Abstract
242484
Introduction: The efficacy and safety of radiopharmaceutical therapies (RPTs) is highly dependent on the absorbed dose (AD) delivered to the targeted tissue and normal organs. Unfortunately, the assessment of ADs still requires standardization. There are methodological disparities among different institutions resulting in substantial variability in reported AD results. In 2021, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) Dosimetry Task Force launched the 177Lu Dosimetry Challenge to gain knowledge of sources of variability within the dosimetry workflow. In this study, we investigated the variability caused by different fitting approaches for determination of the time-integrated activity (TIA).
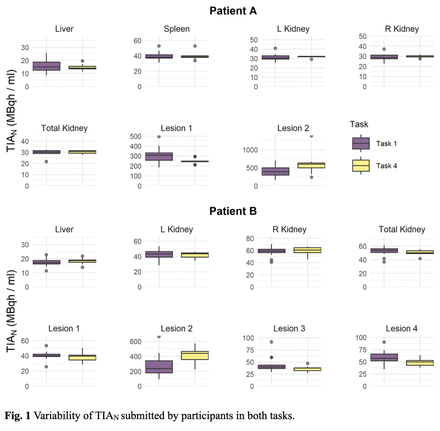
Methods: Two patients treated with 177Lu-DOTATATE underwent a series of 4 post-therapeutic SPECT/CT scans. In task 1, participants were required to perform the complete workflow, including segmentation of volumes of interest (VOIs), time-activity curve (TAC) generation and integration to calculate the TIA, and finally the AD calculation. In task 4, VOIs were provided as DICOM-RTStruct or binary mask images, eliminating segmentation and requiring only TAC fitting and TIA and AD calculation. We investigated the impact on TIA from the different fitting approaches used by participants. We analyzed participants' submitted results and determined that there were 15 different curve-fitting approaches. Variability was assessed in two phases. First, TIAs for organs and tumors calculated with the 15 different curve-fitting strategies were performed by the same physicist on the activity values (1) extracted using VOIs provided in task 4, (2) reported by participants for task 4, and (3) reported for task 1. In the second phase, we assessed the TIA variability of the participant-submitted TIA data. We normalized the TIAs (i.e. TIAN) by the reported volumes of each VOI. Descriptive statistics for TIAN values were computed and variability was quantified using the quartile coefficient of dispersion (QCD).
Results: Bi-exponential functions were the most common approaches for fitting the TAC of both organs and lesions. Variability in TIAN assessed in the first phase, when performed by a single user was <8% for kidney and liver and <11% for lesions. For organs, when VOIs were provided to participants (task 4), TIA variability was <9%; in task 1, where participants created their own VOIs, variability was <16%. For lesions, the variability was <14% for task 4 and <29% for task 1. Variability assessed in the second phase (i.e. evaluating TIA using participants reported fitting method and results in both tasks) was <9% for organs (excluding the healthy liver of patient A, task 1, which had apparent lesions). However, variability for lesions was substantially larger, ranging from 1.1% to 13.1% for task 4 and from 3.5% to 31.5% for task 1. The higher variability associated with task 1 suggests that segmentation is a more significant source of variability than fitting and integration.
Conclusions: The analysis of the fitting and integration step of the dosimetry workflow for SNMMI 177Lu Dosimetry Challenge data suggests that the TIA is robust with respect to fitting methods as long as the person performing the fits reviews it and ensures the TAC is correctly modeled. Segmentation may be a more significant source of variability in TIA results than fitting and integration.