Abstract
132
Objectives: Determination of the target-binding fraction, also referred to as the immunoreactive fraction is a critical quality attribute of antibody-based radiopharmaceuticals in the preclinical as well as clinical setting. This critical parameter is routinely assessed using cell-based assays, which are not only cumbersome, but also prone to inconsistencies arising from several intrinsic and extrinsic factors. To overcome these limitations, we report a simple, rapid and reproducible cell-free quantitative method of analysis for the determination of the target-binding fraction (TBF) of radiopharmaceuticals.
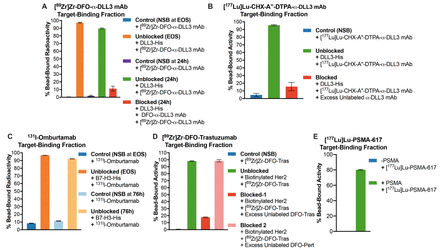
Methods: To overcome the limitations of cell-based assays, we adopted and modified a method previously reported by Zhou et al1. Briefly, we used 20 μL of commercially available 1-micron diameter magnetic beads that are functionalized with either Ni-NTA (Nickel-Nitrilotriacetic acid) or streptavidin. The beads were incubated with 1 μg of poly-histidine-tagged or biotinylated target antigen of choice (DLL3, B7-H3, Her2, PSMA) for 15 min at room temperature, followed by washing with 500 μL of PBS containing 0.05% Tween-20 (PBS-T). Thereafter, 1 ng of the radiolabeled antibody or small molecule radioligand was incubated with the beads for 15 mins. The beads were isolated using a magnet and washed twice with 500 μL of PBS-T. The supernatant and washes were collected for analysis. Finally, the beads, supernatant and washes were measured for radioactivity on a gamma counter. Separate control groups were included in our assays to account for non-specific binding (beads with no target antigen coated) and to validate the specificity of binding (antigen-coated beads co-incubated with a huge excess of unlabeled ligand). The TBF was determined by quantifying the percentage of activity associated with the magnetic beads and accounting for any non-specific binding (NSB).
Results: Using our method with a wide variety of radioligands and their cognate target antigens yielded excellent, reproducible and high (>90%) values for TBFs. Our method of analysis yielded consistent and reliable results regardless of the type of radioisotope or the class of molecules - antibodies or small molecules including PSMA-617 - that were used in the assay. Specifically, we obtained high and comparable TBFs for a DLL3-targeting antibody radiolabeled with 89Zr as well as 177Lu. Unlike cell-based assays with 131I-labeled Omburtamab, which yielded 70% TBF at end of radiosynthesis (EOS) and 50% TBF at 76 h post-radiosynthesis, our assay consistently yielded >90% TBFs at EOS as well as 76h post-radiosynthesis. Furthermore, the specificity of 131I-labeled Omburtamab binding to B7-H3 was confirmed by substituting it with 89Zr-labeled Pertuzumab instead. The binding of 89Zr-labeled Pertuzumab to B7-H3 was 4%, which was comparable to the NSB of 131I-labeled Omburtamab to the beads in the negative control. Most notably, the entirety of our assay including the analysis of data obtained from gamma counting could be completed within 2 hours. In all the cases that were tested, the degree of NSB was low, and the specificity of radioligand binding could be established by blockade with a huge excess of unlabeled ligand.
Conclusions: In light of the limitations posed by cell-based assays, we propose that where and when possible, it might be ideal to immobilize purified target antigen on a solid phase such as Ni-NTA or streptavidin functionalized magnetic beads to quantify the TBF of radiopharmaceuticals. Our simple and rapid method yields reliable and reproducible results whilst improvising and extending the scope of previously described bead-based radioimmunoassays. References: 1 Zhou, Z. et al. Fluorine-18 Labeling of the HER2-Targeting Single-Domain Antibody 2Rs15d Using a Residualizing Label and Preclinical Evaluation. Mol Imaging Biol 19, 867-877, doi:10.1007/s11307-017-1082-x (2017).