Abstract
1580
Introduction: Current adult gastric emptying studies in the United States use a “standard” meal consisting of two eggs, two pieces of toast with jelly, and 120mL of water. Use of this meal and the defined standards for normal gastric emptying in adults are often applied to the pediatric population. To date, no study has assessed the suitability of these standards for children. Furthermore, tolerance of the complete adult standard meal in children varies due to factors including food allergies, cultural factors and patient preference. Alternative meals have been developed in response to these needs, including the development of cheesed-based meals that maintain good radiotracer binding throughout the entire study duration. Although assessment of normative values for each individual meal type would be ideal, ethical and pragmatic considerations prevent such a study to be performed in the pediatric population. Thus, the goal of this study was to assess the suitability of applying the normal gastric emptying criterion for a complete adult meal (<10% by 4 hours post meal ingestion) for the pediatric population and extending the use of this criterion to non-standard cheesed-based meals.
Methods: This IRB-approved retrospective study analyzed data from all pediatric patients who underwent gastric emptying scintigraphy between 9/2013 and 9/2019 at Boston Children’s Hospital (n = 1151). Patients who consumed the complete adult standard meal and non-standard cheesed-based meals (Table 1) were identified for further analysis. The standard gastric emptying protocol with gastric retention values calculated from images acquired at 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4 h (as necessary) were performed for all studies. Patients were divided into normal and delayed gastric emptying based on the adult criterion of <10% gastric retention by 4 hours post meal ingestion. Gastric retention at all time points were compared between cheese-based non-standard meals and the complete standard meal. Meal-dependent differences in gastric emptying with respect to age and sex were also compared. Descriptive statistics were calculated at all time points for each meal. The Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney non-parametric tests were performed as appropriate, with p<0.05 deemed statistically significant.
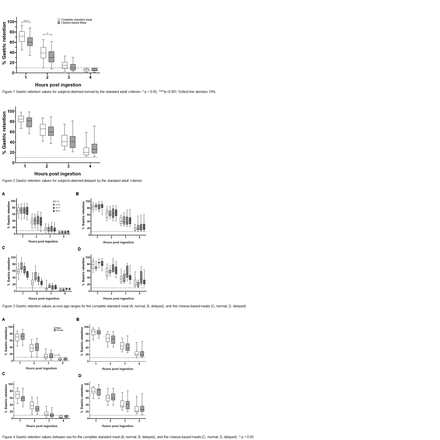
Results: 735 subjects ate the complete standard meal (n = 549 and n = 186 deemed normal and delayed respectively). 81 subjects at cheese-based meals (n = 46 normal, n = 35 delayed). The median (95% upper reference limit) retention percentages for the complete standard meal for patients deemed normal were 72% (93%), 39% (65%), 15% (33%) and 6% (10%) for 1-4 hours respectively (Figure 1). By comparison, cheese-based meals revealed values of 60% (87.6%), 30% (61.2%), 10% (30.4%), 5% (10%). Gastric retention at all timepoints for delayed subjects were well above the 10% threshold for both types of meals and were not statistically different (Figure 2). No significant difference in gastric retention was found between the cheese-based meals and adult complete standard meal across different pediatric age ranges(Figure 3) and between sexes (Figure 4).
Conclusions: The results show that the adult gastric emptying normative values for the complete standard meal can be extended to the pediatric population. Further, cheese-based meals offer viable alternatives to the full adult standard meal in the pediatric population. The standard adult criterion (<10% at 4 h) can be applied well to these non-standard meal types.