Abstract
363
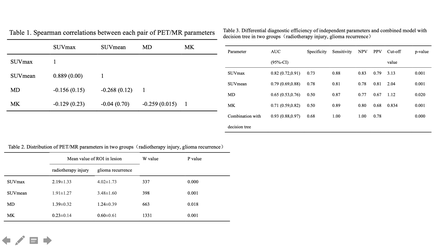
Introduction: High-grade gliomas are usually treated by surgery together with radiotherapy. However, the radiotherapy injury and recurrence of gliomas are often mixed up. Therefore, it would be beneficial to identify the recurrence of gliomas and thus to avoid the delay of treatment. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the differential diagnostic performances of 11C-Methionine positron emission tomography(11C-MET PET)and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) independently, and combined efficacy for radiotherapy injury and recurrent glioma. Materials and Methods: The study was approved by the regional ethics committee. Between April 2014 and August 2018, the patients with glioma diagnosed by histopathology were enrolled after post-operative radiotherapy. The patients with contraindication of PET/MR were excluded. All patients were scanned on a whole-body integrated PET/MR scanner. The scanning protocol includes: (1) 11C-Methionine PET; (2) anatomical sequences including a sagittal T1-weighted MPRAGE sequence and a trans-axial T2-weighted FLAIR sequence; (3) a DKI sequence. Quantitative analysis was performed through placement of regions of interest manually. The multi-parameters from PET/MR images included the maximum and mean values of standardize uptake values (SUVmax, SUVmean), mean kurtosis (MK) and mean diffusivity (MD). The corresponding values of all parameters were also measured in the contralateral white matter regions as Control. All the statistical data were based on the ratio of Lesion/Control. All patients were confirmed by the stereotactic biopsy or surgery with the diagnosis of glioma recurrence or the more than 6 months follow-up with the diagnosis of radiotherapy injury. Spearman correlation analysis was implemented between each parameter pair. The nonparametric test of Wilcoxon rank sum test was used for statistical differences between the radiotherapy injury and glioma recurrence groups. The combined model established by the decision tree was considered as the combination of multi-parameters derived from PET/MR. The optimal principal components were determined by leave-one-out cross validation for the combined model. The ROC analysis was used for the diagnostic efficacy of independent parameters and the combined model. P<0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Results: In this end, 87 patients were enrolled in the study, including 48 cases diagnosed of recurrent glioma and 39 cases diagnosed of radiotherapy injury. Regarding to the correlation analysis, there were significant correlations between SUVmax and SUVmean, while no statistical correlations between other pairs of different parameters (summarized in Table 1). There were significant differences of SUVmax, SUVmean and MK between the group of radiotherapy injury and group of recurrent glioma (Table 2,Figure 1). The ranking of diagnostic performance with independent parameters in differentiating radiotherapy injury and glioma recurrence was that SUVmax> SUVmean>MK>MD by ROC analysis. Compared to all the independent parameters with DKI and 11C-MET PET, the combined model had a better diagnostic efficacy with an area under curve (AUC) of 0.93 according to the cross-validation (Figure 2-3, Table 3). Discussion Our results showed that, no correlations between SUV and MK were found. Therefore, SUV and kurtosis may provide complementary information of tumor histology. This explains why the combined model has a greater diagnostic performance than each parameter alone based models.
Conclusions: The multi-parameters of 11C-MET PET/MR can be complementary in differential diagnosis between the different groups of radiotherapy injury and glioma recurrence. By combining the multiple parameters from 11C-MET PET and DKI, it can further improve the diagnostic efficiency.