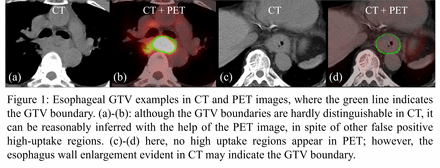
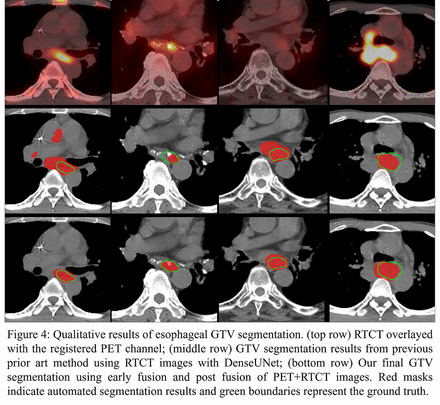
Abstract
498
Objectives: Accurate delineation of gross tumor volume (GTV) is the decisive step in esophageal cancer radiotherapy. Physicians refer to high contrast from positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) and manually delineate GTV on radiation therapy computed tomography (RTCT). However, 18F-FDG PET/CT has not been well-explored for computer-based automated esophageal GTV delineation. In this work, we aim to utilize the complementary information of 18F-FDG PET and RTCT to facilitate the automated GTV delineation task in the esophageal cancer treatment.
Methods: We curated a dataset of diagnostic 18F-FDG PET/CT, RTCT images and 3D GTV masks from 110 patients with stage II or greater esophageal cancer and undergoing radiotherapy. We propose a two-stream 3D deep network fusion pipeline to segment esophageal GTV using 18F-FDG PET and RTCT. First, we align the PET image to RTCT through the registration of PETCT to RTCT using the B-spline based deformable registration algorithm with a robust anatomy-based initialization. Next, we trained a two-stream pipeline that combines and merges predictions from two independent sub-networks, one only trained using the RTCT and one trained using both RTCT and aligned PET images. The former exploits the anatomical contextual information in CT, while the latter takes advantage of PET sensitivity. The predictions of these two streams are then deeply fused together with the original RTCT to provide a final GTV prediction. Furthermore, a 3D progressive holistically nested network (PHNN) model is adopted for effective fusion and segmentation. Five-fold cross-validation is used to fully evaluate our method.
Results: The proposed two-stream 3D deep network fusion method using 18F-FDG PET and RTCT modalities has achieved 0.755±0.148 Dice score (DSC) and 4.7±5.2 cm Hausdorff distance (HD). It significantly outperforms the previous leading RTCT based esophageal GTV segmentation method, i.e. DenseUnet by 10% DSC increase and 8.2 cm HD reduction.
Conclusions: Our work demonstrates that the 18F-FDG PET images can be effectively integrated with RTCT to better segment the esophageal GTV using a two-stream 3D deep network fusion method. We provide significant and tangible improvements compared to the recent RTCT-based representative work, which represents a step forward toward reliable and automated esophageal GTV segmentation.