were underestimated (Correlations between SPECT-quantified and true HMRs were y=0.85[asterisk]x+0.04 for NCAT phantom, R2=1.00; and y=0.80[asterisk]x+0.23 for physical phantom, R2=0.99). HMRs from BD restored images were significantly improved (Correlations between SPECT-quantified and true HMRs were y=1.02[asterisk]x-0.09 for NCAT phantom, R2=1.00; and y=0.91[asterisk]x+0.28 for physical phantom, R2=0.99). For dog and human studies, the mean activities in the myocardium increased by 18.1% and 11.6% respectively after applying the proposed PVC method. CONCLUSIONS: The segmentation-free PVC method with blind deconvolution and anatomical-based filtering was developed and validated on 123I-mIBG SPECT/CT imaging, which can improve the quantification accuracy and reduce noise simultaneously without the need for known PSF. Research support: This study was supported by American Heart Association Grant-In-Aid awards 14GRNT19040010 and 13GRNT17090037, and research contracts from GE Healthcare.