Abstract
345
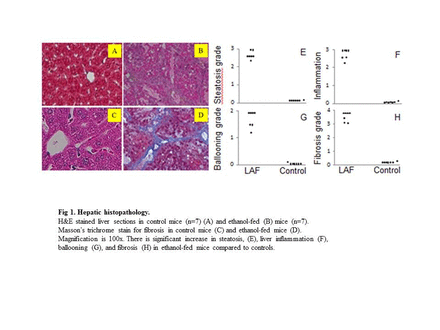
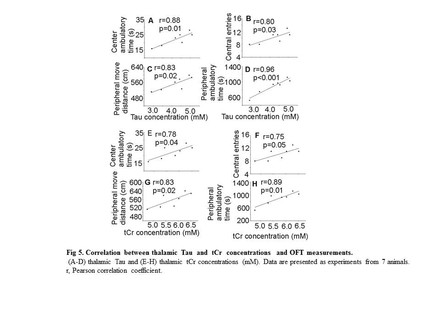
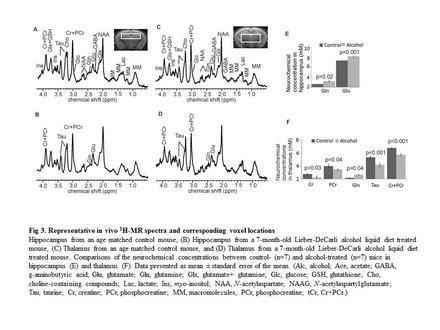
Background: Minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE) is highly prevalent, observed in up to 80% of patients with liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. MHE is defined as HE with cognitive deficits and no grossly evident neurologic abnormalities, thus brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) usually plays no role in diagnosis of MHE. Clinical management is usually delayed due to the lack of in vivo non-invasive quantitative imaging technology needed to reveal changes in brain neurobiochemical biomarkers. Aim: To gain insight into the development of alcoholic liver fibrosis (ALF)-induced MHE, a mouse model of ALF was used to investigate changes in neurochemical levels in the thalamus and hippocampus that relate to behavioral changes. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) of the brain and behavioral testing were performed to determine neurochemical alterations and their relationships to behavioral changes in ALF. Findings: MRS quantification data demonstrated glutamine levels were higher in both the thalamus and hippocampus of alcohol-treated mice than in controls. Thalamic levels of taurine and creatine were significantly diminished. Open field test identified significant depression in ALF mice compared to controls. Further correlation analysis found strong correlation of alcohol-induced behavioral changes with decreased levels of taurine and creatine in thalamus. In addition, brain MRI identified no anatomic structural damage, but significant neuron degeneration, astrocytosis, and neuroapoptosis in thalamus were found by histopathological, immunohistochemistry, and TUNEL analysis. Lastly, decreased taurine and creatine in livers of ALF mice by HPLC may at least in part contribute to the alteration of thalamic taurine and creatine. In conclusion, chronic long-term alcohol consumption gives rise to ALF, neurochemical changes in the nuclei, and behavioral changes which may be linked to MHE. MRS represents a sensitive and noninvasive measurement of pathological alterations in the brain, which may provide insight into the pathogenesis underlying the development of MHE.