Abstract
1466
Objectives: To evaluate the relationships among tau protein deposition, glucose metabolism and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and explore the pathogenesis of AD.
Methods: From April 2016 to April 2018, 40 patients with AD were enrolled in our study; they were 51-82 years of age (mean age, 63.8 years) and included 15 males and 25 females. The MMSE score range was 0-27 (mean 13.6). All patients underwent 18F-FDG, 18F-AV1451 and amyloid imaging, and amyloid imaging of all patients was positive. The cerebrum was divided into 90 brain regions withananatomical automatic labeling (AAL) template asareference. The standardized uptake ratios (SUVRs) of 18F-FDG and 18F-AV1451 PET imaging in each brain region were calculated. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to correlate the two types of imaging results with the corresponding MMSE value.
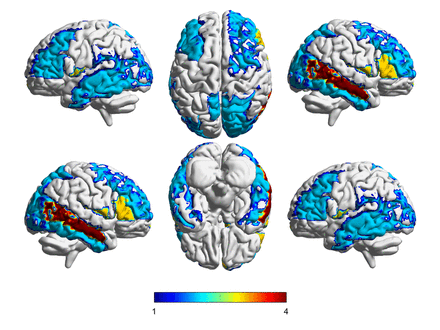
Results: In 18F-FDG imaging, the SUVRs of 44 brain regions were positively correlated with the corresponding MMSE score (r=0.32-0.63, p<0.05)「Fig.1」. In 18F-AV1451 imaging「Fig.2」, the SUVRs of 13 brain regions were negatively correlated with MMSE scores (r=0.31-0.42, p<0.05), while the SUVRs of the bilateral hippocampus, thalamus and caudate nucleus were positively correlated with MMSE values (r=0.32-0.48, p<0.05). Visual observation showed that 18F-AV1451 imaging was complementary to 18F-FDG imaging. Pearson correlation analysis demonstrated that the SUVRs of the two imaging types in 24 brain regions were negatively correlated (r=0.34-0.53, p<0.05)「Fig.3」, and the SUVRs of the right frontal lobe, the right temporal lobe and the right occipital lobe were strongly negatively correlated with one another (r>0.5).
Conclusions: Glucose metabolism and tau protein deposition in some brain regions are associated with MMSE scores in patients with AD. There was a negative correlation between glucose metabolism and tau protein deposition distributed in some regions of the bilateral cerebral cortex.