Abstract
2626
Introduction: The phase 3 VISION trial (NCT03511664) evaluated the efficacy and safety of lutetium (177Lu) vipivotide tetraxetan (also known as [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-167; 177Lu-PSMA-617) in patients with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Targeted radioligand therapy with 177Lu-PSMA-617 plus protocol-permitted standard of care (SoC) significantly improved overall survival and radiographic progression-free survival compared with SoC alone. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events of grade 3 or above was higher with 177Lu-PSMA-617 plus SoC versus SoC alone, but health-related quality of life and pain were not adversely affected. The VISION dosimetry sub-study aimed to quantify the absorbed dose of 177Lu-PSMA-617 in organs at risk of radiotoxicity due to exposure levels or radiosensitivity.
Methods: In this VISION sub-study, dosimetry was performed in a separate cohort of 29 eligible non-randomized participants at four German sites. Patients received SoC plus 177Lu-PSMA-617 7.4 GBq every 6 weeks for a maximum of 6 cycles (44.4 GBq maximum cumulative activity). Whole-body conjugate planar-image scintigraphy and abdominal single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) images were collected at 2, 24, 48, and 168 hours after administration in cycle 1; and at a single time point 24 or 48 hours after administration in cycles 2–6. Whole-body and specific organ absorbed doses for cycles 2–6 were derived using single time point data and time–activity curves generated for cycle 1. Red marrow absorbed doses were estimated based on assay of blood samples and the remainder of body activity from cycle 1. For cycles 2–6, the remainder of body activity was scaled according to the respective imaging data. Absorbed doses were estimated using OLINDA/EXM software version 2.2. Lacrimal gland dosimetry used the MIRD/RADAR method. Dosimetry outcomes were absorbed dose per unit acitivty (Gy/GBq) during cycle 1 and cycles 2–6, and predicted and observed cumulative absorbed dose (Gy) over all 6 cycles (44.4 GBq). Cumulative absorbed doses were predicted by extrapolation from cycle 1 doses in all patients and were measured in patients who completed all 6 cycles. Toxicity was assessed using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0.
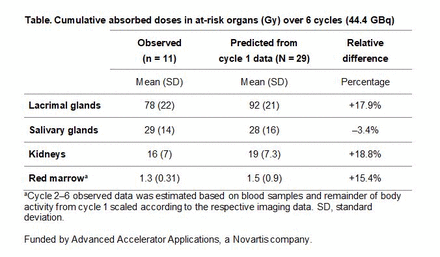
Results: Of 29 patients enrolled in the sub-study, 21 received 2 or 3 cycles, 18 received 4 cycles, 13 received 5 cycles, and 11 received 6 cycles. During cycles 2–6, the at-risk organs receiving the largest absorbed doses per cycle were the lacrimal and salivary glands, with mean values ± standard deviation of 1.80 ± 0.61 Gy/GBq and 0.63 ± 0.30 Gy/GBq, respectively; followed by the kidneys with 0.44 ± 0.21 Gy/GBq and the red marrow with 0.0310 ± 0.0071 Gy/GBq. Over all 6 cycles (n = 11), observed cumulative absorbed doses were 78 ± 22 Gy in the lacrimal glands, 29 ± 14 Gy in the salivary glands, 16 ± 7 Gy in the kidneys, and 1.30 ± 0.31 Gy in the red marrow. These values were very similar to 6-cycle cumulative absorbed doses predicted by extrapolation from cycle 1 data (N = 29) (Table). The toxicity affecting at-risk organs during cycles 2–6 was consistent with the safety profile in the main VISION study. No patient in the sub-study experienced renal toxicity of CTCAE grade ≥ 3.
Conclusions: Cumulative absorbed doses in at-risk organs over multiple cycles can be extrapolated with acceptable accuracy from cycle 1 dosimetry data in patients with mCRPC treated with 177Lu-PSMA-617. The extrapolated cumulative doses were generally slightly overestimated which is important for clinical implementation and safety. 177Lu-PSMA-617 had a good safety profile over 6 cycles with low radiotoxicity in at-risk organs. These findings suggest that cost and patient burden could be reduced by omitting dosimetry in cycles 2–6 without unduly compromising patient safety.