Abstract
24106
Introduction: 211At (half-life: 7.2 hours) is an alpha-emitter which can be used for the targeted alpha therapy in thyroid cancer. In the investigator-initiated clinical trial using 211At, whole-body image acquisition of distribution is essential for estimating absorbed doses. These images require the quantitative accuracy and reproducibility of pixel values for dose estimation, particularly in relation to the time-activity changes after administration. In the present study, we assessed the 211At image quality simulating 3 and 24 hours after administration using multi CZT detector SPECT/CT.
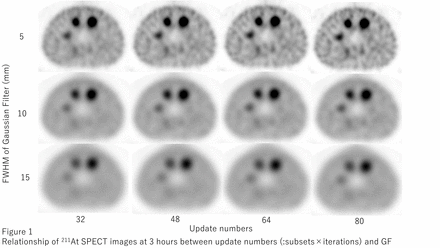
Methods: VERITON-CT (Spectrum Dynamics Medical) was employed in this phantom study. Energy window was set as 79 keV ± 20% targeting the characteristic X-rays emitted from the daughter nuclide of 211Po (half-life: 0.52 seconds). Scan duration was set as 18 minutes/bed, simulating whole-body SPECT acquisition from head to pelvis (3 beds) within one hour in a patient scenario. SPECT acquisition was performed with the ratio of hot sphere to background radioactivity set at 8:1 (radioactivity concentration approximately 17.6-2.2 kBq/mL and 2.4-0.3 kBq/mL, respectively). The reconstruction parameters (number of iterations and subsets, full width at half maximum (FWHM) of Gaussian filter (GF)) were optimized by the analysis of the SPECT images with reference to the guidelines for standardization of bone SPECT imaging 1.0 from the Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine Technology and Japanese guideline for the oncology FDG-PET/CT data acquisition protocol. The SPECT images were assessed for differences across various subsets, iterations, and GF settings through %contrast (: Q17mm > 11%), background noise (: N17mm < 10%), contrast-to-noise ratio, recovery coefficient and visual analysis with consensus from board-certified nuclear medicine physicians.
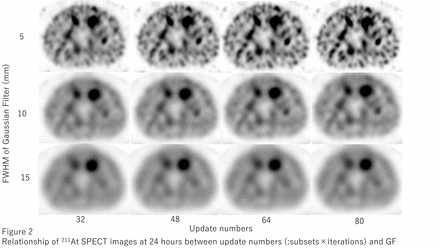
Results: For the SPECT images at 3 hours, Q17mm and N17mm with subsets:8, iterations:6 and GF:5 mm were 16.1 and 9.1%, respectively. The SPECT images with above reconstruction parameters satisfied the threshold of the guideline, however at 24hours, N17mm increased to 26.7% due to less acquisition counts. Instead of GF with 10 mm, N17mm at 24 hours decreased to 13.7% and visual assessment of 17 mm sphere was improved to detect.
Conclusions: From this phantom based research, the 211At SPECT images using multidetector CZT SPECT/CT scanner were optimized as well as diagnostic bone SPECT images be done. Optimal reconstruction parameters for dosimetry until 3 hours were iterations:6, subsets:8 and GF:5 mm. For those until 24 hours, GF should be changed to 10 mm.