Abstract
2632
Introduction: Cardiac amyloidosis is a disorder caused by deposition of amyloid in cardiac tissues. Light chain (AL) and transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis together constitutes >95% of cardiac amyloidosis. Transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR‐CA) is an infiltrative cardiomyopathy caused by extracellular deposition of insoluble transthyretin amyloid fibrils in the myocardium. Transthyretin is a plasma protein mainly synthesized in the liver. Patients with cardiac amyloidosis usually present with symptoms of restrictive cardiomyopathy like heart failure and arrhythmia. Prognosis of these patients depend on the degree of cardiac involvement.
Though endomyocardial biopsy is the confirmatory test, Tc-99m pyrophosphate (Tc-99m PYP) scintigraphy is a non-invasive method to specifically identify ATTR-CA by the possible mechanism of calcium in amyloid deposits binding to phosphate in PYP.
Methods: Inject 10-20 mCi of Tc-99m PYP intravenously. Planar with/without SPECT images of chest are acquired at 1 hour post injection. If there is persistent blood pool activity, repeat image at 3 hour. Patient is positioned supine and using 15-20% energy window with low energy, high resolution collimator at 140 KeV energy, images are acquired. Planar images are acquired in anterior projection and in lateral and left anterior oblique projections as required. Image processing is done using cardiac imaging software.
Results: 71-year-old hypertensive male now presented with stroke. Echocardiogram showed grade III diastolic dysfunction with severely dilated left atrium concerning for cardiac amyloidosis.
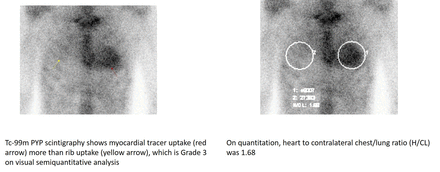
Technetium-99m pyrophosphate scintigraphy was done, which is a noninvasive, easily accessible, simple study for ATTR-CA with >90% sensitivity and specificity. Tc-99m PYP scintigraphy showed myocardial tracer uptake more than rib uptake, which is Grade 3 on visual semiquantitative analysis (grade 0 = no myocardial uptake, and grades 1-3 being myocardial < rib, myocardial = rib, and myocardial > rib respectively). On quantitation, heart to contralateral chest/lung ratio (H/CL) was 1.68.
Conclusions: Planar Tc-99m PYP scintigraphy with myocardial uptake appearing visually ≥ rib uptake, and quantitative heart to contralateral chest/lung uptake ratio calculated ≥1.5 are considered positive for transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. Our case had myocardial uptake more than rib uptake visually and had H/CL ratio 1.68 and hence considered positive for ATTR-CA.
Semi quantitative evaluation (Visual comparison of cardiac to rib uptake)
Grade 0: No myocardial uptake & normal bone uptake
Grade 1: Myocardial uptake < rib uptake
Grade 2: Myocardial uptake = rib uptake
Grade 3: Myocardial uptake > rib uptake & mild/ absent rib uptake
Scores ≥ 2 is considered ATTR positive.
Quantitative evaluation
Myocardial to contralateral chest/lung uptake ratio is calculated by drawing similar regions of interest (ROI) over the heart and contralateral chest on planar images. If the heart to contralateral (H/CL) ratio (fraction of heart ROI mean counts to contralateral chest ROI mean counts) is ≥ 1.5, the study is considered ATTR positive and if < 1.5 is considered ATTR negative.
Tc-99m PYP scintigraphy is highly accurate for diagnosing ATTR-CA in cases of strong clinical suspicion.