Abstract
1365
Objectives To detect destabilization of atherosclerotic plaque that tightly linked to inflammation through 99mTc-labelled anti-CD11b antibody mediated SPECT/CT imaging.
Methods An imaging probe for single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT), named as 99mTc-MAG3-anti-CD11b was fabricated with high labelling rate (>95%) and excellent in vitro stability. The ApoE-knockout (ApoE-/-) mice were selected to establish animal models by feeding with a high-fat diet, while C57BL/6J mice were used for control by feeding with a chow diet. After feeding for 20 weeks, mice weight, serological lipid profiles and cytokines were measured. The levels of CD11b+ cells in circulation system and corresponding cellular expression of CD11b were investigated through flow cytometry. By using Raw-264.7 cell lines as positive cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) lines as negative cells, cell binging and relevant blocking test were performed to investigate affinity and specificity of the probe binding to inflammatory cells. Ex vivo anti-CD11b-PE-Cy7 mediated aortic fluorescence imaging were firstly conducted to identify capability of anti-CD11b for targeting inflamed plaques. Then, 99mTc-MAG3-anti-CD11b mediated SPECT/CT imaging were done aiming to detect these plaques in vivo. Finally, ex vivo aortic breast specific gamma imaging (BSGI), Oil Red O staining and immunohistochemical staining were performed to confirm findings of in vivo SPECT/CT imaging.
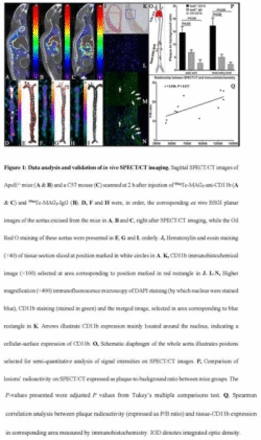
Results A higher CD11b+-cell recruitment with higher CD11b expression and more serious whole-body inflammatory status (in terms of higher serological lipid profiles and cytokines) were identified in ApoE-/- mice. The probe showed high in vitro affinity and specificity to the Raw-264.7 macrophages, as well as inflammatory cells infiltrated in atherosclerotic plaques, either in ex vivo fluorescent imaging or in in vivo micro-SPECT/CT imaging, which were confirmed by ex vivo planar BSGI imaging, Oil-Red-O staining and CD11b-immunohistochemistry staining (Figure 1). A significant positive relationship was identified between the radioactivity intensity on SPECT/CT images and the CD11b expression in plaques on immunohistochemical images.
Conclusions This study demonstrates the feasibility of anti-CD11b antibody mediated noninvasive SPECT/CT imaging of inflammatory leukocytes in murine atherosclerotic plaques. This imaging strategy can identify inflammation-rich plaques at risk for rupture and evaluate the effectiveness of inflammation-targeted therapies in atheroma.