Abstract
P658
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms have shown potential for different tasks in nuclear medicine image analysis such as denoising, segmentation, lesion detection, and dosimetry. However, one of the limitations for the training of reliable AI methods is that they require large volume, high quality, annotated datasets. Given the nature of the clinical data, grouping datasets from different institutions is not always feasible due to privacy and institutional IP concerns. One way to overcome this problem is by following a federated learning approach on which the data never leaves the institution but the training can be performed by passing the model from center to center. However, ensuring that the data is consistent between institutions such that it remains compatible with the inputs to the model being trained, and to perform tasks like collaborative image annotation are still a challenge. The aim of this study was to develop a platform that allows for remote data viewing, that can serve for verification and annotation, with each site maintaining the governance of its own data.
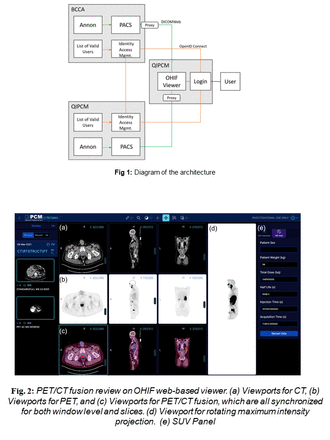
Methods: We created a platform architecture that uses the DICOMweb protocol allowing the platform to connect to multiple PACS server to perform queries and display images. To render and analyze DICOM images, we use the Open Health Imaging Foundation (OHIF) web-based viewer. OHIF has advanced visualization and multi-modal image fusion for PET and CT. Because OHIF is an open source extensible imaging platform, different tools can in principle be added to it as needed. This viewer was deployed on a web server at QIPCM. A research PACS system using the open source DCM4CHE tools was deployed at each of our institutions. I Identity access management system (IAMS), was also set in place at each institution to authorize users to have access to data cohort on the PACS server. The OHIF server was connected to the IAMS at each institution, to allow data viewing and annotation of data shared on both PACS systems to the authorized users.
Results: We tested the platform using anonymized data and phantoms stored in the PACS server at our institutions. BC Cancer users were given permission to view and annotate a subset of data stored in the QIPCM PACS server, and vice versa. The users did not have access to the data for purposes of downloading it or modifying it beyond the annotation tools made available in OHIF. Each institution always maintained the governance of the data. This setup has been containerized using Docker enable easy deployment on different sites.
Conclusions: To aid in federated learning approaches for AI model training, we have presented a set of tools that are web-based applications and have been containerized for easy management and deployment. The tools allow users to securely view and annotate medical images stored at remote institutions, while ensuring the data is compatible with desired AI models. The developed platform uses open source tools to enable easy contributions by the community and to allow the code to be audited. We hope that tools like this enable the faster adoption of AI in nuclear medicine.
Note: The supporting material on the next page will be attached separately during abstract submission and is required for the review process of SNMMI.