Abstract
241803
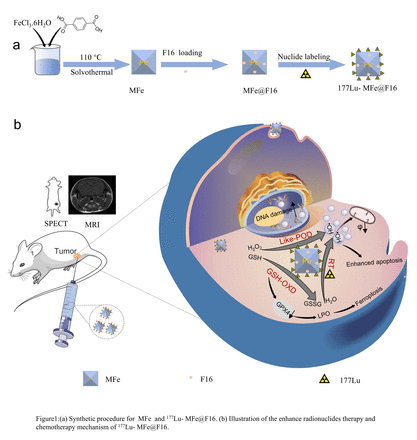
Introduction: Despite the availability of various conventional treatment options, breast cancer still suffers from high mortality rate, high recurrence rate and poor prognosis, especially triple-negative breast cancer. This study is dedicated to construct an iron-based metal framework nano co-transport system for efficient transportation of chemotherapy drugs lipophilic cationic (E)-4-(1H-indol-3-ylvinyl)-N-methylpyridinium iodide (F16) and 177Lu for enhance radionuclides therapy and chemotherapy.
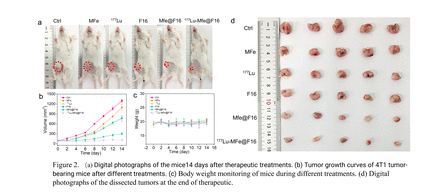
Methods: Firstly, a hot solvent method reaction was used to prepare iron-based metal framework nanozymes (MFe). Then, the lipophilic cationic (E)-4-(1H-indol-3-ylvinyl)-N-methylpyridinium iodide (F16) and 177LuCl3 were molecular self-assembled in MFe to obtain 177Lu-MFe@F16. In order to explore the antitumor effect of 177Lu-MFe@F16 in vivo and in vitro, fluorescence imaging was performed in vitro on different groups of treated 4T1 cells to detect ROS production, DNA damage and apoptosis. 4T1 tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into 6 groups including control group (saline), MFe group (5 mg/kg), MFe@F16 group (5 mg/kg), 177Lu group (100 uCi) and 177Lu-MFe@F16 group (100 uCi), and were treated by a single intratumoral injection of the corresponding dose of the agents, with tumor volume and body weight measured every 2 days for the next 14 days.
Results: In vitro cell fluorescence imaging results showed that 177Lu-MFe@F16 induced the production of more ROS in 4T1 cells, leading to mitochondrial membrane potential disintegration, DNA damage, and ultimately more apoptotic tumor cells. The results of in vivo treatment showed that both 177Lu and F16 group presented a moderate therapeutic effect with inhibition rates of 34.46% and 35.56%, respectively. In addition, the growth of the 4T1 tumor was significantly suppressed in the 177Lu-MFe@F16 group (90.37%), demonstrating the superior therapeutic performance of 177Lu-MFe@F16 group in comparison to that of MFe@F16 group (74.77%). The above research results showed that we have obtained a nano co-transport system for enhance radionuclides therapy and chemotherapy.
Conclusions: In summary, we have successfully constructed a novel nano co-transport system177Lu-MFe@F16 for enhance radionuclides therapy and chemotherapy on triple-negative breast cancer.