Abstract
558
Objectives: 18F- fluciclovine (fluciclovine) is a synthetic amino acid PET radiotracer that is transported via amino acid transporters, including LAT1 which has been shown to be upregulated in endometrial, cervical and ovarian cancer cells. Compared to FDG, fluciclovine has low urinary bladder excretion allowing better target to background ratios for viewing pelvic structures. Fluciclovine is currently FDA approved for imaging PSA recurrent prostate cancer. The utility of fluciclovine in PET/CT imaging of gynecological (GYN) cancers is yet to be explored. The aim of this study is to evaluate the uptake characteristics of fluciclovine in PET/CT imaging of endometrial, cervical and ovarian GYN cancers and its feasibility for potential use in clinical imaging.
Methods: This is a prospective clinical study enrolling 30 women with biopsy proven endometrial (n=10), cervical (n=10), and ovarian (n=10) GYN cancer (initial or recurrence) prior to therapy. After the IV injection of average dose of 8.7 (±0.8) mCi fluciclovine, dual time point fluciclovine PET/CT scans were acquired from the proximal thigh to the skull base using 2 mins/bed position at 4 min (early) and at 24 mins (delay) post injection. Fluciclovine uptake was then quantified in target lesions using SUVmax and compared to SUVmean of background structures; abdominal aorta (at the bifurcation), bone marrow (L3), and liver. In relation to background structures, all lesions with sustained moderate (≥ marrow but < liver) to intense (≥ liver) uptake from early to delay images were considered positive for disease. The tumor SUVmax and background (bone marrow) SUVmean were recorded and analyzed.
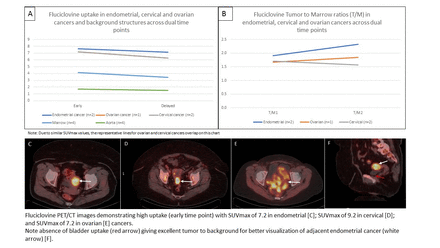
Results: The initial 4 women enrolled with an average age (range) of 62 (42-71) years had a total of 5 biopsy proven lesions. Details of location and histology findings can be found in Table 1. All lesions demonstrated down trending time activity curve from early to delay images. However, uptake was constantly higher than background. Average SUVmax (early, delay) was highest in endometrial (7.7, 7.2) followed by cervical (7.2, 6.3) and ovarian cancers (7.2, 6.3). The average ratios (±SD) of tumor SUV max to marrow SUV mean across early and delay time points are 1.9 (±0.2), 2.3 (±0.8) for endometrial, 1.7 (±0.7), 1.6 (±0.4) for cervical, and 1.7, 1.6 for ovarian cancers.
Conclusions: Initial data on fluciclovine uptake in known endometrial, cervical and ovarian GYN cancer demonstrates sustained higher uptake above background over time. Further prospective feasibility and uptake characterization studies are currently ongoing.