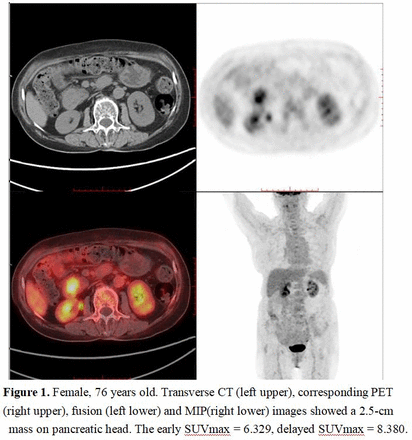
Abstract
472
Purpose: To investigate the FDG PET/CT features of pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma (PASC) in contrast with conventional pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Patients and Methods: Patients with PASC or PDAC confirmed pathologically, who underwent FDG PET/CT, were retrospectively searched from the database in our hospital. PASC group included ten patients. Twenty-three patients with conventional PDAC were randomly selected as control group. Maximum standardized value (SUVmax) was measured.
Results: All lesions of PASC group showed intense FDG uptake, and SUVmax was significantly higher than conventional PDAC at both the early PET/CT phase (10.30±5.30 VS 7.28±6.30, p=0.077) and delayed phase (12.94±6.19 VS 8.69±5.40, p=0.044). The mean retention index (RI) , calculated by ([PET120min SUVmax] - [PET 60min SUVmax] ÷ PET 60min SUVmax ×100%), was significantly higher than conventional PDAC (27.53%±6.31% VS 15.84% ± 8.06%, p=0.026). Three lesions of PASC group showed heterogeneous FDG uptake, while none of 23 lesions in PDAC group showed heterogeneous ( p=0.833). Conclusions: FDG uptake of PASC is more intense than conventional PDAC, and the RI value was also higher than conventional PDAC,which may be helpful for differentiation. FDG uptake of a few PASC is heterogeneous.