Targeting β-cells: Ichise and Harris provide an overview of current developments in β-cell biomarkers and radionuclide-based techniques under investigation to image β-cell mass and function.
Page 1001
Challenges in reversible ligands: Slifstein looks at receptor-binding radioligands that are not conducive to conventional PET quantification and at solutions that kinetic modelers use to address this problem, including a novel approach in an article in this issue of JNM.
Page 1005
PET/CT enterography in Crohn disease: Groshar and colleagues combine 18F-FDG PET and CT enterography in a single examination and correlate PET tracer uptake with CT enterography patterns of disease activity in patients with Crohn disease.
Page 1009

PET/CT in hyperglycemia and diabetes: Rabkin and colleagues assess whether the rate of detection of suspected infectious and inflammatory processes with 18F-FDG PET/CT is adversely affected by hyperglycemic or diabetic patient status.
Page 1015
Novel H3 receptor radioligand: Ashworth and colleagues evaluate a highly potent, selective, and brain-penetrating histamine H3 receptor as a PET radioligand and elucidate the dose–receptor occupancy relationship of this tracer in the human brain.
Page 1021

GABAergic dysfunction in essential tremor: Boecker and colleagues use 11C-flumazenil PET to calculate the availability of benzodiazepine receptor sites of the γ-aminobutyric acid complex in controls and patients with bilateral essential tremor.
Page 1030

β-blockade and adenosine MPI: Reyes and colleagues investigate the effect of oral β-blockers on the presence, extent, and severity of myocardial perfusion abnormality induced by adenosine in patients with coronary artery disease.
Page 1036

SPECT/CT and LVAD infection: Litzler and colleagues report experience with integrated molecular and anatomic hybrid imaging to assess infection in patients with left-ventricular-assist devices.
Page 1044

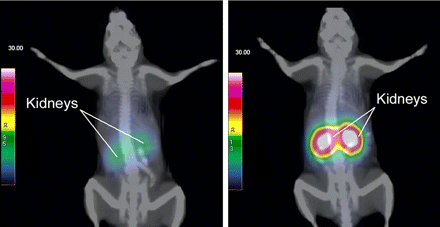
Renal toxicity in radionuclide therapy: Vegt and colleagues provide an educational overview of mechanisms of renal accumulation, techniques to reduce kidney damage, and nephrotoxicity risk factors in peptide-receptor radionuclide therapy and antibody fragment radioimmunotherapy.
Page 1049
GLP-1 receptor PET and SPECT: Wild and colleagues describe the preclinical evaluation of exendin-4–based radiopharmaceuticals for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor PET/CT and SPECT/CT and discuss the potential for improved localization of small insulinomas.
Page 1059
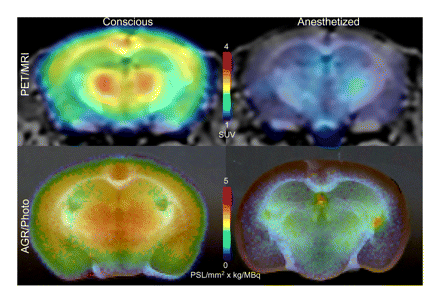
Brain PET in conscious mice: Mizuma and colleagues detail the development of an in vivo PET imaging system for conscious mice and demonstrate its use in determining physiologic regional cerebral glucose metabolic rates.
Page 1068
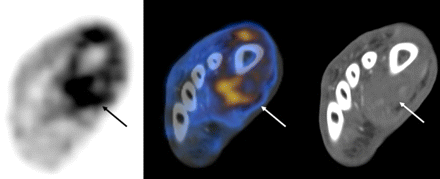
PET and hypoxia in head and neck tumors: Hoeben and colleagues report on small-animal studies to determine whether a novel radiolabeled monoclonal antibody can allow early, noninvasive PET of hypoxia in head and neck tumor xenografts.
Page 1076

111In-NLS-trastuzumab RIT: Costantini and colleagues evaluate in mice the tumor growth–inhibitory properties and normal tissue toxicity of this agent combining trastuzumab with an Auger electron-emitting radionuclide to enhance HER2-targeted immunotherapy of breast cancer.
Page 1084
dCK-specific PET probes: Shu and colleagues describe the development of PET probes with improved metabolic stability and specificity for deoxycytidine kinase, a rate-limiting enzyme in the deoxyribonucleoside salvage pathway and a determinant of therapeutic activity in several prodrugs.
Page 1092

Tumor targeting of a humanized nanobody: Vaneycken and colleagues present a novel strategy to quickly generate humanized Nanobodies for molecular imaging and discuss the potential for improved targeting of cellular antigens.
Page 1099
MMP imaging in aneurysms: Razavian and colleagues investigate in a mouse model whether SPECT/CT imaging of matrix metalloproteinase activation in aneurysms helps to predict propensities for expansion.
Page 1107
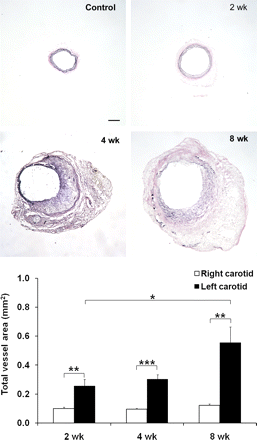
Tenascin-C in myocardial ischemia: Taki and colleagues explore serial changes in expression of this extracellular matrix glycoprotein after myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in mice and describe the potential for monitoring myocardial injury and repair.
Page 1116

Cerenkov imaging of medical isotopes: Ruggiero and colleagues report on the use of inherent optical emissions from decay of radiopharmaceuticals for Cerenkov luminescence imaging of tumors in vivo and correlate results with those from immuno-PET studies.
Page 1123

Second-generation Affibody molecules: Ahlgren and colleagues assess the potential effects of reengineered and optimized Affibody molecules on HER2 targeting, using 111In-ABY-025, a novel tracer.
Page 1131
64Cu-DOTA-PEG diabody: Li and colleagues describe the development of a monodispersed DOTA-PEG–conjugated anti-TAG-72 diabody with low kidney uptake and high tumor-to-blood ratios resulting in improved 64Cu PET.
Page 1139
Dynamic PET denoising: Christian and colleagues introduce a modified and highly constrained backprojection method for processing dynamic PET studies, with documented performance in phantom and small-animal scans.
Page 1147
131I RIT dose and response: Dewaraja and colleagues perform fully 3D dosimetry, coupling SPECT/CT at multiple time points with Monte Carlo–based voxel-by-voxel dosimetry to examine dose–response in patients undergoing 131I-tositumomab treatment for refractory B-cell lymphoma.
Page 1155
ON THE COVER
PET is generally conducted under anesthesia in laboratory animals to restrict movement, but it is important for animals to be conscious during physiologic brain imaging studies. The brain images displayed here, obtained with a new in vivo imaging system for conscious mice, show clear and well-correlated regional uptake of 18F-FDG for both PET and ex vivo autoradiography.
See page 1072.