Abstract
1098
Objectives: Drug-induced pneumonitis is a serious and unpredictable side-effect in patients with lymphoma after chemotherapy. In the past, drug-induced pneumonitis was diagnosed on the basis of respiratory symptoms and chest CT. Recently, 18F-FDG-PET/CT has been used as a standard in assessing patients with lymphoma, especially diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Sometimes, we found new-onset pulmonary lesions in the PET/CT assessment, but the patient had no respiratory discomfort. After exclusion of other possibilities such as infection or lymphoma involvement, some of these patients were diagnosed as drug-induced pneumonitis finally. The aim of this study is to evaluate 18F-FDG-PET/CT in early detecting drug-induced pneumonitis in patients with lymphoma after chemotherapy .
Methods: 234 patients with lymphoma after chemotherapy receiving PET/CT assessment were reviewed retrospectively. None of them had pulmonary lymphoma or other pulmonary diseases before chemotherapy. After exclusion of other possibilities,these patients with newly-onset pulmonary lesions diagnosed as chemotherapy-induced lung injury were enrolled in the study. Their clinical and serial imaging data were evaluated.
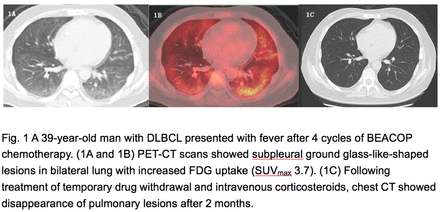
Results: Ten patients (8 men and 2 women, median age 55.0)were finally diagnosed as chemotherapy-induced lung injury,all of which diagnosed as DLBCL. The chemotherapy regimens included R-CHOP (4 cases), R-EPOCH (2 cases), BEACOP (1 case), R-BEACOP (1 case), R-GDP (1 case), and cladribine (1 case),. Five patients had symptoms including fever, breathless, and cough. Others remained asymptomatic during follow-up. PET/CT scans revealed multiple signs such as ground glass-like changes, reticular pattern, patchy shadows, and consolidation. Eight patients showed bilateral lung injury and 2 showed unilateral lung injury. FDG uptake was mild to moderate with maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) from 1.33 to 4.83, standardized uptake ratio-mediastinal blood pool (SUR-BP) was 0.88 to 4.09. We observed that the lesions in patients with clinical symptoms had a relatively higher FDG uptake, with SUVmax from 1.67 to 4.83, median SUVmax3.73, SUR-BP 1.23~4.09, and median SUR-BP 2.66, compared to others having lower uptake, with SUVmax from 1.33~3.33, SUR-BP 0.88~2.30, and median SUR-BP 1.31. Their clinical characteristics and FDG uptake of the pulmonary lesions were described in Table 1. After treatment with temporary drug withdrawal and intravenous corticosteroids, chest CT showed that the pulmonary lesions were relieved obviously in all patients(Figure 1).
Conclusion: PET/CT scan could detect drug toxicity of lungs in asymptomatic patients with lymphoma. Possibly there is a positive correlation between the degree of FDG uptake and respiratory symptoms, and we need more research to confirm it.
Table 1 The clinical characteristics and FDG uptake of the pulmonary lesions in 10 patients