Abstract
1620
Purpose: 18F-FDG PET/CT is an emerging tool for the evaluation of Takayasu’s Arteritis, (TAK) but its wide application is limited by the lack of reliable quantitative criteria for inflammatory activity assessment. The purpose of this study is to assess and compare the performance of novel criterion PETVAS with traditional criteria SUVmax and inflammatory biomarkers (PTX-3, CRP, ESR) in a TAK patient cohort.
Methods: A total of 64 PET/CT scans acquired from 54 TAK patients were analyzed in this study. Their inflammatory activity was qualitatively determined (active/non-active) by physician’s global assessment and quantitatively scored by ITAS-2010 scoring system. These two criteria were set as relative gold standard. SUVmax and PETVAS were determined by consensus review. Levels of PTX-3, CRP and ESR were measured by ELISA, immunoturbidimetric assay and Westergren method, respectively. The performance of qualitative diagnosis was compared by using receiver operating characteristic curve. The quantitative correlation was assessed using the Spearman correlation coefficient.
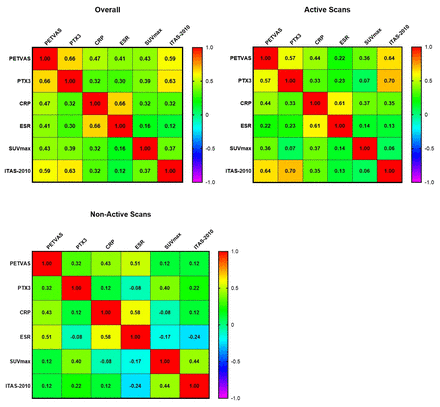
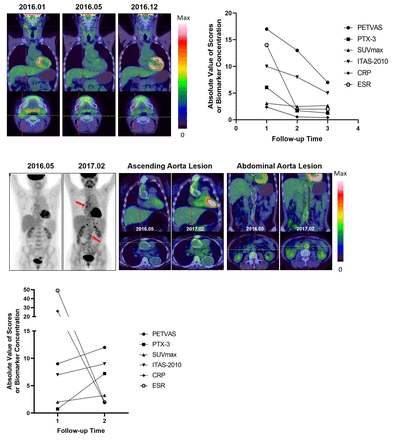
Results: The biomarkers (CRP, ESR, PTX-3), PET uptake values (SUVmax, PETVAS) and ITAS-2010 scores were all significantly higher in active group than those in non-active group. The area under curve and Youden Index of PETVAS and PTX-3 were respectively higher than those of SUVmax, CRP, ESR and ITAS-2010 (Figure 1, Table 1). At the cutoff value of 8.50 and 1.303, PETVAS and PTX-3 respectively achieved optimal sensitivity/specificity of 76.5%/83.3% and 85.3%/80.0%. PETVAS and PTX-3 respectively had a higher spearman correlation coefficient with ITAS-2010 than other criteria, among all the patients or within the active group (Figure 2). The numerical alteration trends of PETVAS and PTX-3 during follow-up were qualitatively consistent with clinical progress or remission, while other criteria could be observed to have certain degrees of misjudgment (Figure 3).
Conclusions: In TAK evaluation, the global inflammatory burden criterion PETVAS is superior in qualitative active/non-active determination and quantitative inflammatory activity assessment, compared with SUVmax. Inflammatory biomarker PTX-3 has a comparable performance as well as a good correlation to PETVAS and ITAS-2010, which is superior to CRP and ESR. These findings demonstrate the superiority of the assessment strategy of PETVAS + PTX-3 compared with the SUVmax + CRP/ESR strategy.
Qualitative Diagnostic Performance of TAK Criteria