Abstract
434
Objectives: Innovative radiation therapy strategies are needed to effectively treat advanced acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in older patients, since toxicity may preclude high dose myeloablative radiation for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT). We show that re-induction and targeted myeloablation using Iodine (131I) apamistamab(Iomab-B) an anti-CD45 antibody for HCT can be achieved without exceeding dose-limiting organ toxicities or potentially damaging doses to marrow stroma that could delay engraftment after transplant. High interpatient variation in radiolabeled antibody kinetics make it necessary to incorporate patient-specific measurements for normal organ dosimetry. Current patient data from an ongoing SIERRA phase III clinical trial was reviewed to ascertain to what extent personalized dosimetry provided therapeutic safety while minimizing dose-related normal organ toxicities, including failure-to-engraft transplant complications.
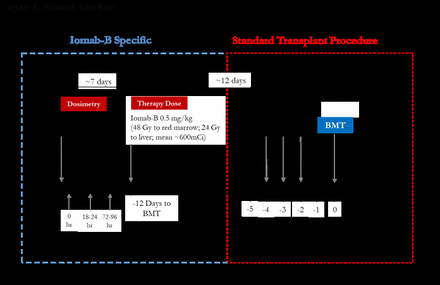
Methods: Results from the first 25% of patients enrolled in SIERRA phase III trial are presented. Based on the schedule in Figure 1, 38 patients with median age 63 (range 55-76) with active, relapsed or refractory AML were administered tracer dose of Iomab-B (260 to 740 MBq, or 7 to 20 mCi) and underwent gamma camera imaging to evaluate individual biokinetics and normal-organ radiation dose. Images were acquired prior to (for attenuation correction) and immediately after Iomab-B infusion, at 18-24 h, and 72-96 hours post-infusion including chest and abdomen region. Methods were consistent with recommendations of the Medical Internal Radiation Dose committee. Therapy infusion levels were limited to maximum liver doses of 24 Gy and red marrow dose of 48 Gy.
Results: The mean red marrow uptake (and standard deviation) of Iomab-B was 17.3% ±7.0% of injected I-131 activity (range 5.7% to 36%). Iodine-131 clearance from red marrow followed single-exponential clearance kinetics with a mean disappearance half-time of 47.7 ±22.6 hours (range 29.4 to 172 hours). Calculated absorbed doses to red marrow averaged 0.724 ±0.297 mGy per MBq (2.68 ±1.1 centigray per millicurie) administered activity (range 0.27 to 1.75 mGy/MBq or 1.0 to 6.49 cGy/mCi). Therapy-infused I-131 activities averaged 27.2 GBq (736 mCi) and calculated red marrow absorbed doses after Iomab-B therapy averaged 18.6 ±7.87 Gy (range 6.54 to 42.4 Gy). All patients with data available (N=28) engrafted both in the Iomab-B arm (N=18) and in the cross over to Iomab-B group (N=10) as shown in Table 1.
Conclusions: Gamma camera imaging based dosimetry allows for normal organ dose estimations and patient specific dosimetry for high-dose iodine-131-IOMAB immunotherapy in advanced acute myelogenous leukemia patients. Variable iodine-131-Iomab uptake and clearance from liver and red marrow led to large variations in planned Iomab-B therapy doses. Re-induction and targeted conditioning using high-dose Iomab-B prior to hematopoietic stem cell transplant in patients with AML facilitated engraftment in all patients in this preliminary analysis. Support. Phase III clinical trial supported by Actinium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., New York.