Abstract
2801
Introduction: Cortisol is known to promote adipocyte differentiation and maturation, and prolonged exposure to excess cortisol contributes to development of obesity and metabolic dysregulation. The intracellular enzyme 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) catalyzes the conversion of inactive cortisone to active cortisol. Recently, we demonstrated reduced 11β-HSD1 levels in vivo in the human brain with increasing body mass index (BMI), while increasing brain 11β-HSD1 was seen with increasing age, using the PET radioligands [11C]- and [18F]AS2471907 (1). In addition to high uptake in the brain, [18F]AS2471907 has high uptake and specific binding in the liver (2). The amount of 11β-HSD1 in tissues such as liver and brain measured simultaneously by PET imaging may help elucidate the complex interplay of cortisol activation in the setting of metabolic dysregulation. With this in mind, we performed human PET imaging studies to examine 11β-HSD1 levels in the liver in addition to the brain.
Methods: Nine individuals (5F/4M, 29-64 y) with a range of BMIs (22.6 - 34.4 kg/m2) underwent PET/CT imaging with arterial sampling (n=7), after injection of [18F]AS2471907, by acquiring 18 x 5 min whole-body continuous bed motion images after a 10 min initial scan over the heart. Two acquisitions were centered over the liver for the duration of the scan. Regions-of-interest (ROI) for the liver were manually drawn on a summed PET image (60-90 min). Seventeen brain ROIs were selected from the anatomical automatic labeling (AAL) template and applied to the dynamic PET images to generate time-activity-curves (TACs). Volume of distribution (VT, mL/cm3) was estimated for each ROI using the multilinear analysis-1 (MA1) method with t*=10 min and tmax=90 min using the metabolite-corrected arterial plasma input function (IF). Mean whole-brain VT values were calculated by averaging all ROIs. Reversible 1- and 2-tissue compartment models, MA1, and the Logan graphical analysis, with the metabolite-corrected arterial plasma IF were applied to the liver TACs. Given the possibility of irreversible kinetics in the liver, Ki (min-1), the rate of irreversible tracer uptake, was calculated using the Patlak method. Liver SUV 60-90 min was also calculated.
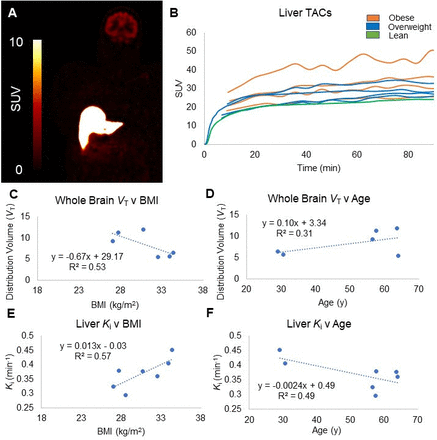
Results: Uptake of [18F]AS2471907 in the brain and liver can be seen in a representative whole-body coronal slice (SUV 60 ‑ 90min) (Fig 1A). Liver TACs show varied uptake levels among lean, overweight, and obese subjects (Fig 1B). Mean ± SEM of the parent fraction in plasma was 88±1% at 90 min (n=7). Kinetic modeling demonstrated decreasing whole brain VT estimates with increasing BMI (R2=0.53; Fig 1C) and increasing VT with increasing age (R2=0.31; Fig 1D), similar to our previously published study examining only the brain in a larger cohort [1]. While TACs were fit well, none of the reversible models provided stable estimates for liver VT. Under the assumption of irreversible kinetics, the Patlak method provided good TAC fits and good Ki estimates. In contrast to the correlation of brain VT with BMI and age, liver Ki positively correlated with BMI (R2=0.57; Fig 1D) and negatively correlated with age (R2=0.49; Fig 1E).
Conclusions: These preliminary studies suggest obesity is associated with increased levels of 11β-HSD1 in the liver but decreased levels in the brain; while aging may increase brain 11β-HSD1 levels. One caveat is higher liver to brain 11β-HSD1 enzyme levels could make tracer kinetics in the liver look irreversible when in fact the kinetics may be very slow. Additional studies are needed to clarify this issue, and to ascertain the correlation of brain and liver 11β-HSD1 levels with obesity and its significance.
REFERENCES:
[1] Bini, et al, Molecular Imaging and Biology, 2020.
[2] Bini, et al, IEEE Trans on Radiation and Plasma Medical Sciences, 2021