Abstract
P394
Introduction: The size of the pixelated scintillation crystal depends on the size of the imaging target in the PET system. Inter-crystal scattering (ICS: Compton scattering of annihilation photons from one crystal to adjacent crystals within a crystal block) ratio increases as the size of the scintillation crystal decrease. False lines-of-interest (LORs) determined by ICS results in image quality degradation. If all ICS events are discarded, the sensitivity of the PET system is compromised. Therefore, various ICS recovery methods have been proposed to find the exact first interaction position of an annihilation photon in the crystal block using energy or depth-of-interaction (DOI) information or photoelectric event distributions. However, the conventional ICS recovery methods are rarely applied to actual PET systems because their accuracy is not high enough. Even if applied, the image quality improvement owing to them is insignificant. In this study, a probability density function of scattered photon absorption in the scintillation crystal was derived, and based on this mathematical formula, a new ICS recovery method for determining the first interaction position of LOR was proposed.
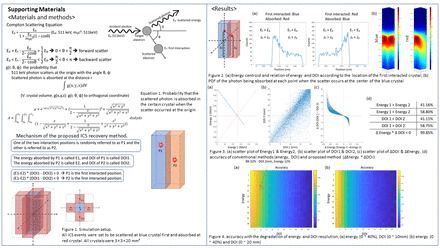
Methods: The ICS phenomenon was mathematically analyzed by combining the Klein-Nishina formula for the probability of scattering angle, the Compton scattering equation for the relationship between scattering angle and energy, and the absorption equation for the probability of the distance scattered photons flew (Equation 1). Based on this mathematical analysis result, we propose a new ICS recovery method. For two interaction positions P1 and P2 in arbitrary order and their corresponding DOI positions (DOI1 and DOI2) and absorbed energy (E1 and E2), P1 is chosen as the first interaction position If ΔDOI (=DOI1-DOI2) and ΔE (=E1-E2) have the different polarity, otherwise, P2 is chosen. A Monte Carlo simulation study was also performed to validate the proposed method with the known ground truth of the first interaction position of annihilation photons. In the simulation, Compton scattering events of 17,000 511 keV photons were generated from the center of a 3 mm x 3 mm x 20 mm LSO crystal surrounded by four LSO crystals with the same size, and the second interaction position and absorbed energy were recorded (Figure 1). The accuracy of determining the first interaction position using the proposed method was compared with those of conventional ICS recovery methods which use only one of energy and DOI. Considering the actual situation, the accuracy according to DOI and energy resolution was also measured.
Results: The peak of the energy centroid histogram in the simulation result and the peak in the probability distribution by the equation both occur at the backscatter position. (Figure 2) Simulation results showed that the accuracy of the proposed method was over 99% in identifying the first interaction position of 511 keV annihilation photons, whereas the accuracy of the method using only one of energy and DOI information was 58.80% and 58.75% respectively (Figure 3). The accuracy of the proposed method decreased as the DOI, and energy resolution of the PET detector degraded. However, it still showed high accuracy of 89% when the PET detector has a DOI resolution of 2 mm and an energy resolution of 12% (Figure 4). Accuracy was affected more by DOI resolution degradation than energy resolution. The performance of conventional methods using only DOI, or energy information was similar in mathematical analysis and simulation study.
Conclusions: In this study, a new ICS event recovery method using both energy and DOI information is proposed, which showed significantly better performance than conventional methods using only single information. Experimental verification of the proposed method using a dual-ended readout DOI PET detector is in progress.