Abstract
24131
Introduction: Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) is a condition characterized by the deposition of misfolded transthyretin (TTR) proteins in the heart, eventually leading to heart failure. The diagnosis of ATTR-CM is facilitated by employing a visual score (VS) and the heart-to-contralateral lung ratio (H/CL ratio), derived from planar [99mTc]PYP scintigraphy. This technique reflects the extent of amyloid deposition. However, these parameters obtained from planar imaging can be affected by blood pool uptake and overlying rib activity, especially in the early stages of the disease when TTR deposits are minimal. Recently, the effectiveness of volumetric quantitation using single-photon emission tomography (SPECT) in the diagnosis of ATTR-CM has been highlighted in several studies. To date, there has not been a comprehensive analysis of both 2D and 3D image-derived parameters and their clinical values in diagnosing ATTR-CM.
Methods: From February to July 2022, consecutive patients who underwent [99mTc]PYP SPECT/CT were analyzed. The heart volume of interest (VOI) was delineated by selecting the left ventricular myocardial region using threshold-based tools from Q. Volumetrix (Xeleris Workstation, GE, USA), based on SPECT images. In cases where myocardial uptake was not observed, the entire left ventricle was encompassed. The lung VOI was automatically selected based on CT images, using Hounsfield units less than -400. Also, the VOIs for the spine and paraspinal muscles were manually delineated for background normalization. (Figure 1).
The planar H/CL ratio and the volumetric heart-to-lung ratio (H/L ratio) were measured on planar and SPECT/CT images, respectively. The mean, peak, and maximum standardized uptake values (SUV) were derived from calculations based on the heart VOI. To standardize uptake levels across the heart, bone, and soft tissue compartments, the retention index (RI) was also calculated. This index is represented by the formula:
RI = (SUVpeak cardiac/SUVpeak vertebral) × SUVpeak paraspinal muscle.
All data was subsequently analyzed using either the Pearson or Spearman correlation, depending on the normality of distribution. To evaluate the overall discriminatory performance, a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed, and the area under the curve (AUC) was computed. The diagnosis of ATTR-CM was determined based on clinical guidelines and histopathological evidence.
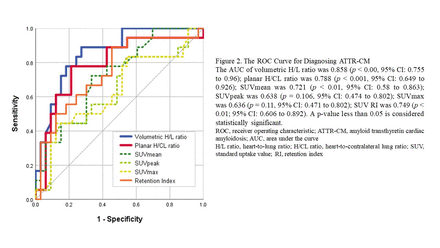
Results: A total of 51 patients were enrolled, among whom 18 received a final diagnosis of ATTR-CM (2 had a VS of 3, 10 had a VS of 2, 5 had a VS of 1, 1 had a VS of 0). The planar H/CL ratio exhibited a strong correlation with the volumetric H/L ratio (r = 0.729, p < 0.01). The planar H/CL ratio also showed a moderate correlation with the visual score (r = 0.588, p < 0.01), SUV RI (r = 0.484, p < 0.01), SUVmean (r = 0.437, p < 0.01), and SUVpeak (r = 0.322, p < 0.05). A weak correlation was observed with SUVmax (r = 0.322, p < 0.05). ROC analysis revealed that the volumetric H/L ratio was superior to the VS, planar, and SUV-based metrics in differentiating patients with and without ATTR-CM. It achieved a sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy of 88%, 72.7%, and 78.4%, respectively (AUC: 0.858, 95% CI: 0.755 to 0.96; p < 0.001) (Figure 2).
Conclusions: Our preliminary findings indicate that the volumetric H/L ratio, derived from SPECT/CT, correlates well with the planar visual score. Compared to planar and SUV metrics, the volumetric H/L ratio emerges as a more sensitive parameter. It can be more effectively utilized to assess the burden of cardiac amyloid load.