Abstract
241090
Introduction: Respiratory motion during SPECT data acquisition is an important patient-related factor that distorts the signal distribution, leading to the blurring of projection data. Quantitative images acquired without motion correction can result in incorrect estimated activities and absorbed doses. The increasing use of SPECT for dosimetry in radiopharmaceutical therapies and the increasing development of new quantitative methods requires more accurate motion correction methods. Newly developed optical surface imaging (OSI) systems have been introduced in external beam radiation therapy, allowing for continuous and touchless optical surface scanning of patients' external surfaces. Applying this technology to SPECT imaging, we developed a new method to extract respiratory signals for phase sorting based on simulation data and compared the results with the ground truth and traditional data-driven methods.
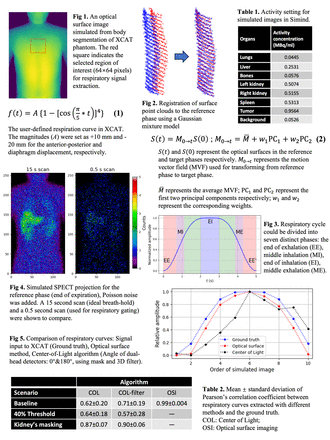
Methods: Using the 4D XCAT anthropomorphic human CT, and activity images at 10 respiratory phases were generated. Two tumors, 10 and 20 mm in diameter, were positioned in the liver. The patient organ and tumor activities were derived from SPECT images of a patient taken one hour after the injection of 6.85 GBq 177Lu-DOTATATE and are presented in Table 1. The SIMIND Monte Carlo was used to create 120 SPECT projections, after which Poisson noise was introduced. The ground truth respiratory signal was set using Equation 1 and input into the XCAT software. Point clouds within the 64x64 body surface region of interest in the attenuation map were used to simulate the OSI system, followed by the addition of Gaussian noise (0.5 mm standard deviation). A Gaussian Mixture Model was applied for image registration of OSI in different phases, and Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used for dimension reduction (Fig. 1, 2 and Equation 2). For comparison, we used a data-driven approach based on the center-of-light (COL) strategy. This method estimates respiration by monitoring the axial changes of COL for counts in the sub-projections. As the breathing cycle typically lasts around 5 seconds (see Fig. 3), the curve can be divided into 7 amplitude-based segments. To address the rapid changes during the middle inhalation and middle exhalation phases, we implemented a 0.5s gating time in the COL algorithm. Moreover, we compared the COL from various preprocessed projections: filtering (3D filter with a 32 × 32 spatial and 2-temporal dimension box kernel), kidney region masking (obtaining from 3D images and projecting to different angles), and threshold sets for counting rates.
Results: The correlation between the ground-truth signal and the OSI-based signal remains highly consistent and stable (0.99±0.004, p-value < 0.001 for comparing OSI and COL-filter with Kidney’s masking), which was further illustrated by the comparison curves depicted in Fig. 5. Due to the short sampling time (as seen in Fig. 4) compared to the conventional 15s sampling used in clinical settings, the 0.5s gating introduced significant noise to the projections. Pearson’s correlations (Table 2) for COL and COL of filtered projections (COL-filter) exhibit suboptimal outcomes (Mean ± Standard deviation was 0.62±0.20 and 0.71±0.19, respectively). Although a noticeable enhancement was observed when using the kidney region mask (0.87±0.07 and 0.90±0.06 using the filter, p-value < 0.001), it still performed less effectively than the OSI method.
Conclusions: We assessed a novel respiratory phase sorting approach based on optical surface signals and compared it to a pre-existing data-driven method. Our approach demonstrated several potential advantages, including non-contact operation, increased stability, no requirement to observe the ROI mask in projections, and greater compatibility with various imaging systems. These attributes suggest the potential application of this method in 4D SPECT imaging, which could lead to improved motion-incorporated 4D reconstruction for gated SPECT.