Abstract
611
Objectives White matter (WM) microstructural changes involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD)1 can be characterized with diffusion MRI models2-4. Here we assess correlations of WM Tract Integrity (WMTI) model with amyloid load and hippocampal volume (HV) in normal controls (NC) and aMCI.
Methods Subjects (8 NC, 5 aMCI, 1 AD, age-matched) were scanned on a 3T MR-PET system. A PET image was acquired 40 min after injection of 18F-Florbetapir. An anatomical MR image provided structural segmentation. The SUV in six cortical areas, normalized to the cerebellum, provided mean cortical SUVr5. Diffusion-weighted images yielded parametric diffusion maps6, and mean values in WM ROIs involved by AD7-9 (Fornix (Fx), Cingulum, Uncinate Fasciculus, Corpus Callosum, Superior Corona Radiata) were extracted. Pearson correlations are reported.
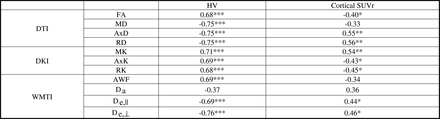
Results All WM ROIs show significant correlations of diffusion metrics (especially De,⊥ and AWF, markers of demyelination and axonal damage) with HV. Metrics in the Fx Crus also correlate with amyloid load (Table and Fig.1).
Conclusions In a population of NC and aMCI, metrics of chronic axonal degeneration in WM ROIs spatially connected to the hippocampus and cortex correlate significantly with metrics of gray matter AD pathology. Future work involves comparison between NC and aMCI, and investigation of the spatial-temporal progression of AD pathology10.
Research Support Research was supported by the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation.
Correlation coefficients of diffusion metrics in the Fx Crus with HV and cortical SUVr.
*: p<0.05 **: p<0.01; ***: p<0.001. DTI/DKI: Diffusion Tensor/Kurtosis Imaging; FA: Fractional anisotropy; M/Ax/R-D/K: Mean/axial/radial diffusivity/kurtosis; AWF: Axonal water fraction; Da: Axonal diffusivity; De,||/De,⊥: Extra-axonal axial/radial diffusivity.