Abstract
636
Objectives: It is unclear which asymptomatic patients with ≥ 70% diameter carotid stenosis may benefit from carotid endarterectomy (CEA) intervention. We have identified a natriuretic peptide receptor (NPRC) that is present in deep intimal macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells and is up-regulated in plaque with features of instability. We have developed a nanoparticle radiotracer, 64Cu-CANF-Comb, directly targeting this receptor. We hypothesize that uptake of this radiotracer will correlate with both presence of NPRC on immunohistochemistry (IHC) of ex vivo carotid specimens in patients who went on to CEA surgery, and to features of instability (large lipid pool, hemorrhage).
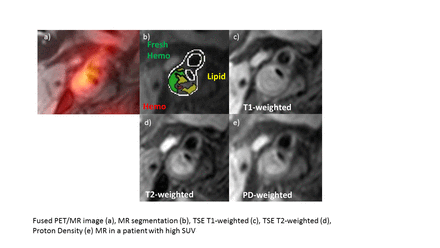
Methods: Fourteen patients (average age 73.5, range 60-85 years; 7 men, 7 women) scheduled for CEA underwent carotid PET/MRI imaging approximately 18 hours after injection of 3.5-5.1 mCi 64Cu-CANF-Comb. PET acquisition was list mode for ~ 30 min. MR imaging consisted of high-resolution (0.5-0.7 mm) bright blood 3D GRE, T2 3D SPACE, dark blood TSE T1, and T2/PD imaging using small neck surface coils. CEA specimens were collected post surgery for IHC. Eight specimens were stained with an antibody (anti-NPRC, 1:100 in blocking serum) and a secondary antibody labeled with a blue chromogen and counterstained with nuclear fast red. Five 100X random fields were randomly selected in the superficial intima, deep intima and media of the specimens. NPRC positive cells were counted in each field, and an average was derived for the 15 fields. A supervised classifier software program in Matlab was developed to segment the carotid MR images to determine the maximal morphological component (calcium, fibrous cap, lipid pool, hemorrhage). Highest PET SUV of plaque was compared to NPRC readout on IHC and to primary plaque component on MRI.
Results: Highest SUV in the region of carotid stenotic plaque removed for CEA across subjects (N=8) ranged from 0.27-2.72, mean 1.18 (SD .82) and showed strong correlation with IHC presence of NPRC, r= 0.90, 95% CI (0.501, 0.980), P = 0.002. NPRC presence on IHC was highest in the deep intima. On MRI, SUV showed strong correlation with percent plaque volume of combined lipid rich necrotic core and hemorrhage, r= 0.90, 95% CI (0.469, 0.986), P = 0.007 (N=7).
Conclusions: We have translated a receptor-targeted PET radiotracer, 64Cu-CANF-Comb, into human subjects and show that PET uptake correlates with plaque expression of NPRC, the receptor it targets. This receptor is expressed in deep intimal macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells in carotid plaque with features of instability.