Abstract
241467
Introduction: Novel theranostic approaches using radiopharmaceuticals targeting PSMA have emerged for treating metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). The physical properties and commercial availability of Lutetium-177 (177Lu) makes it one of the most used radionuclide for radiopharmaceutical therapy (RPT). In this review we aimed at comparing the dosimetry of the most used [177Lu]Lu-PSMA RPT compounds.
Methods: This is a systematic review and meta-analysis of [177Lu]Lu-PSMA RPT (617, I&T, and J591) dosimetry for prostate cancer. Absorbed doses in Gy/GBq for each organ at risk(kidney, parotid and submandibular glands, bone marrow, liver, lacrimal glands) and for tumor lesions (bone and non-bone lesions) were extracted. These were used to estimate the pooled average absorbed dose of each agent, and normalize to the injected activity (Gy/cycle) used in VISION (7.4 GBq), SPLASH (6.8 GBq), and PROSTACT Trials (5.8 GBq), respectively.
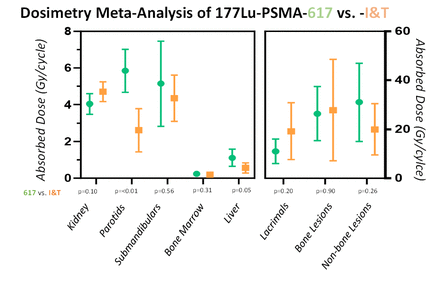
Results: 29 published manuscripts comprising 535 patients were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled dose (weighted average across studies) for 177Lu-PSMA-617 and 177Lu-PSMA-I&T were 4.04 (n=17 studies/n=297 patients) and 4.70 (n=10/153) Gy/GBq for kidney (p=0.10), 5.85 (n=14/216) and 2.62 (n=5/86) Gy/GBq for parotids (p=<0.01), 5.15 (n=5/81) and 4.35 (n=1/18) Gy/GBq for submandibular (p=0.56), 11.03 (n=6/121) and 19.23 (n=3/53) Gy/GBq for lacrimal glands (p=0.20), 0.24 (n=12/183) and 0.19 (n=4/68) Gy/GBq for bone marrow (p=0.31), and 1.11 (n=9/154) and 0.56 (n=4/56) Gy/GBq for liver (p=0.05), respectively. Average tumor doses tended to be higher for 177Lu-PSMA-617 than for 177Lu-PSMA-I&T in soft tissue, (4.19 vs. 2.94 Gy/GBq); p=0.26. 177Lu-PSMA-617 and 177Lu-PSMA-I&T, achieved comparable bone lesion doses (3.56 vs. 4.10 Gy/GBq); p=0.90. In the sole Lu177-PSMA-J591 study including 35 patients, absorbed doses to the kidney, bone marrow, and liver were 1.41, 0.32 and 2.10 Gy/GBq respectively. Absorbed doses to the salivary glands, lacrimal glands, and tumors for Lu177-PSMA-J591 have not been published yet.
Conclusions: In this meta-analysis there was no significant difference between absorbed dose from 177Lu-PSMA-I&T and 177Lu-PSMA-617. There was a possible trend towards higher kidney dose with 177Lu-PSMA-I&T, and higher tumor lesion dose with 177Lu-PSMA-617. It remains unknown if this has any clinical impact. The dosimetry methodologies were strikingly heterogenous among studies emphasizing the need for standardization. Dosimetry data for 177Lu-PSMA-J591 was limited.