Abstract
252092
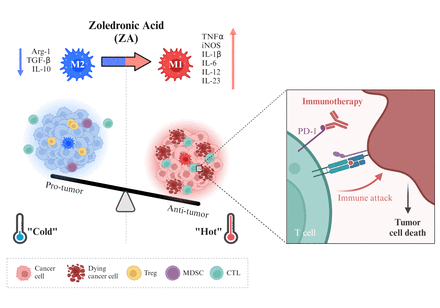
Introduction: Immunologically "cold" tumors are characterized by an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) enriched with M2-type tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and often exhibit resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), making them a promising target for cancer immunotherapy. Thus, Reprogramming M2 TAMs in such tumors has emerged as a promising strategy to enhance ICI efficacy. Zoledronic acid (ZA) has been shown to reprogram pro-tumor M2 macrophages into anti-tumor M1 macrophages. Therefore, we designed mannosylated nanoliposomes (M-Lipo) capable of binding to mannose receptors overexpressed on the surface of M2 TAMs and incorporated ZA into them (M-Lipo/ZA) to effectively target M2 TAMs and induce M2 reprogramming. In this study, we assessed the potential of M-Lipo/ZA to modulate the TME, converting "cold" tumors into "hot" tumors and enhancing ICI efficacy.
Methods: RAW 264.7 mouse macrophage cell line was polarized into M2-type by interleukin(IL)-4 and IL-10 and then treated with ZA at concentrations of 2, 5, 10, and 25 μM. Gene expression related to M2 differentiation, including Myc and Ccl7, was measured using qRT-PCR. Additionally, protein-level changes in M2 markers (Arg1, CD206) were assessed using flow cytometry and Western blotting. C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously implanted with NanoLuc-expressing MC38 ("hot") and B16F10 ("cold") tumors. Mice were treated with M-Lipo/ZA (2 mg/kg) for 14 days, followed by whole RNA sequencing of "cold" tumor tissues to analyze gene expression changes related to macrophage differentiation. Additionally, mice were treated with M-Lipo/ZA (100 μg/kg) in combination with anti-PD-1 antibodies (1 mg/kg) every other day for 14 days. Tumor size was monitored using bioluminescence imaging (BLI), and immune cell infiltration (CD45+) and Arg1, CD206 expression were evaluated using flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry.
Results: First, Western blot analysis showed that while ZA alone did not induce significant changes, M-Lipo/ZA significantly reduced the expression of Arg1 and CD206 (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05). Additionally, ZA treatment led to a dose-dependent decrease in the expression of Myc and Ccl7. Furthermore, RNA sequencing of "cold" tumor tissues treated with M-Lipo/ZA revealed significant downregulation of Arg1 and CD206, confirming the modulation of the tumor microenvironment (TME). Interestingly, genes associated with M2 polarization, such as Myc and Ccl7, were also reduced. The combination treatment of M-Lipo/ZA and anti-PD-1 antibodies resulted in a significant reduction in tumor size in both "hot" (p < 0.01) and "cold" (p < 0.05) tumor models, as confirmed by BLI. Flow cytometry showed increased immune cell infiltration (CD45+) and decreased Arg1 expression in both tumor types, with a more pronounced effect in "cold" tumors. Immunohistochemistry further confirmed decreased expression of Arg1 and CD206 within the TME.
Conclusions: M-Lipo/ZA reprograms the TME of "cold" tumors by targeting and depleting M2 TAMs, leading to an increase in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and a reduction in M2 TAMs, thereby converting the TME to resemble that of a "hot" tumor. As a result, M2 TAM reprogramming significantly enhances ICI responsiveness and reduces tumor volume. These findings suggest that M-Lipo/ZA is a promising therapeutic strategy for overcoming resistance in "cold" tumors and improving cancer immunotherapy.