Abstract
273
Objectives: explore the value of radiomics analysis based on 18F-FDG and 18F-FLT PET/CT images in the differentiation of benign and malignant pulmonary nodules (PNs).
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 113 patients getting clinicians into trouble of differential diagnosis between benign and malignant PNs on 18F-FDG PET/CT images, all of whom were followed by additional preoperative 18F-FLT PET/CT scans within a week. Three analysis methods including visual analysis, radiomics analysis based on 18F-FDG PET/CT images alone and radiomics analysis based on dual tracer PET/CT images were evaluated in the differential diagnostic value of benign and malignant PNs. Radiomics analysis went in details like dividing the dataset into training set and test set in a ratio of 7:3 (The distribution of the dataset was shown in Table 1), extracting specific quantitative features via analysis of variance (ANOVA) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), constructing the logistic regression (LR) model, and evaluating their performances via receiver operating characteristic (ROC), sensitivity and specificity.
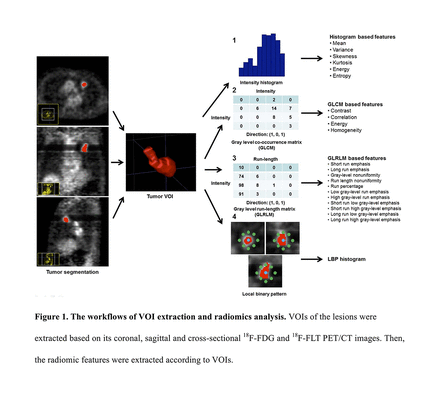
Results: A total of 123 lesions were acquired from 113 patients (74 men, 39 women; mean age 56.4 years; age range, 27-83 years). To be more detailed, 63 benign lesions were respectively diagnosed as inflammation (n=12), tuberculosis (n=29), or other diseases confirmed by follow-up (n=22) while 60 malignant lesions included adenocarcinoma (n=30), squamous cell carcinoma (n=16), small cell carcinoma (n=1), bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (n=6) and others (n=7), as presented in Table 2. Based on visual analysis of 18F-FDG PET/CT images,the diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity were 61.6%, 90% and 28.8% respectively. 678 radiomics features (see Supplemental Table) were extracted from Volumes of Interest (VOIs) of PNs (The process was revealed in Fig. 1). And 19 features were selected by ANOVA. After LASSO optimization, 14 valuable features were screened out (Fig. 2 shows the above two steps). As vividly indicated in Fig. 3, based on 18F-FDG PET/CT plus 18F-FLT signature, the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity and specificity under the test set are 0.838, 0.778, and 0.750 respectively while under the training set, they are 0.879, 0.810, and 0.750 successively. And based on 18F-FDG PET/CT, the AUC, sensitivity and specificity under the test set are 0.810, 0.778, and 0.688 respectively while under the training set, they are 0.834, 0.786, and 0.778 successively (The results were listed in Table 3).
Conclusions: Radiomics analysis based on dual-tracer PET/CT images may be clinically potential and feasible for the discernable evaluation of benign and malignant PNs.
Table 1. The distribution of the dataset between benign and malignant PNs.
Table 2. The pathological diagnosis of 123 lesions
Table 3. The AUC, sensitivity, specificity of three analysis methods under the test set.