Abstract
509
Objectives Left atrial fibrosis is a prominent feature in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and the degree of fibrosis as measured by delayed enhancement magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has prognostic and therapeutic implications. However, MRI imaging of the thin-walled left atrium can be technically challenging and is prone to artifacts. FDG-PET has the potential to assess left atrial fibrosis as the absence of metabolism. In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of assessing left atrial fibrosis using FDG-PET and compare the degree of fibrosis in clinically-referred patients in sinus rhythm and AF.
Methods 28 patients in sinus rhythm and 31 with paroxysmal AF were randomly selected from patients undergoing FDG-PET myocardial viability assessment from 2013 to 2015. Gated rest Rb-82 and F-18 FDG-PET imaging with CT attenuation correction were performed. Images were manually segmented to isolate the left atrium. Volumetric assessment was performed over all vertical long axis, horizontal long axis, and short axis images to visually score extent of FDG uptake on a semi-quantitative basis. The extent of FDG uptake defects was defined as small or normal (<10%), medium (10-30%), large (31-50%), and extensive (>50%).
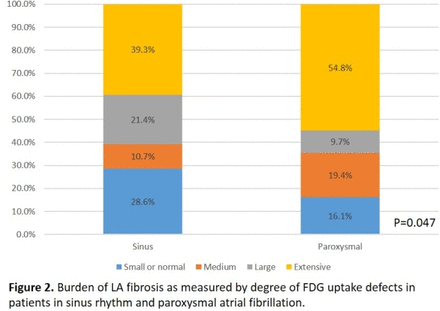
Results Images for the classification of FDG uptake defects are shown in Figure 1. In patients in sinus rhythm, 8 (28.6%) patients were classified as having small or normal FDG uptake defects, 3 (10.7%) with medium, 6 (21.4%) with large, and 11 (39.4%) with extensive. In patients with paroxysmal AF, 5 (16.1%) had small or normal FDG uptake defects, 6 (19.4%) had medium, 3 (9.7%) had large, and 17 (54.8%) had extensive defects. Overall, patients with paroxysmal AF had more FDG uptake defects than those in sinus rhythm. (P<0.05) (Figure 2).
Conclusions FDG-PET appears capable of assessing left atrial myopathy in patients with and without AF. Patients with AF have a higher burden of left atrial fibrosis compared to those in sinus rhythm. Further research is required to determine if FDG-PET can be used to identify those at risk for developing AF or predict therapeutic response to ablation.