Abstract
83
Objectives: NR2B is the most studied NMDA receptor subunit within the NMDA receptor complex and its expression is largely limited to forebrain regions and dorsal horn of the spinal cord [1]. NR2B is considered to be a therapeutic target for schizophrenia, stroke, and neurodegenerative diseases, especially neuro-pain. Therapeutics targeting NR2B rather than the NMDA channel may have fewer side-effects [1]. The quantification of NR2B subunits could help to elucidate the involvement of this subunit and the NMDA receptor in neuropsychiatric disorders and also assist in drug development [2]. Previously, we have reported 4 PET radioligands for the NR2B subunit within NMDA receptors, namely (R) and (S) forms of [11C]NR2B-SMe and [11C]NR2B-Me [3]. The NIMH Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP) evaluated the 4 PET radioligands against the common 120 or so protein targets in brain, and found intereference from σ1, σ2, and hERG at different levels. Because sigma receptors (σ1, σ2) are physically intertwined with NMDA receptors [4], the possible influence of these receptors on PET imaging of NR2B with the mentioned radioligands was a concern. Here we aimed to assess whether NR2B-SMe had potent interaction with σ1 receptors in rat brain by challenging the PET σ1 receptor specific signal obtained in rats with the known selective radioligand, [18F]FTC146 [5]. Methods: PET imaging of brain was performed after intravenous administration of [18F]FTC146 to rats at baseline and after administration with NR2B-selective ligands, such as NR2B-SMe and Ro 25 6981, or σ1 receptor-selective ligands, such as FTC146, and BD1047 (each at 0.01−3 mg/kg, i.v. at 10 min before radioligand injection).
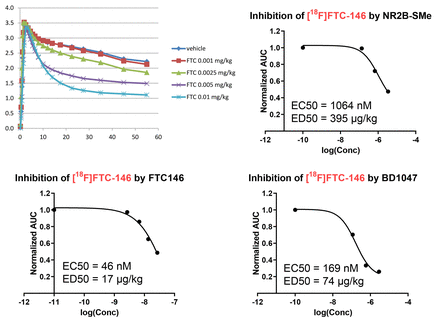
Results: The precursor of [18F]FTC146 was synthesized as reported [5]. The radiolabeling method was modified from its original report, and the radioligand was obtained in 4−6% yields from cyclotron-produced [18F]F- and with a radiochemical purity of >98% and a mean molar activity of 76 GBq/μmol. PET imaging of [18F]FTC146 in rats at baseline showed moderately high brain radioactivity uptakes, reaching 4-5 SUV at 5 min (Figure). Pre-blocking with self, BD1047, a NR2B-selective ligand, either Ro 25 6981 or NR2B-SMe, were similarly effective (up to 95%) (Figure), but with markedly different ED50 values of 46 nmol/kg for FTC146, 169 nmol/kg for BD1047, and 1064 nmol/kg for NR2B-SMe. (Figure. The whole brain PET time activity curves in rats at baseline, preblocking using different dose of FTC146, and dose-response curves for NR2B-SMe, FTC146, and BD1047.)
Conclusions: The σ1 receptor-selective radioligand [18F]FTC146 was used in PET imaging of rat brain. It showed high brain uptake, which could be pre-blocked by self, a σ1 receptor ligand BD1047, and a NR2B-selective ligand NR2B-SMe, but at markedly different ED50 values. The ED50 for avidly brain-penetrant NR2B-SMe gave by far the highest value, implying only weak interaction with σ1 receptors. Influence of σ1 receptors on the PET imaging of NR2B receptors with [11C]NR2B-SMe is therefore likely negligible. Research Support: Intramural Research Program of the National Insitutes of Health (NIMH). References: [1] Zhuo M, Neuropharmacology, 2017, 112, 228. [2] Kassenbrock A, et al., Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016; 16, 1830. [3] Cai L et al., J. Nucl. Med. 2020, In press. [4] Pabba M and Sibille E. Mol. Neuropsychiatry, 2015, 1, 47. [5] James ML et al., J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8272.