Visual Abstract
Abstract
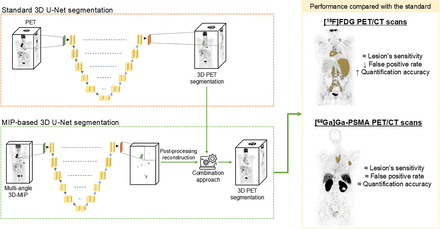
This study investigated the added value of using maximum-intensity projection (MIP) images for fully automatic segmentation of lesions using deep learning (DL) in [18F]FDG and [68Ga]Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET/CT scans. Methods: We used 489 staging [18F]FDG PET/CT scans from patients diagnosed with melanoma, lymphoma, or lung cancer (391 scans for training and 98 for internal testing). As an external test set, 117 staging [18F]FDG PET/CT scans from lymphoma patients (another center, 2 scanners) were used. For [68Ga]Ga-PSMA, 355 whole-body [68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT scans from patients with prostate cancer were used (285 scans for training and 70 scans for testing). All scans had corresponding expert-based segmentation (ground truth). Three approaches per radiopharmaceutical were used for fully automatic segmentation: 3-dimensional U-Net applied directly on PET images (standard-DL–based), 3-dimensional U-Net applied on multiangle MIP images (MIP-DL–based), and a combined approach (standard-DL+MIP-DL–based). The performance was evaluated in comparison with ground truth segmentation through lesion detection scores, voxelwise segmentation overlap metrics, and quantification of clinically relevant imaging features. Results: For [18F]FDG PET scans, the MIP-DL–based method showed a lower lesion false-discovery rate than did the standard-DL–based approach, although not significant in internal and external test sets. Sensitivity in lesion detection did not vary significantly, and a reduction in voxelwise metrics was observed (median Dice coefficient of 0.65 vs. 0.80 in the internal test set). Significantly increased performance was obtained with the combined approach in both test sets. In the internal test set, the median false-discovery rate was 0% (12% using the standard-DL), and a considerable increase in the agreement of lesion features was observed (intraclass correlation coefficient range, 0.42–0.94 for standard-DL–based and 0.80–0.94 for the combined approach). Similar results were observed in the external set. Regarding [68Ga]Ga-PSMA scans, there was no significant increase in the performance of MIP-DL–based and combined approaches compared with standard-DL, which was already outstanding in lesion detectability. Conclusion: Fully automatic segmentation of lesions in whole-body or total-body [18F]FDG PET/CT scans may benefit from the addition of the MIP-DL–based segmentation compared with the standard-DL–based method. It reduces the number of false-positive lesions and improves the patients’ tumor burden quantification. In [68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT scans, no benefits were observed compared with standard-DL–based segmentation.
- [18F]FDG PET/CT
- [68Ga]Ga-PSMA PET/CT
- segmentation
- computer-assisted image analysis
- artificial intelligence
Footnotes
Published online Mar. 13, 2025.
- © 2025 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
This article requires a subscription to view the full text. If you have a subscription you may use the login form below to view the article. Access to this article can also be purchased.
SNMMI members
Login to the site using your SNMMI member credentials
Individuals
Login as an individual user